Abstract
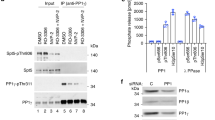
THE poly(A) tail found on almost all eukaryotic messenger RNAs1,2 is important in enhancing translation initiation and determining mRNA stability3,4. Control of poly (A)-tail synthesis thus has the potential to be a key regulatory step in gene expression and is indeed known to be important during early development in many organisms5. To study a possible basis for such regulation, we examined phosphorylation of poly(A) polymerase (PAP) by p34cdc2/cyclin B (maturation/mitosis-promoting factor, MPF). We show here that PAP can be phosphorylated in vivo and in vitro by MPF. Consistent with this, PAP becomes hyperphosphorylated both during meiotic maturation ofXenopus laevis oocytes and in HeLa cells arrested at M phase, times in the cell-cycle when MPF is known to be active6,7. We show further that hyperphosphorylation by MPF dramatically reduces the activity of purified PAP, and that PAP isolated from mitotic HeLa cells is similarly inhibited by hyperphosphorylation. This repression probably contributes to the well established reductions in poly (A) + RNA and/or protein synthesis known to occur in M-phase cells8–15.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keller, W. Cell 81, 829–832 (1995).
Manley, J. L. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 5, 222–228 (1995).
Beelman, C. A. & Parker, R. Cell 81, 179–183 (1995).
Curtis, D., Lehmann, R. & Zamore, P. D. Cell 81, 171–178 (1995).
Wickens, M. Semin. Dev. Biol. 3, 399–412 (1992).
Kobayashi, H. et al. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 56, 437–447 (1991).
Norbury, C. & Nurse, P. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 61, 441–470 (1992).
Stewart, D., Shaeffer, J. & Humphrey, M. Science 161, 791–793 (1968).
Fan, H. & Penman, S. J. Mol. Biol. 50, 665–670 (1970).
Wilt, F. H. Cell 11, 673–681 (1977).
Sagata, N., Shiokawa, K. & Yamana, K. Dev. Biol. 77, 431–448 (1980).
Kanki, J. P. & Newport, J. W. Dev. Biol. 146, 191–213 (1991).
Dambrough, C. & Ford, F. J. Dev. Biol. 71, 323–340 (1979).
Pawlowski, P. J. & Rodriguez, L. V. Dev. Biol. 40, 71–77 (1974).
Slater, D. W. & Slater, I. Nature 240, 333–337 (1972).
Raabe, T., Bollum, F. J. & Manley, J. L. Nature 353, 229–234 (1991).
Elledge, S. J. & Harper, J. W. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 6, 847–852 (1994).
Vesely, J. et al. Eur. J. Biochem. 224, 771–786 (1994).
Zhao, W. & Manley, J. L. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16, 2378–2386 (1996).
Wahle, E., Martin, G., Schlitz, E. & Keller, W. EMBO J. 10, 4251–4252 (1991).
Thuresson, A. et al. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 91, 979–983 (1994).
Ballantyne, S. et al. RNA 1, 64–78 (1995).
Bienroth, S., Wahle, E., Suter-Crazolera, C. & Keller, W. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 19768–19776 (1991).
Murthy, K. G. K. & Manley, J. L. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 14804–14811 (1992).
Gerhart, J., Wu, M. & Kirschner, M. J. Cell. Biol. 98, 1247–1255 (1984).
Manley, J. L. et al. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 77, 3855–3859 (1980).
Wang, Y. & Prives, C. Nature 376, 88–91 (1995).
Prives, C. & Foukal, D. Meth. Cell Biol. 36, 185–210 (1991).
Martin, G. & Keller, W. EMBO J. 15, 2593–2603 (1996).
Raabe, T., Murthy, K. G. K. & Manley, J. L. Mol. Cell. Biol. 14, 2946–2957 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colgan, D., Murthy, K., Prives, C. et al. Cell-cycle related regulation of poly(A) polymerase by phosphorylation. Nature 384, 282–285 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/384282a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/384282a0
This article is cited by
-
Nuclear deadenylation/polyadenylation factors regulate 3′ processing in response to DNA damage
The EMBO Journal (2010)
-
The structure of the 5′-untranslated region of mammalian poly(A) polymerase-α mRNA suggests a mechanism of translational regulation
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2010)
-
The role of cordycepin in cancer treatment via induction or inhibition of apoptosis: implication of polyadenylation in a cell type specific manner
Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology (2007)
-
Cell signalling and the control of pre-mRNA splicing
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2004)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.