Abstract
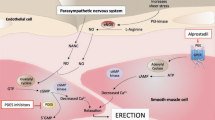
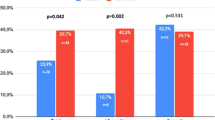
We compared the effectiveness of sildenafil citrate and alprostadil in improving arterial penile inflow (peak systolic velocity (PSV)) and penile rigidity in 55 patients with erectile dysfunction caused by atherosclerosis. A total of 35 patients with pure vasculogenic impotency were randomly assigned to alprostadil (Av group; n=11), sildenafil (Sv group; n=12), or placebo (P group; n=12), and 20 patients with nonvasculogenic impotency were randomly assigned to alprostadil (A group; n=10) or Sildenafil (S group; n=10): Av and A used alprostadil injection (capable of giving a full erection) once a week for 1 month, Sv and S took daily oral sildenafil (25 mg) for 1 month, and P took daily oral placebo for one month. The PSV was measured with Duplex sonography and penile rigidity was assessed using the IIEF-15 questionnaire, both of which were administered before and after treatment. Although both treatments improved penile rigidity, they increased PSV only in the Av and Sv groups. Our results suggest that alprostadil and oral therapy should be the starting therapy in men with vasculogenic impotency, whereas alprostadil should be avoided as the first-line approach in men with nonvasculogenic impotency.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pickard RS, Oates CP, Sethia KK, Powell PH . The role of color Duplex ultrasonography in the diagnosis of vasculogenic impotence. Br J Urol 1991; 68: 537–540.
Mancini M et al. The presence of arterial anatomical variations can affect the results of duplex sonographic evaluation of penile vessels in impotent patients. J Urol 1996; 155: 1919–1923.
Akkus E et al. Repetition of colors Doppler ultrasonography: is it necessary? Int J Impot Res 1998; 10: 51–55.
Chiou RK et al. Study of cavernosal arterial anatomy using color and power Doppler sonography: impact on hemodynamic parameter measurement. J Urol 1999; 162: 358–360.
Allen RP, Engel RME, Smolev JK, Brendler CB . Comparison of duplex sonography and nocturnal penile tumescence in the evaluation of impotence. J Urol 1994; 151: 1525–1529.
Mancini M et al. Duplex ultrasound evaluation of cavernosal peak systolic velocity and waveform acceleration in the penile flaccid state: clinical significance in the assessment of the arterial supply in patients with erectile dysfunction. Int J Androl 2000; 23: 199–204.
Quam JP et al. Duplex and color doppler sonografic evaluation of vasculogenic impotence. Am J Roentgenol 1989; 153: 1141–1147.
Lue TF, Hricak H, Marich KW, Tanagho EA . Vasculogenic impotence evaluated by high-resolution ultrasonography and pulsed doppler spectrum analysis. Radiology 1985; 155: 777–781.
Chiang PH et al. Color duplex sonography in the assessment of impotence. Br J Urol 1991; 68: 181–186.
Lee B et al. Standardization of penile blood flow parameters in normal men using intracavernous prostaglandin E1 and visual sexual stimulation. J Urol 1993; 149: 49–52.
Karadeniz T et al. Judgment of color Doppler ultrasound with respect to cavernous artery occlusion pressure in dynamic infusion cavernosometry when evaluating arteriogenic impotence. Urol Int 1996; 57: 85–88.
Fowkes FG et al. Edinburgh Artery Study: prevalence of asymptomatic and symptomatic peripheral arterial disease in the general population. Int J Epidemiol 1991; 20: 384–392.
O'Kane PD, Jackson G . Erectile dysfunction: is there silent obstructive coronary artery disease? Int J Clin Pract 2001; 55: 219–220.
Moreland RB . Pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction: the contributions of trabecular structure to function and the role of functional antagonism. Int J Impot Res 2000; 12(Suppl 4): S39–S46.
Saenz de Tejada I . Molecular mechanisms for the regulation of penile smooth muscle contractility. Int J Impot Res 2000; 12(Suppl 4): S34–S38.
Bode-Boger SM et al. L-Arginine induces nitric oxide dependent vasodilation in patients with critical limb ischemia. Circulation 1996; 93: 85–90.
Knispel HH, Goessl C, Beckmann R . Effects of papaverine and prostaglandin E1 on corpus cavernosum smooth muscle of arteriogenically and diabetically impotent men. Eur Urol 1994; 26: 35–39.
Creutzig A, Creutzig H, Alexander K . Effect of intra-arterial prostaglandin E1 in patients with peripheral arterial occlusive disease. Eur J Clin Invest 1986; 16: 480–485.
Marshall GA, Breza J, Lue TF . Improved hemodynamic response after long-term intracavernous injection for impotence. Urology 1994; 43: 844–848.
Kunelius P, Lukkarinen O . Intracavernous self-injection of prostaglandin E1 in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 1999; 11: 21–24.
Porst H et al. Intracavernous alprostadil alfadex — an effective and well tolerated treatment for erectile dysfunction. Results of a long-term European study. Int J Impot Res 1998; 10: 225–231.
Montorsi F et al. Sildenafil taken at bedtime significantly increases nocturnal erections: results of a placebo-controlled study. Urology 2000; 56: 906–911.
Jackson G . Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibition: effects on the coronary vasculature. Int J Clin Pract 2001; 55: 183–188.
Cappelleri JC et al. Diagnostic evaluation of the erectile function domain of the International Index of Erectile Function. Urology 1999; 54: 346–351.
Jarow JP, Pugh VW, Routh WD, Dyer RB . Comparison of penile duplex ultrasonography to pudendal arteriography: variant penile arterial anatomy affects interpretation of duplex ultrasonography. Invest Radiol 1993; 28: 806–810.
Benson CB, Aruny JE, Vickers Jr MA . Correlation of duplex sonography with arteriography in-patients with erectile dysfunction. Am J Roentgenol 1993; 160: 71–73.
Aboseif SR et al. Erectile response to acute and chronic occlusion of the internal pudendal and penile arteries. J Urol 1989; 141: 398–402.
Carlson LA, Eriksson I . Femoral artery infusion of prostaglandin E1 in severe peripheral vascular disease. Lancet 1973; 1: 155–156.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mancini, M., Raina, R., Agarwal, A. et al. Sildenafil citrate vs intracavernous alprostadil for patients with arteriogenic erectile dysfunction: a randomised placebo controlled study. Int J Impot Res 16, 8–12 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901123
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901123
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The flow index provides a comprehensive assessment of erectile dysfunction by combining blood flow velocity and vascular diameter
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Can self-directed pelvic floor exercises improve erectile function?
Nature Clinical Practice Urology (2005)