Abstract
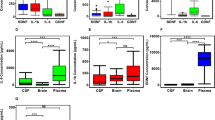
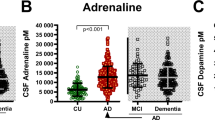
Neurotrophin 3 (NT-3) is a member of the neurotrophin gene family which supports the survival of specific neurons. NT-3 was shown to prevent the death of adult central noradrenergic neurons in vivo, a neuronal population which is associated with the pathophysiology of major depression. We quantitated CSF levels of NT-3 in elderly patients with major depression (DE) and compared them to patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD), and mentally healthy control subjects (CTR). CSF levels of NT-3 were markedly and significantly elevated in the DE group, as compared to either the AD or the CTR group (P < 0.01, and P < 0.001, respectively). in terms of diagnostic accuracy, measurement of nt-3 levels in de resulted in 73.9% sensitivity, and 89.7% specificity. increased csf levels of nt-3 may indicate a disturbance of the central noradrenergic system in patients with de. nt-3 may constitute a biochemical candidate marker for clinical diagnosis and for the evaluation of therapeutic strategies in de.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bothwell M . Functional interactions of neurotrophins and neurotrophin receptors Annu Rev Neurosci 1995; 18: 223–253
Price DL, Tanzi RE, Borchelt DR, Sisodia SS . Alzheimer's disease: genetic studies and transgenic models Annu Rev Genet 1998; 32: 461–493
Hyman C, Hofer M, Barde YA, Juhasz M, Yancopoulos GD, Squinto SP et al. BDNF is a neurotrophic factor for dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra Nature 1991; 350: 230–232
Knüsel B, Winslow JW, Rosenthal A, Burton LE, Seid DP, Nicolics K et al. Promotion of central cholinergic and dopaminergic neuron differentiation by brain-derived neurotrophic factor but not neurotrophin 3 Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1991; 88: 961–965
Mamounas LA, Blue ME, Siuciak JA, Altar CA . Brain-derived neurotrophic factor promotes the survival and sprouting of serotonergic axons in rat brain J Neurosci 1995; 15: 7929–7939
Arenas E, Persson H . Neurotrophin-3 prevents the death of adult central noradrenergic neurons in vivo Nature 1994; 367: 368–371
Leonard BE . The role of noradrenaline in depression: a review J Psychopharmacol 1997; 11: S39–S47
Gall CM, Gold SJ, Isackson PJ, Seroogy KB . Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 mRNAs are expressed in ventral midbrain regions containing dopaminergic neurons Mol Cell Neurosci 1992; 3: 56–63
Lindholm D, Hamner S, Zirrgiebel U . Neurotrophins and cerebellar development Perspect Dev Neurobiol 1997; 5: 83–94
Maisonpierre PC, Belluscio L, Squinto S, Ip NY, Furth ME, Lindsay RM et al. Neurotrophin-3: a neurotrophic factor related to NGF and BDNF Science 1990; 247: 1146–1451
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlau EM . Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease Neurology 1984; 34: 939–944
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR . Mini Mental State. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician J Psychiatr Res 1975; 12: 189–198
Spiegel R, Brunner C, Ermini-Funfschilling D, Monsch A, Notter M, Puxty J et al. A new behavioral assessment scale for geriatric out- and in-patients: the NOSGER (Nurses’ Observation Scale for Geriatric Patients) J Am Geriatr Soc 1991; 39: 339–347
Montgomery SA, Asberg M . A new depression scale designed to be sensitive to change Br J Psychiatry 1979; 134: 382–389
McDowell IF, Wisdom GB, Trimble ER . Apolipoprotein E phenotype determined by agarose gel electrofocusing and immunoblotting Clin Chem 1989; 35: 2070–2073
Hansen PS, Gerdes LU, Klausen IC, Gregersen N, Faergeman O . Genotyping compared with protein phenotyping of the common apolipoprotein E polymorphism Clin Chim Acta 1994; 224: 131–137
Leonard BE . The role of noradrenaline in depression: a review J Psychopharmacol 1997; 11: S39–S47
Gilmore JH, Jarskog LF, Lindgren JC, McEvoy JP, Xiao H . Neurotrophin-3 levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with schizophrenia or medical illness Psychiatry Res 1997; 73: 109–113
Murase K, Igarashi K, Hayashi K . Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) levels in the developing rat nervous system and in human samples Clin Chim Acta 1994; 227: 23–36
Kunugi H, Hattori M, Ueki A, Isse K, Hirasawa H, Nanko S . Possible association of missense mutation (Gly[-63]Glu) of the neurotrophin-3 gene with Alzheimer's disease in Japanese Neurosci Lett 1998; 241: 65–67
Smith MA, Makino S, Altemus M, Michelson D, Hong SK, Kvetnansky R et al. Stress and antidepressants differentially regulate neurotrophin 3mRNA expression in the locus coeruleus Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92: 8788–8792
Nibuya M, Morinobu S, Duman RS . Regulation of BDNF and trkB mRNA in rat brain by chronic electroconvulsive seizure and antidepressant drug treatments J Neurosci 1995; 15: 7539–7547
Duman RS, Heninger GR, Nestler EJ . A molecular and cellular theory of depression Arch Gen Psychiatry 1997; 54: 597–606
Altar CA . Neurotrophins and depression Trends Pharmacol Sci 1999; 20: 59–61
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grants 3100–049397.96/1 (Schweizerischer Nationalfonds) (UO, CH, FM-S), and SFB505 (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft) (UO). We thank F Jancu for technical support and K Kräuchi, PhD, for help in statistical analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hock, C., Heese, K., Müller-Spahn, F. et al. Increased cerebrospinal fluid levels of neurotrophin 3 (NT-3) in elderly patients with major depression. Mol Psychiatry 5, 510–513 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4000743
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4000743
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Cerebrospinal fluid neuroplasticity-associated protein levels in patients with psychiatric disorders: a multiplex immunoassay study
Translational Psychiatry (2020)
-
The role of neurotrophins in psychopathology and cardiovascular diseases: psychosomatic connections
Journal of Neural Transmission (2019)
-
Peripheral blood brain-derived neurotrophic factor in bipolar disorder: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis
Molecular Psychiatry (2016)
-
2D-DIGE proteome analysis on the platelet proteins of patients with major depression
Proteome Science (2014)
-
Fluoxetine prevents development of an early stress-related molecular signature in the rat infralimbic medial prefrontal cortex. Implications for depression?
BMC Neuroscience (2012)