Abstract
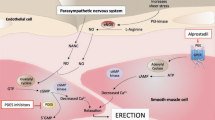
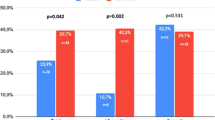
Oral therapy has become first line treatment for patients with mild to moderate erectile dysfunction (ED). Studies have shown that sildenafil may not be effective in all patients, and has been associated with a variety of adverse effects and an adverse interaction with nitrates and inhibitors of cytochrome P450 enzymes. The objective was to compare the efficacy and safety of three different oral combinations with the highest dose of sildenafil in men with moderate to severe ED. Randomized, double blind, unblinded active-controlled, Phase II study was carried out at three sites in Mexico. After a 4-week placebo run-in period, patients received all four of the following treatments using a 4-way cross-over design: 40 mg phentolamine (PM) +6 mg apomorphine (Apo); 40 mg PM +150 mg papaverine (Pap); 40 mg PM +6 mg Apo +150 mg Pap (Tricombo); 100 mg sildenafil (SC). With the exception of sildenafil tablets, all study medication was blinded. Moderate to severe ED was defined as a less than 50% vaginal penetration success rate during the placebo run-in period. A total of 44 patients were enrolled, of whom 36 completed all four treatment periods. All treatments produced a significant effect in primary efficacy variable (Sexual Encounter Profile) compared to baseline, however, no statistically significant differences were found between treatments. A significant period effect was observed. Also, the four treatments were found not to differ significantly in five out of six secondary efficacy variables. The lowest incidence of treatment-related adverse events (AE) occurred in the 40 mg PM +6 mg Apo group (9.8%), followed by 100 mg SC (15%), and the other two combinations (16.7 and 17.5%, respectively). Nasocongestion and headache were the most frequently reported AE. An oral combination of vasoactive agents may provide an alternative approach to sildenafil. Based on these results a combination of phentolamine and apomorphine warrants further clinical investigation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feldman HA et al . Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urology 1994 151: 54–61.
Hanash KA. . Comparative results of goal oriented therapy for erectile dysfunction. J Urology 1997 157: 2135–2138.
Hatzichristou DG, Bertero EB, Goldstein I. . Decision making in the evaluation of impotence: the patient profile-oriented algorithm. Sexuality and Disability 1994 12: 29–37.
Rosen RC, Goldstein I, Padma-Nathan H. . A process of case model evaluation and treatment of erectile dysfunction. Robert Wood Johnson Medical School: New Brunswick, New Jersey, May 1998
Goldstein I et al . Oral sildenafil in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. New Engl J Med 1998 338: 1397–1404.
Goldstein I. . A 36-week, open label non-comparative study to assess the long-term safety of sildenafil citrate (Viagra®) in patients with erectile dysfunction. Int J Clin Pract 1999 102: Suppl 8–9.
Schwartz I, McCarthy D. . Sildenafil in the treatment of erectile dysfunction [letter]. New Engl J Med 1998 339: 699–700.
McMahon CG, Samali R, Johnson H. . Efficacy, safety and patient acceptance of sildenafil citrate as treatment for erectile dysfunction. J Urol 2000 164: 1192–1196.
Kloner RA, Zusman RM. . Cardiovascular effects of sildenafil citrate and recommendations for its use. Am J Cardiol 1999 84: 11N–17N.
Zentgraf M, Baccouche M, Junemann KP. . Diagnosis and therapy of erectile dysfunction using papaverine and phentolamine. Urol Int 1988 43: 65–75.
Truss MC, Becker AJ, Schiltheiss D, Jonas U. . Intracavernous pharmacotherapy. World J Urol 1997 15: 71–77.
Soli M et al . Vasoactive cocktails for erectile dysfunction: chemical stability of PGE1, papaverine and phentolamine. J Urol 1998 160: 551–555.
Mydlo JH, Volpe MA, Macchia RJ. . Initial results utilizing combination therapy for patients with a suboptimal response to either alprostadil or sildenafil monotherapy. Eur Urol 2000 38: 30–34.
Kaplan SA et al . Combination therapy using oral alpha-blockers and intracavernosal injection in men with erectile dysfunction. Urology 1998 52: 739–743.
Przedborski S et al . Peripheral and central pharmacokinetics of apomorphine and its effect on dopamine metabolism in humans. Mov Disord 1995 10: 28–36.
Heaton JP et al . Recovery of erectile function by the oral administration of apomorphine. Urology 1995 45: 200–206.
Traish AM et al . A heterogeneous population of alpha-1 adrenergic receptors mediates contraction of human corpus cavernosum smooth muscle to norepinephrine. J Urology 1995 153: 222–227.
Poch G, Kukovetz WR. . Papaverine-induced inhibition of phosphodiesterase activity in various mammalian tissues. Life Sci I 1971 10: 133–144.
Phase I Safety Study in Healthy Volunteers of Different Oral Combinations of Papaverine, Phentolamine, and Apomorphine; Data on File, Zonagen Inc.
Machim D, Campbell MJ. . Statistical tables for the design of clinical trials. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford 1987
Gould L. . A new approach to the analysis of clinical drug trials with withdrawals. Biometrics 1980 36: 721–727.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lammers, P., Rubio-Aurioles, E., Castell, R. et al. Combination therapy for erectile dysfunction: a randomized, double blind, unblinded active-controlled, cross-over study of the pharmacodynamics and safety of combined oral formulations of apomorphine hydrochloride, phentolamine mesylate and papaverine hydrochloride in men with moderate to severe erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 14, 54–59 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3900816
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3900816
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Apomorphine for the Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Archives of Sexual Behavior (2020)
-
Dopaminergic Therapies for Non-motor Symptoms in Parkinson’s Disease
CNS Drugs (2017)
-
Sildenafil citrate efficacy 8 h postdose in men with mild to moderate erectile dysfunction
International Journal of Impotence Research (2008)
-
Centrally acting drugs for erectile dysfunction: Do they have a future?
Current Sexual Health Reports (2007)
-
Preference studies are of value to the field of sexual medicine: Con
Current Sexual Health Reports (2006)