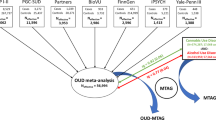
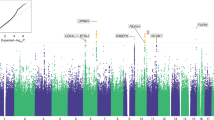
Abstract
Dopaminergic abnormalities are implicated in the pathogenesis of substance abuse.1 Recently, two reports have been published suggesting an association between opioid dependence and presence of long alleles of the dopamine D4 receptor (DRD4) gene exon III VNTR.2,3 We have attempted to replicate this finding using a two-tiered strategy employing independent case-control and family-based association samples. Our study was possibly the largest candidate gene association study to date on opioid dependence in a sample of 815 subjects, 396 of whom were patients. We found long alleles of the DRD4 exon III VNTR in similar frequency among 285 heroin addicts and 197 controls. Furthermore, no preferential transmission of long alleles to affected offspring was observed in a sample of 111 patients and their parents. Our results, therefore, do not support the hypothesis that alleles of the DRD4 exon III VNTR are susceptibility factors for opioid dependence in man.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nutt DJ . Addiction: brain mechanisms and their treatment implications Lancet 1996; 347: 31–36
Kotler M, Cohen H, Segman R, Gritsenko I, Nemanov L, Lerer B et al. Excess dopamine D4 receptor (D4DR) exon III seven repeat allele in opioid-dependent subjects Mol Psychiatry 1997; 2: 251–254
Li T, Xu K, Deng H, Cai G, Liu J, Liu X et al. Association analysis of the dopamine D4 gene exon III VNTR and heroin abuse in Chinese subjects Mol Psychiatry 1997; 2: 413–416
Merikangas KR, Stolar M, Stevens DE, Goulet J, Preisig MA, Fenton B et al. Familial transmission of substance use disorders Arch Gen Psychiatry 1998; 55: 973–979
Tsuang M, Lyons MJ, Eisen SA, Goldberg J, True W, Lin M et al. Genetic influences on DSMIIIR drug abuse and dependence: a study of 3372 twin pairs Am J Med Genet 1996; 67: 473–477
Cadoret RJ, Troughton E, O'Gorman TW, Heywood E . An adoption study of genetic and environmental factors in drug abuse Arch Gen Psychiatry 1986; 43: 1131–1138
Spielman RS, McGinnis RE, Ewens WJ . Transmission test for linkage disequilibrium: the insulin gene region and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) Am J Hum Genet 1993; 52: 506–516
Nöthen MM, Propping P, Fimmers R . Association versus linkage studies in psychosis genetics J Med Genet 1993; 30: 634–637
Risch N, Merikangas K . The future of genetic studies of complex human diseases Science 1996; 273: 1516–1517
Chang FM, Kidd JR, Livak KJ, Pakstis AJ, Kidd KK . The world-wide distribution of allele frequencies at the human dopamine D4 receptor locus Hum Genet 1996; 98: 91–101
Falk CT, Rubinstein P . Haplotype relative risks: an easy reliable way to construct a proper control sample for risk calculations Ann Hum Genet 1987; 51: 227–233
Terwilliger JD, Ott J . A haplotype-based ‘haplotype relative risk’ approach to detecting allelic associations Hum Hered 1992; 42: 337–346
Gelernter J, Kranzler H, Coccaro E, Siever L, New A, Mulgrew CL . D4 dopamine-receptor (DRD4) alleles and novelty seeking in substance-dependent, personality-disorder, and control subjects Am J Hum Genet 1997; 61: 1144–1152
Van Tol HHM, Wu CM, Guan H-C, Ohara K, Bunzow JR, Civelli O et al. Multiple dopamine D4 receptor variants in the human population Nature 1992; 358: 149–152
Asghari V, Schoots O, van Kats S, O'Hara K, Jovanovic V, Guan HC et al. Dopamine D4 receptor repeat: analysis of different native and mutant forms of the human and rat genes Mol Pharmacol 1994; 46: 364–373
Asghari V, Sanyal S, Buchwaldt S, Paterson A, Jovanovic V, Van Tol HHM . Modulation of intracellular cyclic AMP levels by different human dopamine D4 receptor variants J Neurochem 1995; 65: 1157–1165
Catalano M, Nobile M, Novelli E, Nöthen MM, Smeraldi E . Distribution of a novel mutation in the first exon of the human dopamine D4 receptor gene in psychotic patients Biol Psychiatry 1993; 34: 459–464
Lichter JB, Barr CL, Kennedy JL, Van Tol HHM, Kidd KK, Livak KJ . A hypervariable segment in the human dopamine receptor D4 (DRD4) gene Hum Mol Genet 1993; 2: 767–773
Nöthen MM, Cichon S, Hemmer S, Hebebrand J, Remschmidt H, Lehmkuhl G et al. Dopamine D4 receptor gene: frequent occurrence of a null allele and observation of homozygosity Hum Mol Genet 1994; 3: 2207–2212
Seeman P, Ulpian C, Chouinard G, Van Tol HHM, Dwosh H, Lieberman JA et al. Dopamine D4 receptor variant, D4Glycine 194, in Africans, but not in Caucasians: no association with schizophrenia Am J Med Genet 1994; 54: 384–390
Cichon S, Nöthen MM, Catalano M, Di Bella D, Maier W, Lichtermann D et al. Identification of two novel polymorphisms and a rare deletion variant in the human dopamine D4 receptor gene Psychiat Genet 1995; 5: 97–103
Sander T, Harms H, Dufeu P, Kuhn S, Rommelspacher H, Schmidt LG . Dopamine D4 receptor exon III alleles and variation of novelty seeking in alcoholics Am J Med Genet 1997; 74: 483–487
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to all patients and relatives for participation in this study granted by BMBF No. 01EB9418. We thank Susanne Albrecht, Daniela Bohnen, Kathrin Meyer zur Capellen, Gernot Schoch, Eva Sohne, Christian Sulzbach and Olaf Weiffenbach for their help in diagnosis and sample collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franke, P., Nöthen, M., Wang, T. et al. DRD4 exon III VNTR polymorphism—susceptibility factor for heroin dependence? Results of a case-control and a family-based association approach. Mol Psychiatry 5, 101–104 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4000583
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4000583
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
GPCR and Alcohol-Related Behaviors in Genetically Modified Mice
Neurotherapeutics (2020)
-
Genetics of dopamine receptors and drug addiction
Human Genetics (2012)
-
Genetic factors influencing alcohol dependence
British Journal of Pharmacology (2008)
-
Dopamine D4 receptor polymorphism modulates cue-elicited heroin craving in Chinese
Psychopharmacology (2006)
-
The dopamine D4 receptor and the hyperactivity phenotype: a developmental-epidemiological study
Molecular Psychiatry (2002)