Abstract
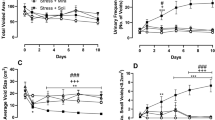
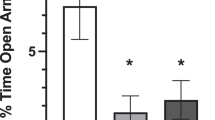
When exposed to prolonged stress, rats develop gastric ulceration, enhanced colon motility with depletion of its mucin content and signs of physiological and behavioral arousal. In this model, we tested whether antidepressants (fluoxetine and bupropion), anxiolytics (diazepam and buspirone) or the novel nonpeptide corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) type-1 receptor (CRH-R1) antagonist, antalarmin, modify these responses. Fluoxetine, bupropion, diazepam and antalarmin all suppressed stress-induced gastric ulceration in male Sprague–Dawley rats exposed to four hours of plain immobilization. Antalarmin produced the most pronounced anti-ulcer effect and additionally suppressed the stress-induced colonic hypermotility, mucin depletion, autonomic hyperarousal and struggling behavior. Intraperitoneal CRH administration reproduced the intestinal but not the gastric responses to stress while vagotomy antagonized the stress-induced gastric ulceration but not the intestinal responses. We conclude that brain CRH-R1 and vagal pathways are essential for gastric ulceration to occur in response to stress and that peripheral CRH-R1 mediates colonic hypermotility and mucin depletion in this model. Nonpeptide CRH-R1 antagonists may therefore be prophylactic against stress ulcer in the critically ill and therapeutic for other pathogenetically related gastrointestinal disorders such as peptic ulcer disease and irritable bowel syndrome.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Selye H . A syndrome produced by diverse nocuous agents Nature 1936 138: 32–36
Schilling D et al. Low seroprevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with stress ulcer bleeding—a prospective evaluation of patients on a cardiosurgical intensive care unit Intensive Care Med 2000 26: 1832–1836
Weiner H . Use of animal models in peptic ulcer disease Psychosom Med 1996 58: 524–545
Williams CL, Villar RG, Peterson JM, Burks TF . Stress-induced changes in intestinal transit in the rat: a model for irritable bowel syndrome Gastroenterology 1988 94: 611–621
Sjodin I, Svedlund J, Dotevall G, Gillberg R . Symptom profiles in chronic peptic ulcer disease. A detailed study of abdominal and mental symptoms Scand J Gastroenterol 1985 20: 419–427
Lydiard RB, Falsetti SA . Experience with anxiety and depression treatment studies: implications for designing irritable bowel syndrome clinical trials Am J Med 1999 107: 65S–73S
De Bellis MD et al. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysregulation in sexually abused girls J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1994 78: 249–255
Heim C, Owens MJ, Plotsky PM, Nemeroff CB . Persistent changes in corticotropin-releasing factor systems due to early life stress: relationship to the pathophysiology of major depression and post-traumatic stress disorder Psychopharmacol Bull 1997 33: 185–192
Ackerman SH, Hofer MA, Weiner H . Early maternal separation increases gastric ulcer risk in rats by producing a latent thermoregulatory disturbance Science 1978 201: 373–376
Almounajed G, Drossman DA . Newer aspects of the irritable bowel syndrome Prim Care 1996 23: 477–495
Russo MW, Gaynes BN, Drossman DA . A national survey of practice patterns of gastroenterologists with comparison to the past two decades J Clin Gastroenterol 1999 29: 339–343
Drossman DA et al. US householder survey of functional gastrointestinal disorders. Prevalence, sociodemography, and health impact Dig Dis Sci 1993 38: 1569–1580
Brodie DA . Experimental peptic ulcer Gastroenterology 1968 55: 125–134
Cho CH, Koo MW, Garg GP, Ogle CW . Stress-induced gastric ulceration: its aetiology and clinical implications Scand J Gastroenterol 1992 27: 257–262
Pare WP, Glavin GB . Restraint stress in biomedical research: a review Neurosci Biobehav Rev 1986 10: 339–370
Levenstein S . Stress and peptic ulcer: life beyond Helicobacter BMJ 1998 316: 538–541
Habib KE, Gold PW, Chrousos GP . Neuroendorinology of stress Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 2001 30: 695–728
Peters MN, Richardson CT . Stressful life events, acid hypersecretion, and ulcer disease Gastroenterology 1983 84: 114–119
Bresnick WH, Rask-Madsen C, Hogan DL, Koss MA, Isenberg JI . The effect of acute emotional stress on gastric acid secretion in normal subjects and duodenal ulcer patients J Clin Gastroenterol 1993 17: 117–122
Pare WP . Stress ulcer susceptibility and depression in Wistar Kyoto (WKY) rats Physiol Behav 1989 46: 993–998
Glavin GB . Vulnerability to stress ulcerogenesis in rats differing in anxiety: a dopaminergic correlate J Physiol Paris 1993 87: 239–243
Feldman M, Walker P, Green JL, Weingarden K . Life events stress and psychosocial factors in men with peptic ulcer disease. A multidimensional case-controlled study Gastroenterology 1986 91: 1370–1379
Ries RK, Gilbert DA, Katon W . Tricyclic antidepressant therapy for peptic ulcer disease Arch Intern Med 1984 144: 566–569
Mangla JC, Pereira M . Tricyclic antidepressants in the treatment of peptic ulcer disease Arch Intern Med 1982 142: 273–275
Shrivastava RK, Siegel H . The role of tricyclics and benzodiazepine compounds in the treatment of irritable gut syndrome and peptic ulcer disease Psychopharmacol Bull 1984 20: 616–621
Haggerty JJ Jr, Drossman DA . Use of psychotropic drugs in patients with peptic ulcer Psychosomatics 1985 26: 277–280 283–284
Shrivastava RK, Shah BK, Siegal H . Doxepin and cimetidine in the treatment of duodenal ulcer: a double-blind comparative study Clin Ther 1985 7: 181–189
Ogawa N, Hara C, Takaki S . Anxiolytic activity of SC-48274 compared with those of buspirone and diazepam in experimental anxiety models Jpn J Pharmacol 1993 61: 115–121
Williams CL, Peterson JM, Villar RG, Burks TF . Corticotropin-releasing factor directly mediates colonic responses to stress Am J Physiol 1987 253: G582–G586
Lenz HJ, Raedler A, Greten H, Vale WW, Rivier JE . Stress-induced gastrointestinal secretory and motor responses in rats are mediated by endogenous corticotropin-releasing factor Gastroenterology 1988 95: 1510–1517
Pothoulakis C, Castagliuolo I, Leeman SE . Neuroimmune mechanisms of intestinal responses to stress. Role of corticotropin-releasing factor and neurotensin Ann N Y Acad Sci 1998 840: 635–648
Ray A, Henke PG, Gulati K, Sen P . The amygdaloid complex, corticotropin releasing factor and stress-induced gastric ulcerogenesis in rats Brain Res 1993 624: 286–290
Nakane T, Kanie N, Audhya T, Hollander CS . The effects of centrally administered neuropeptides on the development of gastric lesions in the rat Life Sci 1985 36: 1197–1203
Vale W, Spiess J, Rivier C, Rivier J . Characterization of a 41-residue ovine hypothalamic peptide that stimulates secretion of corticotropin and beta-endorphin Science 1981 213: 1394–1397
Sutton RE, Koob GF, Le Moal M, Rivier J, Vale W . Corticotropin releasing factor produces behavioural activation in rats Nature 1982 297: 331–333
Habib KE et al. Oral administration of a corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonist significantly attenuates behavioral, neuroendocrine, and autonomic responses to stress in primates Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2000 97: 6079–6084
Tache Y et al. Inhibition of gastric acid secretion in rats by intracerebral injection of corticotropin-releasing factor Science 1983 222: 935–937
Martinez V, Rivier J, Wang L, Tache Y . Central injection of a new corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) antagonist, astressin, blocks CRF- and stress-related alterations of gastric and colonic motor function J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1997 280: 754–760
Lydiard RB . Anxiety and the irritable bowel syndrome: psychiatric, medical, or both? J Clin Psychiatry 1997 58: 51–58 discussion 59–61
Habib KE et al. CRH type-1 receptor antagonism attenuates behavioral, endocrine and autonomic responses to stress in primates Neuropsychopharmacology 2000 23(S2): S119
Gold PW, Goodwin FK, Chrousos GP . Clinical and biochemical manifestations of depression. Relation to the neurobiology of stress (2) N Engl J Med 1988 319: 413–420
Chen YL et al. Synthesis and oral efficacy of a 4-(butylethylamino)pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine: a centrally active corticotropin-releasing factor1 receptor antagonist J Med Chem 1997 40: 1749–1754
Maillot C, Million M, Wei JY, Gauthier A, Tache Y . Peripheral corticotropin-releasing factor and stress-stimulated colonic motor activity involve type 1 receptor in rats Gastroenterology 2000 119: 1569–1579
Gilligan PJ, Robertson DW, Zaczek R . Corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) receptor modulators: progress and opportunities for new therapeutic agents J Med Chem 2000 43: 1641–1660
Beaumont G . Adverse effects of antidepressants Int Clin Psychopharmacol 1990 5 Suppl 3: 61–66
Castagliuolo I et al. Acute stress causes mucin release from rat colon: role of corticotropin releasing factor and mast cells Am J Physiol 1996 271: G884–G892
Hall CS . Emotional behavior in the rat J Comp Psychol 1934 18: 385–403
Webster EL et al. In vivo and in vitro characterization of antalarmin, a nonpeptide corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) receptor antagonist: suppression of pituitary ACTH release and peripheral inflammation Endocrinology 1996 137: 5747–5750
Ushijima I et al. The role of adenosinergic, GABAergic and benzodiazepine systems in hyperemotionality and ulcer formation in stressed rats Psychopharmacology 1986 89: 472–476
Ida Y, Tanaka M, Tsuda A, Tsujimaru S, Nagasaki N . Attenuating effect of diazepam on stress-induced increases in noradrenaline turnover in specific brain regions of rats: antagonism by Ro 15–1788 Life Sci 1985 37: 2491–2498
de Boer SF, Slangen JL, van der Gugten J . Effects of chlordiazepoxide and buspirone on plasma catecholamine and corticosterone levels in rats under basal and stress conditions Endocrinol Exp 1990 24: 229–239
Cooper BR, Hester TJ, Maxwell RA . Behavioral and biochemical effects of the antidepressant bupropion (Wellbutrin): evidence for selective blockade of dopamine uptake in vivo J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1980 215: 127–134
Caccia S, Fracasso C, Garattini S, Guiso G, Sarati S . Effects of short- and long-term administration of fluoxetine on the monoamine content of rat brain Neuropharmacology 1992 31: 343–347
Weichert RF 3rd, Ellison JP, Woolverton WC, Drapanas T . Postvagotomy serotonin depletion in mucosal mast cells of the rat stomach Surg Forum 1970 21: 318–320
Habib KE, Negro PJ, Sciullo D, Dib A, Gold PW . Protective role of the sympathoadrenal system against stress-induced gastric mucosal injury in the rat Gastroenterology 1999 116: G0783
Bakke HK, Murison R . Plasma corticosterone and restraint induced gastric pathology: age-related differences after administration of corticotropin releasing factor Life Sci 1989 45: 907–916
Glavin GB et al. The neurobiology of stress ulcers Brain Res Brain Res Rev 1991 16: 301–343
Habib KE . Role of brain-adrenal-gastric axis in modulating gastric responses to stress in albino rats MSc, Minia University 1994
Lenz HJ, Burlage M, Raedler A, Greten H . Central nervous system effects of corticotropin-releasing factor on gastrointestinal transit in the rat Gastroenterology 1988 94: 598–602
Bueno L et al. Effects of corticotropin-releasing factor on plasma motilin and somatostatin levels and gastrointestinal motility in dogs Gastroenterology 1986 91: 884–889
Murison R, Bakke HK . The role of corticotropin-releasing factor in rat gastric ulcerogenesis Ann N Y Acad Sci 1990 597: 71–80
Tache Y . The peptidergic brain-gut axis: influence on gastric ulcer formation Chronobiol Int 1987 4: 11–17
Chrousos GP . The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and immune-mediated inflammation N Engl J Med 1995 332: 1351–1362
Cho CH, Ogle CW, Dai S . Acute gastric ulcer formation in response to electrical vagal stimulation in rats Eur J Pharmacol 1976 35: 215–219
Hernandez DE . Neuroendocrine mechanisms of stress ulceration: focus on thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) Life Sci 1986 39: 279–296
Weiner H . From simplicity to complexity (1950–1990): the case of peptic ulceration–II. Animal studies Psychosom Med 1991 53: 491–516
Grijalva CV, Novin D . The role of the hypothalamus and dorsal vagal complex in gastrointestinal function and pathophysiology Ann N Y Acad Sci 1990 597: 207–222
Habib KE, Negro PJ, Negro PP, Gold PW . Endogenous opioids contribute to gastric ulcerogenesis during immobilization stress in male Sprague–Dawley rats. Recognition of β-endorphin immunoreactivity in the gastric mucosa Gastroenterology 1999 116: G0782
Fukudo S, Nomura T, Hongo M . Impact of corticotropin-releasing hormone on gastrointestinal motility and adrenocorticotropic hormone in normal controls and patients with irritable bowel syndrome Gut 1998 42: 845–849
Petrusz P et al. Corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF)-like immunoreactivity in the gastro-entero-pancreatic endocrine system Peptides 1984 5: 71–78
Wolter HJ . Corticotropin-releasing factor is contained within perikarya and nerve fibres of rat duodenum Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1984 122: 381–387
Kawahito Y et al. Local secretion of corticotropin-releasing hormone by enterochromaffin cells in human colon Gastroenterology 1994 106: 859–865
Kawahito Y et al. Corticotropin releasing hormone in colonic mucosa in patients with ulcerative colitis Gut 1995 37: 544–551
Iwakiri Y, Chijiiwa Y, Motomura Y, Osame M, Nawata H . Presence of functional receptors for corticotropin releasing hormone in caecal circular smooth muscle cells of guinea pig Life Sci 1997 60: 857–864
Hanani M, Wood JD . Corticotropin-releasing hormone excites myenteric neurons in the guinea-pig small intestine Eur J Pharmacol 1992 211: 23–27
Mancinelli R, Azzena GB, Diana M, Forgione A, Fratta W . In vitro excitatory actions of corticotropin-releasing factor on rat colonic motility J Auton Pharmacol 1998 18: 319–324
Harada S et al. Urocortin mRNA is expressed in the enteric nervous system of the rat Neurosci Lett 1999 267: 125–128
Muramatsu Y et al. Urocortin and corticotropin-releasing factor receptor expression in the human colonic mucosa Peptides 2000 21: 1799–1809
Valentino RJ, Kosboth M, Colflesh M, Miselis RR . Transneuronal labeling from the rat distal colon: anatomic evidence for regulation of distal colon function by a pontine corticotropin-releasing factor system J Comp Neurol 2000 417: 399–414
Whitehead WE, Crowell MD, Davidoff AL, Palsson OS, Schuster MM . Pain from rectal distension in women with irritable bowel syndrome: relationship to sexual abuse Dig Dis Sci 1997 42: 796–804
Lembo T et al. Effects of the corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) on rectal afferent nerves in humans Neurogastroenterol Motil 1996 8: 9–18
Lechner SM, Curtis AL, Brons R, Valentino RJ . Locus coeruleus activation by colon distention: role of corticotropin-releasing factor and excitatory amino acids Brain Res 1997 756: 114–124
Monnikes H, Schmidt BG, Tebbe J, Bauer C, Tache Y . Microinfusion of corticotropin releasing factor into the locus coeruleus/subcoeruleus nuclei stimulates colonic motor function in rats Brain Res 1994 644: 101–108
Calogero AE . Neurotransmitter regulation of the hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone neuron Ann N Y Acad Sci 1995 771: 31–40
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Rita J Valentino for her thoughtful discussion and Mr Keith Zachman for his help in conducting the animal experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gabry, K., Chrousos, G., Rice, K. et al. Marked suppression of gastric ulcerogenesis and intestinal responses to stress by a novel class of drugs. Mol Psychiatry 7, 474–483 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001031
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001031
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Stress and the Stomach: Corticotropin-Releasing Factor May Protect the Gastric Mucosa in Stress Through Involvement of Glucocorticoids
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2012)
-
Antiulcer activity of fluvoxamine in rats and its effect on oxidant and antioxidant parameters in stomach tissue
BMC Gastroenterology (2009)
-
Stress and disorders of the stress system
Nature Reviews Endocrinology (2009)
-
CRF1receptor signaling pathways are involved in stress-related alterations of colonic function and viscerosensitivity: implications for irritable bowel syndrome
British Journal of Pharmacology (2004)