Abstract
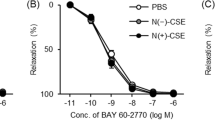
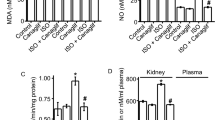
We compared the effects of a nitric oxide (NO)-releasing sildenafil (NCX-911), NO-independent soluble guanylate cyclase activator (BAY41-2272) and sildenafil on the anococcygeus muscle from streptozotocin-induced 16-weeks diabetic rats. NCX-911, BAY41-2272 and sildenafil reduced the phenylephrine-induced tone in the control group (EC50=1088.8±165.0, 151.6±9.3 and 827.1±167.3 nM, respectively). The potencies of NCX-911 and BAY41-2272 were not altered, but that of sildenafil was significantly reduced in the diabetic group. EC50 values for NCX-911, BAY41-2272 and sildenafil in the diabetic group were 1765.9±303.5, 209.7±27.3 and 2842.2±640.3 nM, respectively (P<0.05 for sildenafil). Nitrergic relaxation responses were significantly decreased in the diabetic group. The remaining nitrergic relaxation responses were potentiated by BAY41-2272 but not by sildenafil or NCX-911. These results confirm that endogenous NO derived from nitrergic nerves is significantly decreased in diabetes, and suggest that NO-releasing PDE5 inhibitors and NO-independent soluble guanylate cyclase activators could be more useful than PDE5 inhibitors in the treatment of ED in long-term diabetes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kubin M, Wagner G, Fugl-Meyer AR . Epidemiology of erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 2003; 15: 63–71.
Goldstein I et al. Oral sildenafil in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Sildenafil Study Group. N Engl J Med 1998; 338: 1397–1404.
Rendell MS, Rajfer J, Wicker PA, Smith MD . Sildenafil for treatment of erectile dysfunction in men with diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Sildenafil Diabetes Study Group. JAMA 1999; 281: 421–426.
Stuckey BG et al. Sildenafil citrate for treatment of erectile dysfunction in men with type 1 diabetes: results of a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2003; 26: 279–284.
Cellek S et al. Selective nitrergic neurodegeneration in diabetes mellitus—a nitric oxide-dependent phenomenon. Br J Pharmacol 1999; 128: 1804–1812.
Cellek S, Moncada S . Nitrergic neurotransmission in the physiology of penile erection and pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction. In: Toda N, Moncada S, Furchgott R, Higgs EA (eds). Nitric Oxide and the Peripheral Nervous System. Portland Press: London, 2000, pp 61–76.
Cellek S, Foxwell NA, Moncada S . Two phases of nitrergic neuropathy in streptozotocin diabetic rats. Diabetes 2003; 52: 2353–2362.
Cellek S, Rees RW, Kalsi J . A Rho-kinase inhibitor, soluble guanylate cyclase activator and nitric oxide-releasing PDE5 inhibitor: novel approaches to erectile dysfunction. Expert Opin Invest Drugs 2002; 11: 1563–1573.
Brioni JD et al. Activators of soluble guanylate cyclase for the treatment of male erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 2002; 14: 8–14.
Gibson A, McFadzean L . Biology of the anococcygeus muscle. Int Rev Cytol 2001; 205: 1–35.
Cheah LS, Gwee MC, Nirthanan S . Characterisation of the rat isolated retractor penis muscle as a model for the study of nitrergic transmission. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 2002; 47: 79–85.
Kasakov L, Cellek S, Moncada S . Characterization of nitrergic neurotransmission during short- and long-term electrical stimulation of the rabbit anococcygeus muscle. Br J Pharmacol 1995; 115: 1149–1154.
Way KJ, Reid JJ . Nitric oxide-mediated neurotransmission is attenuated in the anococcygeus muscle from diabetic rats. Diabetologia 1994; 37: 232–237.
Andersson KE . Pharmacology of penile erection. Pharmacol Rev 2001; 53: 417–450.
Saenz de Tejada I et al. Impaired neurogenic and endothelium-mediated relaxation of penile smooth muscle from diabetic men with impotence. N Engl J Med 1989; 320: 1025–1030.
Pickard RS, King P, Zar MA, Powell PH . Corpus cavernosal relaxation in impotent men. Br J Urol 1994; 74: 485–491.
Pickard RS, Powell PH, Zar MA . Nitric oxide and cyclic GMP formation following relaxant nerve stimulation in isolated human corpus cavernosum. Br J Urol 1995; 75: 516–522.
Azadzoi KM, Saenz de Tejada I . Diabetes mellitus impairs neurogenic and endothelium-dependent relaxation of rabbit corpus cavernosum smooth muscle. J Urol 1992; 148: 1587–1591.
Rehman J et al. Diminished neurogenic but not pharmacological erections in the 2- to 3-month experimentally diabetic F-344 rat. Am J Physiol 1997; 272: H1960–H1971.
Khan MA et al. The effect of superoxide dismutase on nitric oxide-mediated and electrical field-stimulated diabetic rabbit cavernosal smooth muscle relaxation. Br J Urol Int 2001; 87: 98–103.
Vernet D et al. Reduction of penile nitric oxide synthase in diabetic BB/WORdp (type I) and BBZ/WORdp (type II) rats with erectile dysfunction. Endocrinology 1995; 136: 5709–5717.
Podlasek CA et al. Characterization and localization of nitric oxide synthase isoforms in the BB/WOR diabetic rat. J Urol 2001; 166: 746–755.
Akingba AG, Burnett AL . Endothelial nitric oxide synthase protein expression, localization, and activity in the penis of the alloxan-induced diabetic rat. Mol Urol 2001; 5: 189–197.
El-Sakka AI et al. Effects of diabetes on nitric oxide synthase and growth factor genes and protein expression in an animal model. Int J Impot Res 1999; 11: 123–132.
Cashen DE, MacIntyre DE, Martin WJ . Effects of sildenafil on erectile activity in mice lacking neuronal or endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Br J Pharmacol 2002; 136: 693–700.
Thompson CS et al. The effect of sildenafil on corpus cavernosal smooth muscle relaxation and cyclic GMP formation in the diabetic rabbit. Eur J Pharmacol 2001; 425: 57–64.
Seidler M et al. In vitro effects of a novel class of nitric oxide (NO) donating compounds on isolated human erectile tissue. Eur Urol 2002; 42: 523–528.
Riffaud JP et al. Pharmacological profile of sildenafil nitrate (NCX 911) in various models of penile erection. Inflammation Res 2001; 50(Suppl 3): S84.
Stasch JP et al. NO-independent regulatory site on soluble guanylate cyclase. Nature 2001; 410: 212–219.
Kalsi JS et al. BAY41-2272, a novel nitric oxide independent soluble guanylate cyclase activator, relaxes human and rabbit corpus cavernosum in vitro. J Urol 2003; 169: 761–766.
Becker EM et al. NO-independent regulatory site of direct sGC stimulators like YC-1 and BAY41-2272. BMC Pharmacol 2001; 1: 13–25.
Bischoff E et al. BAY41-2272: a stimulator of soluble guanylate cyclase induces nitric oxide-dependent penile erection in vivo. Urology 2003; 61: 464–467.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by St Peter's Andrology Research Fund and Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation. JS Kalsi is a recipient of the Young Investigator's Award from the International Society for Sexual and Impotence Research. S Cellek is a fellow of Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation. The authors thank NicOx (France) and Bayer (Germany) for providing the compounds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalsi, J., Ralph, D., Madge, D. et al. A comparative study of sildenafil, NCX-911 and BAY41-2272 on the anococcygeus muscle of diabetic rats. Int J Impot Res 16, 479–485 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901224
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901224
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
NO-independent stimulators and activators of soluble guanylate cyclase: discovery and therapeutic potential
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2006)