Abstract
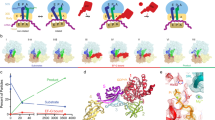
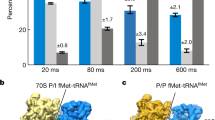
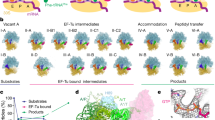
The delivery of a specific amino acid to the translating ribosome is fundamental to protein synthesis. The binding of aminoacyl-transfer RNA to the ribosome is catalysed by the elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu). The elongation factor, the aminoacyl-tRNA and GTP form a stable ‘ternary’ complex that binds to the ribosome. We have used electron cryomicroscopy and angular reconstitution1 to visualize directly the kirromycin-stalled ternary complex in the A site of the 70S ribosome of Escherichia coli. Electron cryomicroscopy had previously given detailed ribosomal structures at 25 and 23 Å (refs 2, 3) resolution, and was used to determine the position of tRNAs on the ribosome4,5. In particular, the structures5 of pre-translocational (tRNAs in A and P sites) and post-translocational ribosomes (P and E sites occupied) were both visualized at a resolution of ∼20 Å. Our three-dimensional reconstruction at 18 Å resolution shows the ternary complex spanning the inter-subunit space with the acceptor domain of the tRNA reaching into the decoding centre. Domain 1 (the G domain) of the EF-Tu is bound both to the L7/L12 stalk and to the 50S body underneath the stalk, whereas domain 2 is oriented towards the S12 region on the 30S subunit.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
van Heel, M. Angular reconstitution: aposteriori assignment of projection directions for 3D reconstruction. Ultramicroscopy 21, 111–124 (1987).
Frank, J. et al. Amodel of protein synthesis based on cryo-electron microscopy of the E. coli ribosome. Nature 376, 441–444 (1995).
Stark, H. et al. The 170S E. coli ribosome at 23 Å resolution: fitting the ribosomal RNA. Structure 3, 815–821 (1995).
Agrawal, R. K. et al. Direct visualization of A-, P-, and E-site transfer RNAs in the Escherichia coli ribosome. Science 271, 1000–1002 (1996).
Stark, H. et al. Arrangement of tRNAs in pre- and posttranslational ribosomes revealed by electron cryomicroscopy. Cell 88, 19–28 (1997).
Wolf, H., Chinali, G. & Parmeggiani, A. Mechanism of the inhibition of protein synthesis by kirromycin. Eur. J. Biochem. 75, 67–75 (1977).
Mesters, J. R. et al. The structural and functional basis for the kirromycin resistance of mutant EF-Tu species in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 13, 4877–4885 (1994).
Rodnina, M. V., Fricke, R., Kuhn, L. & Wintermeyer, W. Codon-dependent conformational change of elongation factor Tu preceding GTPO hydrolysis on the ribosome. EMBO J. 14, 2613–2619 (1995).
van Heel, M., Harauz, G., Orlova, E. V., Schmidt, R. & Schatz, M. Anew generation of the IMAGIC image processing system. J. Struct. Biol. 116, 17–24 (1996).
Nissen, P. et al. Crystal structure of the ternary complex of Phe-tRNAPhe, EF-Tu, and a GTP analog. Science 270, 1464–1472 (1995).
Tapprich, W. E. & Dahlberg, A. E. Asingle base mutation at position 2661 in E. coli 23S ribosomal RNA affects the binding of ternary complex to the ribosome. EMBO J. 9, 2649–2655 (1990).
Moazed, D., Robertson, J. M. & Noller, H. F. Interaction of elongation factors EF-G and EF-Tu with a conserved loop in 23S RNA. Nature 334, 362–364 (1988).
Girshovich, A. S., Bochkareva, E. S. & Vasiliev, V. D. Localization of elongation factor Tu on the ribosome. FEBS Lett. 197, 192–198 (1986).
Girshovich, A. S., Kurtskhalia, T. V., Ovchinnikov, Y. A. & Vasiliev, V. D. Localization of the elongation factor G on Escherichia coli ribosome. FEBS Lett. 130, 54–59 (1981).
Traut, R. R. et al. Location and domain structure of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein L7/L12: Site specific cysteine crosslinking and attachment of fluorescent probes. Biochem. Cell Biol. 73, 949–958 (1995).
Dey, D., Oleinikov, A. V. & Traut, R. R. The hinge region of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein L7/L12 is required for factor binding and GTP hydrolysis. Biochimie 77, 925–930 (1995).
Langer, J. A. & Lake, J. A. Elongation factor Tu localized on the exterior surface of the small ribosomal subunit. J. Mol. Biol. 187, 617–621 (1986).
Capel, M. S. et al. Acomplete mapping of the proteins in the small ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. Science 238, 1403–1406 (1987).
Noller, H. F. et al. Structure and function of ribosomal RNA. Biochem. Cell Biol. 73, 997–1009 (1995).
Dontsova, O. et al. Three widely separated positions in the 16S RNA lie in or close to the ribosomal decoding region; a site-directed cross-linking study with mRNA analogues. EMBO J. 11, 3105–3116 (1992).
Mueller, F. & Brimacombe, R. Anew model for the three-dimensional folding of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA. J. Mol. Biol.(in the press).
Powers, T. & Noller, H. F. Evidence for functional interaction between elongation factor Tu and 16S ribosomal RNA. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 90, 1364–1368 (1993).
van Ryk, D. I. & Dahlberg, A. E. Structural changes in the 530 loop of Escherichia coli 16S rRNA in mutants with impaired translational fidelity. Nucleic Acids Res. 23, 3563–3570 (1995).
Santer, U. V. et al. Amutation at the universally conserved position 529 in Escherichia coli 16S rRNA creates a functional but highly error prone ribosome. RNA 1, 89–94 (1995).
Berchtold, H. et al. Crystal structure of active elongation factor Tu reveals major domain rearrangements. Nature 365, 126–132 (1993).
Kjeldgaard, M., Nissen, P., Thirup, S. & Nyborg, J. The crystal structure of elongation factor EF-Tu from Thermus aquaticus in the GTP conformation. Structure 1, 35–50 (1993).
Polekhina, G. et al. Helix unwinding in the effector region of elongation factor EF-Tu-GDP. Structure 4, 1141–1151 (1996).
Abel, K., Yoder, M., Hilgenfeld, R. & Jurnak, F. An alpha to beta conformational switch in EF-Tu. Structure 4, 1153–1159 (1996).
Rodnina, M. V., Fricke, R. & Wintermeyer, W. Transient conformational states of aminoacyl-tRNA during ribosome binding catalyzed by Elongation Factor Tu. Biochemistry 33, 12267–12275 (1994). Article title?
Rodnina, M. V., Pape, T., Fricke, R., Kuhn, L. & Wintermeyer, W. Initial binding of the elongation factor Tu-GTP-aminoacyl-tRNA complex preceding codon recognition on the ribosome. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 646–652 (1996).
Rodnina, M. V. & Wintermeyer, W. GTP consumption of elongation factor Tu during translation of heteropolymeric mRNAs. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92, 1945–1949 (1995).
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Nyborg for the X-ray coordinates of the ternary complex. We acknowledge support with the IMAGIC system from M. Schatz and R. Schmidt of Image Science GmbH. The work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, grants to W.W., M.vH. and R.B.; H.S. was financed in part by an award to R. Henderson of the MRC Laboratory for Molecular Biology, Cambridge, UK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stark, H., Rodnina, M., Rinke-Appel, J. et al. Visualization of elongation factor Tu on the Escherichia coli ribosome. Nature 389, 403–406 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/38770
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/38770
This article is cited by
-
Cryo-EM of elongating ribosome with EF-Tu•GTP elucidates tRNA proofreading
Nature (2020)
-
Ensemble cryo-EM elucidates the mechanism of translation fidelity
Nature (2017)
-
Human ribosomal P1-P2 heterodimer represents an optimal docking site for ricin A chain with a prominent role for P1 C-terminus
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
A strategy for co-translational folding studies of ribosome-bound nascent chain complexes using NMR spectroscopy
Nature Protocols (2016)
-
A consolidated analysis of the physiologic and molecular responses induced under acid stress in the legume-symbiont model-soil bacterium Sinorhizobium meliloti
Scientific Reports (2016)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.