Abstract
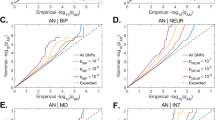
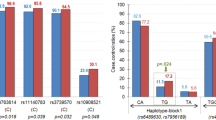
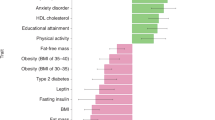
Anorexia nervosa (AN) and bulimia nervosa (BN) are eating disorders (ED) with complex genetic and environmental components. Genetic studies and animal models support the participation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the vulnerability to AN and BN. We investigated the genetic contribution of the BDNF-specific receptor neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor type 2 (NTRK2) to the susceptibility to ED. We have screened the entire NTRK2 gene in 91 patients with ED and have identified 14 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). A population-based association study with six SNPs from the NTRK2 locus was performed in 164 ED patients and 121 controls. Significant evidence of association for markers –69C>G and IVS13+40G>A was detected. We also observed a strong association between the C-A-insC haplotype (–69/IVS13+40/2784–2785) and binge-eating/purging AN (ANP, P=0.006; OR=2.27), and a reduced frequency of haplotype G-A-delCl in BN patients (P=0.034; OR=0.6). The analysis of ED-related phenotypes revealed a clear association between NTRK2, high scores of Harm avoidance measured by the temperament and character inventory (TCI-R; P=0.003) and minimum body mass index (minBMI; P<0.001). Our data support a contribution of NTRK2 to the genetic susceptibility of ED, mainly ANP, and ED-related phenotypic traits, such as Harm avoidance and minBMI.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garner DM . Pathogenesis of anorexia nervosa. Lancet 1993; 341: 1631–1635.
Xu B, Goulding EH, Zang K, Cepoi D, Cone RD, Jones RK et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates energy balance downstream of melanocortin-4 receptor. Nat Neurosci 2003; 6: 736–742.
Kernie SG, Liebl DJ, Parada LF . BDNF regulates eating behavior and locomotor activity in mice. EMBO J 2000; 19: 1290–1300.
Lyons WE, Mamounas LA, Ricaurte GA, Coppola V, Reid SW, Bora SH et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor-deficient mice develop aggressiveness and hyperphagia in conjunction with brain serotonergic abnormalities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 15239–15244.
Rios M, Fan G, Fekete C, Kelly J, Bates B, Kuehn R et al. Conditional deletion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the postnatal brain leads to obesity and hyperactivity. Mol Endocrinol 2001; 15: 1748–1757.
Ribases M, Gratacos M, Armengol L, de Cid R, Badia A, Jimenez L et al. Met66 in the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) precursor is associated with anorexia nervosa restrictive type. Mol Psychiatry 2003; 8: 745–751.
Ribases M, Gratacos M, Fernandez-Aranda F, Bellodi L, Boni C, Anderluh M et al. Association of BDNF with anorexia, bulimia and age of onset of weight loss in six European populations. Hum Mol Genet 2004; 13: 1205–1212.
Ribases M, Gratacos M, Fernandez-Aranda F, Bellodi L, Boni C, Anderluh M et al. Association of BDNF with restricting anorexia nervosa and minimum body mass index: a family-based association study of eight European populations. Eur J Hum Genet 2005; 13: 428–434.
Koizumi H, Hashimoto K, Itoh K, Nakazato M, Shimizu E, Ohgake S et al. Association between the brain-derived neurotrophic factor 196G/A polymorphism and eating disorders. Am J Med Genet 2004; 127B: 125–127.
Gabrovsek M, Brecelj-Anderluh M, Bellodi L, Cellini E, Di Bella D, Estivill X et al. Combined family trio and case–control analysis of the COMT Val158Met polymorphism in European patients with anorexia nervosa. Am J Med Genet 2004; 124B: 68–72.
Gorwood P, Ades J, Bellodi L, Cellini E, Collier DA, Di Bella D et al. The 5-HT(2A) -1438G/A polymorphism in anorexia nervosa: a combined analysis of 316 trios from six European centres. Mol Psychiatry 2002; 7: 90–94.
Stephens M, Donnelly P . A comparison of bayesian methods for haplotype reconstruction from population genotype data. Am J Hum Genet 2003; 73: 1162–1169.
Stephens M, Smith NJ, Donnelly P . A new statistical method for haplotype reconstruction from population data. Am J Hum Genet 2001; 68: 978–989.
Bulik CM, Sullivan PF, Carter FA, Joyce PR . Initial manifestations of disordered eating behavior: dieting versus binging. Int J Eat Disord 1997; 22: 195–201.
Bulik CM, Sullivan PF, Kendler KS . An empirical study of the classification of eating disorders. Am J Psychiatry 2000; 157: 886–895.
Gendall KA, Joyce PR, Sullivan PF, Bulik CM . Personality and dimensions of dietary restraint. Int J Eat Disord 1998; 24: 371–379.
Niu T, Qin ZS, Xu X, Liu JS . Bayesian haplotype inference for multiple linked single-nucleotide polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 70: 157–169.
Wonderlich S, Mitchell JE . The role of personality in the onset of eating disorders and treatment implications. Psychiatr Clin N Am 2001; 24: 249–258.
Cloninger CR, Svrakic DM, Przybeck TR . A psychobiological model of temperament and character. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1993; 50: 975–990.
Gallegos M, Ahringer J, Crittenden S, Kimble J . Repression by the 3′ UTR of fem-3, a sex-determining gene, relies on a ubiquitous mog-dependent control in Caenorhabditis elegans. EMBO J 1998; 17: 6337–6347.
Ozaki K, Ohnishi Y, Iida A, Sekine A, Yamada R, Tsunoda T et al. Functional SNPs in the lymphotoxin-alpha gene that are associated with susceptibility to myocardial infarction. Nat Genet 2002; 32: 650–654.
Surinya KH, Cox TC, May BK . Identification and characterization of a conserved erythroid-specific enhancer located in intron 8 of the human 5-aminolevulinate synthase 2 gene. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 16798–16809.
Tokuhiro S, Yamada R, Chang X, Suzuki A, Kochi Y, Sawada T et al. An intronic SNP in a RUNX1 binding site of SLC22A4, encoding an organic cation transporter, is associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Genet 2003; 35: 341–348.
Bulik CM, Sullivan PF, Fear JL, Pickering A . Outcome of anorexia nervosa: eating attitudes, personality, and parental bonding. Int J Eat Disord 2000; 28: 139–147.
Fassino S, Abbate-Daga G, Amianto F, Leombruni P, Boggio S, Rovera GG . Temperament and character profile of eating disorders: a controlled study with the Temperament and Character Inventory. Int J Eat Disord 2002; 32: 412–425.
Fassino S, Daga GA, Piero A, Leombruni P, Rovera GG . Anger and personality in eating disorders. J Psychosom Res 2001; 51: 757–764.
Klump KL, Bulik CM, Pollice C, Halmi KA, Fichter MM, Berrettini WH et al. Temperament and character in women with anorexia nervosa. J Nerv Ment Dis 2000; 188: 559–567.
Tomotake M, Ohmori T . Personality profiles in patients with eating disorders. J Med Invest 2002; 49: 87–96.
Friedman WJ, Black IB, Kaplan DR . Distribution of the neurotrophins brain-derived neurotrophic factor, neurotrophin-3, and neurotrophin-4/5 in the postnatal rat brain: an immunocytochemical study. Neuroscience 1998; 84: 101–114.
Klein R, Nanduri V, Jing SA, Lamballe F, Tapley P, Bryant S et al. The trkB tyrosine protein kinase is a receptor for brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3. Cell 1991; 66: 395–403.
Neves-Pereira M, Mundo E, Muglia P, King N, Macciardi F, Kennedy JL . The brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene confers susceptibility to bipolar disorder: evidence from a family-based association study. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 71: 651–655.
Sklar P, Gabriel SB, McInnis MG, Bennett P, Lim YM, Tsan G et al. Family-based association study of 76 candidate genes in bipolar disorder: BDNF is a potential risk locus. Brain-derived neutrophic factor. Mol Psychiatry 2002; 7: 579–593.
Shimizu E, Hashimoto K, Okamura N, Koike K, Komatsu N, Kumakiri C et al. Alterations of serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in depressed patients with or without antidepressants. Biol Psychiatry 2003; 54: 70–75.
Hall D, Dhilla A, Charalambous A, Gogos JA, Karayiorgou M . Sequence variants of the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) gene are strongly associated with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Am J Hum Genet 2003; 73: 370–376.
Kaye WH, Gwirtsman HE, George DT, Ebert MH . Altered serotonin activity in anorexia nervosa after long-term weight restoration. Does elevated cerebrospinal fluid 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid level correlate with rigid and obsessive behavior? Arch Gen Psychiatry 1991; 48: 556–562.
Bever KA, Perry PJ . Dexfenfluramine hydrochloride: an anorexigenic agent. Am J Health Syst Pharm 1997; 54: 2059–2072.
Cole W, Lapierre YD . The use of tryptophan in normal-weight bulimia. Can J Psychiatry 1986; 31: 755–756.
Jimerson DC, Lesem MD, Kaye WH, Brewerton TD . Low serotonin and dopamine metabolite concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid from bulimic patients with frequent binge episodes. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1992; 49: 132–138.
Kaye WH, Greeno CG, Moss H, Fernstrom J, Fernstrom M, Lilenfeld LR et al. Alterations in serotonin activity and psychiatric symptoms after recovery from bulimia nervosa. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1998; 55: 927–935.
Kuikka JT, Tammela L, Karhunen L, Rissanen A, Bergstrom KA, Naukkarinen H et al. Reduced serotonin transporter binding in binge eating women. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2001; 155: 310–314.
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients for participation in the study. Financial support was received from the ‘Psychiatry Genetics network (G03/184), ‘Instituto de Salut Carlos III—FIS’, the ‘Departament d'Universitats i Societat de la informació, Generalitat de Catalunya’ and ‘Genoma España’ (CEGEN). Marta Ribases was recipient of a BEFI fellowship from the FIS (Spanish Ministry of Health).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Molecular Psychiatry website (http://www.nature.com/mp)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ribases, M., Gratacos, M., Badia, A. et al. Contribution of NTRK2 to the genetic susceptibility to anorexia nervosa, Harm avoidance and minimum body mass index. Mol Psychiatry 10, 851–860 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001670
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001670
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A common NTRK2 variant is associated with emotional arousal and brain white-matter integrity in healthy young subjects
Translational Psychiatry (2016)
-
Evaluation of Neurotrophic Tyrosine Receptor Kinase 2 (NTRK2) as a positional candidate gene for variation in estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR) in Mexican American participants of San Antonio Family Heart Study
Journal of Biomedical Science (2015)
-
A debate on current eating disorder diagnoses in light of neurobiological findings: is it time for a spectrum model?
BMC Psychiatry (2012)
-
TrkB Agonist Antibody Dose-Dependently Raises Blood Pressure in Mice With Diet-Induced Obesity
American Journal of Hypertension (2010)
-
Correlation of BDNF blood levels with interoceptive awareness and maturity fears in anorexia and bulimia nervosa patients
Journal of Neural Transmission (2010)