Abstract
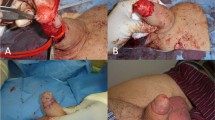
Although augmentation phalloplasty is not an established procedure, some patients still need enlargement of their penis. Current penile augmentation is girth enhancement of penile body by dermofat graft. We performed this study to identify the efficacy and the patient’s satisfaction of human glans penis augmentation with injectable hyaluronic acid gel. In 100 patients of subjective small penis (Group I) and 87 patients of small glans after dermofat graft (Group II), 2 cm3 of hyaluronic acid gel was injected into the glans penis, subcutaneously. At 1 y after injection, changes of glandular diameter were measured by tapeline. Patient’s visual estimation of glandular size (Gr 0–4) and patient’s satisfaction (Grade (Gr) 0–4) were evaluated, respectively. Any adverse reactions were also evaluated. The mean age of patients was 42.2 (30–70) y in Group I and 42.13 (28–61) y in Group II. The maximal glandular circumference was significantly increased compared to basal circumference of 9.13±0.64 cm in Group I (P<0.01) and 9.49±1.05 cm in Group II (P<0.01) at 1 y after injection. Net increase of maximal glandular circumference after glans augmentation was 14.93±0.80 mm in Group I and 14.78±0.89 mm in Group II. In patient’s visual estimation, more than 50% of injected volume was maintained in 95% of Group 1 and 100% of Group II. The percentage of postoperative satisfaction (Gr 4, 5) was 77% in Group 1 and 69% in Group II. There was no abnormal reaction in area feeling, texture, and color. In most cases, initial discoloration by glandular swelling recovered to normal within 2 weeks. There were no signs of inflammation and no serious adverse reactions in all cases. These results suggest that injectable hyaluronic acid gel is a safe and effective material for augmentation of glans penis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Olenius M . The first clinical study using a new biodegradable implant for the treatment of lips, wrinkles, and folds. Aesth Plast Surg 1998; 22: 97–101.
Duranti F et al. Injectable hyaluronic acid gel for soft tissue augmentation. Dermatol Surg 1998; 24: 1317–1325.
Goa KL, Benfield P . Hyaluronic acid. A review of its pharmacology and use as a surgical aid in ophthalmology, and its therapeutic potential in joint disease and wound healing. Drugs 1994; 47: 536–566.
Moon DG, Kwak TI, Kim JJ . Cho HY . Effects of hyaluronic acid gel in penile augmentation. Int J Impot Res 2002; 14(Suppl 3): S40.
Burton JL, Cunliffe WJ . The subcutaneous fat. In: Rook A, Wilkinson DS, Champion RH, Ebling FJG, Burton JL (eds). Textbook of Dermatology. Blackwell: Oxford, 1986, pp 1870–1871.
Knapp TR, Kaplan EN, Daniels JR . Injectable collagen for soft tissue augmentation. Plast Reconstruct Surg 1977; 60: 898–905.
Comper WD, Laurent TC . Physiological function of connective tissue polysaccharides. Physiol Rev 1978; 58: 255–315.
Selmanowitz VJ, Orentreich N . Medical-grade fluid silicone: a monographic review. J Dermatol Surg Oncol 1977; 3: 597–611.
Elson ML . Soft tissue augmentation. A review. Dermatol Surg 1995; 21: 491–500.
Pollack SV . Silicone, fibrel, and collagen implantation for facial lines and wrinkles. J Dermatol Surg Oncol 1990; 16: 957–961.
Larsen NE et al. Hylan gel biomaterials: Dermal and immunologic compatibility. J Biomed Mater Res 1993; 27: 1129–1134.
Richter W . Nonimmunogenicity of purified hyaluronic acid preparations tested by passive cutaneous anaphylaxis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 1974; 47: 211–217.
Richter W, Ryde E, Zetterstrom EO . Nonimmunogenicity of purified sodium hyaluronate preparation in man. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 1979; 59: 45–48.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J., Kwak, T., Jeon, B. et al. Human glans penis augmentation using injectable hyaluronic acid gel. Int J Impot Res 15, 439–443 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901044
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901044
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Hyaluronic acid injection to coronal sulcus of the penis for the treatment of premature ejaculation: a retrospective observational study
BMC Urology (2023)
-
Surgical treatment of premature ejaculation: a narrative review
International Journal of Impotence Research (2023)
-
Glans penis augmentation: when, how, and why?
International Journal of Impotence Research (2022)
-
Aesthetic Penile Augmentation Procedures: A Comprehensive and Current Perspective
Current Urology Reports (2022)
-
Penile girth augmentation by injectable fillers: a comprehensive review of imaging features and inflammatory complications
Abdominal Radiology (2021)