Abstract
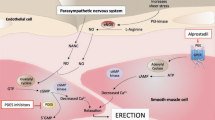
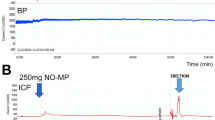
The objective of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of topically applied prostaglandin E1 (PGE1)+5% SEPA (soft enhancement of percutaneous absorption) on the glans penis in a feline erection model. Erectile response after glans penis administration of PGE1+5% SEPA cream (Topiglan, MacroChem Co., Lexington, MA, USA) was compared to the erectile response after intracavernosal administration of the triple-drug combination (1.65 mg papaverine, 25 μg phentolamine, and 0.5 μg PGE1). The placebo cream and increasing concentrations (0.25%, 2.5 mg/ml; 0.5%, 5 mg/ml; and 1%, 10 mg/ml) of PGE1+5% SEPA were applied in a total volume of 0.1 ml via a plastic needle-less syringe. The control triple-drug combination was administrated intracavernosally via a 30-gauge needle at the completion of each experiment to serve as a control reference. With each application of placebo, PGE1+SEPA, and the triple-drug combination, changes in intracavernosal pressure and systemic blood pressure were continuously monitored. Topical application of PGE1+SEPA induced increases in intracavernosal pressure in a dose-dependent manner, with minimal effects on systemic blood pressure. The increases obtained with 1% PGE1 Topiglan cream were similar to the intracavernosal pressure values elicited by the standard intracavernosal triple-drug combination. These data demonstrate that topical glans penis application of PGE1+SEPA can induce an erectile response in cats with minimal systemic adverse effects. Oral pharmacological agents are the first-line treatment for male ED. Studies investigating the effectiveness of noninvasive modalities such as topical therapy should continue, because these agents have the potential to avoid the systemic effects commonly seen with oral therapies. Additionally, topical therapy may also benefit patients who are unresponsive to oral agents or have explicit contraindications. Topical PGE1 application to the glans penis may become an important treatment option in selected patients suffering from erectile dysfunction.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
NIH Consensus Development Panel on Impotence. Impotence. JAMA 1993; 270: 83–90.
Lue TF . Erectile dysfunction. N Engl J Med 2000; 342: 1802–1813.
Melman A, Rehman J . Pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction. Mol Urol 1999; 3: 87–102.
Levine LA . Diagnosis and treatment of erectile dysfunction. Am J Med 2000; 109: 3S–30S.
Carson CC . Oral and injectable medications for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Curr Urol Rep 2000; 1: 307–312.
Yap RL, McVary KT . Topical agents and erectile dysfunction: is there a place? Curr Urol Rep 2002; 3: 471–476.
Porst H . The rationale for prostaglandin E1 in erectile failure: a survey of worldwide experience. J Urol 1996; 155: 802–815.
Goldstein I, Payton TR, Scheichter PJ . A double-blind, placebo-controlled, efficacy and safety study of topical gel formulation of 1% alprostadil (Topiglan) for the in-office treatment of erectile dysfunction. Urology 2001; 57: 301–305.
McMahon CG . Topiglan MacroChem. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 2002; 3: 602–606.
Bivalacqua TJ et al. Potentiation of erectile response and cAMP accumulation by combination of prostaglandin E1 and rolipram, a selective inhibitor of the type 4 phosphodiesterase (PDE4). J Urol 1999; 162: 1848–1855.
Bivalacqua TJ et al. Feline penile erection induced by transurethral administration of sodium nitroprusside. Urol Res 1999; 27: 432–436.
McVary KT, Polepalle S, Riggi S, Pelham RW . Topical prostaglandin E1 Sepa gel for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. J Urol 1999; 162: 726–731.
Berner B, John VA . Pharmacokinetic characterization of transdermal delivery systems. Clin Pharmacokinet 1994; 126: 121–134.
Sharlip ID . Evaluation and nonsurgical management of erectile dysfunction. Urol Clin North Am 1998; 25: 647–659.
Engel JD, McVary KT . Transurethral alprostadil as therapy for patients who withdrew from or failed prior intracavernous injection therapy. Urology 1998; 15: 687–692.
Nunez BD, Anderson DC . Nitroglycerin ointment in the treatment of impotence. J Urol 1993; 150: 1241–1243.
Cavallini G . Minoxidil versus nitroglycerin: a prospective double-blind conrolled trial in transcutaneous erection facilitation for organic impotence. J Urol 1991; 146: 50–53.
Gomaa A et al. Topical treatment of erectile dysfunction: randomized double blind placebo controlled trial of cream containing aminophylline, isosorbide dinitrate, and co-dergocrine mesylate. Br J Med 1996; 312: 1512–1515.
Gozes I, Fridkin M . A fatty neuropeptide. Potential drug for noninvasive impotence treatment in rat model. J Clin Invest 1992; 90: 810–814.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by an unrestricted educational grant by MacroChem Corporation, Lexington, MA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Usta, M., Sanabriav, J., Bivalacqua, T. et al. Feline penile erection induced by topical glans penis application of combination alprostadil and SEPA (Topiglan). Int J Impot Res 16, 73–77 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901145
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901145
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Retention and migration of alprostadil cream applied topically to the glans meatus for erectile dysfunction
International Journal of Impotence Research (2005)