Abstract
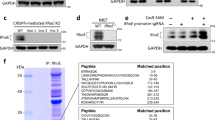
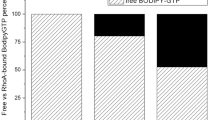
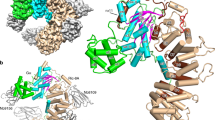
Members of the Rho family of small G proteins transduce signals from plasma-membrane receptors and control cell adhesion, motility and shape by actin cytoskeleton formation1–4. They also activate other kinase cascades. Like all other GTPases, Rho proteins act as molecular switches, with an active GTP-bound form and an inactive GDP-bound form5. The active conformation is promoted by guanine-nucleotide exchange factors, and the inactive state by GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs) which stimulate the intrinsic GTPase activity of small G proteins6. Rho-specific GAP domains are found in a wide variety of large, multi-functional proteins7. Here we report the crystal structure of an active 242-residue C-terminal fragment of human p50rhoGAP8. The structure is an unusual arrangement of nine α-helices, the core of which includes a four-helix bundle. Residues conserved across the rhoGAP family are largely confined to one face of this bundle, which may be an interaction site for target G proteins. In particular, we propose that Arg 85 and Asn 194 are involved in binding G proteins and enhancing GTPase activity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paterson, H. F. et al. J. Cell Biol. 111, 1001–1007 (1990).
Ridley, A. J. & Hall, A. Cell 70, 389–399 (1992).
Ridley, A. J., Paterson, H. F., Johnson, C. L., Diekmann, D. & Hall, A. Cell 70, 401–410 (1992).
Ridley, A. J. J. Cell Sci. (suppl.) 18, 127–131 (1994).
Bourne, H. R., Sanders, D. A. & McCormick, F. Nature 348, 125–132 (1990).
Boguski, M. S. & McCormick, F. Nature 366, 643–654 (1993).
Lamarche, N. & Hall, A. Trends Genet. 10, 436–440 (1994).
Lancaster, C. A. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 26, 1137–1142 (1994).
Hall, A. et al. J. Mol. Biol. 211, 11–16 (1990).
Mussachio, A., Cantley, L. C. & Harrison, S. C. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 14373–14378 (1997).
Zheng, Y., Bagrodia, S. & Cerione, R. A. J. Cell Biol. 269, 18727–18730 (1994).
Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. Data Colleciton and Processing (eds Sawyer, L., Isaacs, N. & Bailey, S.) 556–562 (SERC Daresbury Laboratory, Warringon, 1993).
CCP4 Acta Crystallogr. D50, 760–763 (1994).
Terwilliger, T. C., Kim, S. H. & Eisenberg, D. Acta Crystallogr. A43, 1–5 (1987).
Otwinowski, Z. Isomorphous Replacement and Anomalous Scattering (eds Wolf, W., Evans, P. R. & Leslie, A. G. W.) 80–86 (SERC Daresbury Laboratory, Warrington, 1991).
Jones, T. A., Zhou, J.-Y., Cowan, S. W. & Kjeldgaard, M. Acta Crystallogr. A47, 110–119 (1991).
Lamzin, V. S. & Wilson, K. S. Acta Crystallogr. D49, 127–149 (1993).
Carson, M. J. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 24, 958–961 (1991).
Settleman, J., Varasingham, V., Foster, L. C. & Weinberg, R. A. Cell 64, 539–549 (1992).
Lifschitz, B. et al. Oncogene 2, 113–117 (1988).
Cicchetti, P., Mayer, B. J., Thiel, G. & Baltimore, D. Science 257, 803–806 (1992).
Otsu, M. et al. Cell 65, 91–104 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barrett, T., Xiao, B., Dodson, E. et al. The structure of the GTPase-activating domain from p50rhoGAP. Nature 385, 458–461 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/385458a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/385458a0
This article is cited by
-
SH3 domain regulation of RhoGAP activity: Crosstalk between p120RasGAP and DLC1 RhoGAP
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Assignment of 1H, 13C and 15N resonances and secondary structure of the Rgd1-RhoGAP domain
Biomolecular NMR Assignments (2018)
-
Human brain arteriovenous malformation: an analysis of differential expressed genes
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal (2016)
-
Loss of the RhoGAP SRGP-1 promotes the clearance of dead and injured cells in Caenorhabditis elegans
Nature Cell Biology (2011)
-
Exportin 7 defines a novel general nuclear export pathway
The EMBO Journal (2004)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.