Abstract
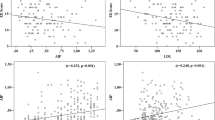
The objective of this study is to investigate the relation between serum lipids (cholesterol, LDL, HDL, triglyceride (TG)) and erectile dysfunction (ED). The experimental methods involved comparison of 100 patients with organic ED (mean age of 43.59±10.51 y), with 100 healthy individuals (mean age of 43.72±9.76 y) regarding their lipid profile from January 2000 to June 2003 (cholesterol, TG, HDL, LDL). The results showed that there was a significant difference between mean plasma cholesterol and LDL levels in the individuals suffering from ED and the control group (P=0.04 and 0.02, respectively). The TG and HDL mean plasma level differences were not significant (P=0.583 and 0.299, respectively). Odds ratios for high plasma cholesterol level (>240 mg/dl) and high plasma LDL level (>160 mg/dl) were 1.74 and 1.97. The R2 was 0.04 for both cholesterol and LDL. Applying linear regression, the coefficient for cholesterol and LDL reduced the International Index of Erectile Function questionnaire scores by −0.036 and −0.035. In conclusion, this study, the correlation of cholesterol and LDL levels with ED strongly supports the role of hyperlipidemia treatment in both the prevention and management of ED.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lewis R, Hatzichristou D, Laumann E, McKinlay J . Epidemiology and natural history of erectile dysfunction; risk factors including iatrogenic and aging. In: Jardin A, Wagner G, Khoury S, Giuliano F, Padma-Nathan H, Rosen R (eds). Erectile Dysfunction. First International Consultation on Erectile Dysfunction. Health Publications, Ltd.: Plymouth, 2000, pp 21–52.
Broderick GA . Intracavernous pharmacotherapy. Treatment for the aging erectile response. Urol Clin N Am 1995; 23: 111–126.
Johannes CB et al. Incidence of erectile dysfunction in men 40 to 69 years old: longitudinal results from the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol 2000; 163: 460–463.
Mellinger BC, Weiss J . Sexual dysfunction in the elderly male. Am Urol Assoc Update Ser 1992; 11: 146–152.
Virag R, Boully P, Frydman D . Is impotence an arterial disorder? Lancet 1985; 1: 181–184.
Juenemann KP et al. Does lipid metabolism influence the pathogenesis of vascular impotence? Int J Impot Res 1990; 2(Suppl 2): 33.
Sullivan ME, Keoghane SR, Miller MAW . Vascular risk factors and erectile dysfunction. BJU Int 2001; 87: 838–845.
Tanner FC et al. Oxidised low density lipoproteins inhibit relaxations of porcine coronary arteries. Circulation 1991; 83: 2012–2020.
Rosenfeld ME . Oxidised LDL affects multiple atherogenic cellular responses. Circulation 1991; 83: 2137–2140.
Kugiyama K et al. Impairment of endothelium-dependent arterial relaxation by lysolecithin in modified low-density lipoproteins. Nature 1990; 344: 160–162.
Leung WH, Lau CP, Wong CK . Beneficial effect of cholesterol-lowering therapy on coronary endothelium-dependent relaxation in hypercholesterolaemic patients. Lancet 1993; 341: 1496–1500.
Saltzman EA, Guay AT, Jacobson J . Improvement in erectile function in men with organic erectile dysfunction by correction of elevated cholesterol levels: a clinical observation. J Urol 2004; 172: 255–258.
Azadzoi KM, Saenz de Tejada I . Hypercholesterolaemia impairs endothelium dependent relaxation of rabbit corpus cavernosum smooth muscle. J Urol 1991; 146: 238–240.
Kim JH et al. Experimental hypercholesterolaemia in rabbits induces cavernosal atherosclerosis with endothelial and smooth muscle cell dysfunction. J Urol 1994; 151: 198–205.
Wei M et al. Total cholesterol and high density lipoprotein cholesterol as important predictors of erectile dysfunction. Am J Epidemiol 1994; 140: 930–937.
Manning M et al. The role of blood lipids in erectile failure. Int J Impotence Res 1996; 8: 167 (D179).
Kim SC . Hyperlipidemia and erectile dysfunction. Asian J Androl 2000; 2: 161–166.
Atahan O, Kayigil O, Hizel N, Metin A . Is apolipoprotein-(a) an important indicator of vasculogenic erectile dysfunction? Int Urol Nephrol 1998; 30: 185–191.
Walczak MK, Lokhandwala N, Hodge MB, Guay AT . Prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors in erectile dysfunction. J Gend Specif Med 2002; 5: 19–24.
Sanchez-Cruz JJ et al. Male erectile dysfunction and health-related quality of life. Eur Urol 2003; 44: 245–253.
Feldman HA et al. Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol 1994; 151: 54–61.
Pinnock CB, Stapleton AM, Marshall VR . Erectile dysfunction in the community: a prevalence study. Med J Aust 1999; 171: 353–357.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikoobakht, M., Nasseh, H. & Pourkasmaee, M. The relationship between lipid profile and erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 17, 523–526 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901350
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901350
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Time-course changes of nLDL-induced erectile dysfunction
International Journal of Impotence Research (2017)
-
Peripheral atherosclerosis in patients with arterial erectile dysfunction
International Journal of Impotence Research (2014)
-
Vascular risk factors and erectile dysfunction in a cohort of healthy men
International Journal of Impotence Research (2006)
-
Hyperlipidemia linked to erectile dysfunction
Nature Clinical Practice Urology (2006)
-
Why do patients with heart failure suffer from erectile dysfunction? A critical review and suggestions on how to approach this problem
International Journal of Impotence Research (2005)