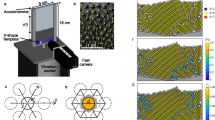
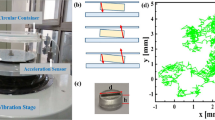
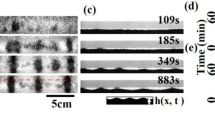
Abstract
THE formation of two-dimensional patterns in biological, chemical and physical systems is often described by the nonlinear interaction of plane waves1. An alternative approach views patterns as ensembles of interacting localized objects, analogous to the assembly of crystals from atoms. For macroscopic pattern-forming systems, one objection to the latter approach is that no 'atoms' exist; however spatially localized excitations can play an analogous role. One-dimensional localized states are observed in many systems—for example, solitary waves in water2–4 and optical fibres5—and can organize into simple patterns6,7. But few examples of two-dimensional localized states are known, and these tend to be unstable and/or do not show simple pattern-forming interactions8–11. Here we report the observation of stable, two-dimensional localized excitations zin a vibrating layer of sand. These excitations, which we term 'oscillons', have a propensity to assemble into 'molecular' and 'crystalline' structures. Our experimental results, together with the observation of similar localized excitations in model differential equations12–14, indicate a crucial, cooperative role for hysteresis and dissipation in the formation of oscillons, and suggest that similar behaviour may occur in continuous media.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cross, M. C. & Hohenberg, P. C. Rev. Mod. Phys. 65, 851–1112 (1993).
Russell, J. S. Report on Waves 311–390 (Murray, London, 1844).
Wu, J., Keolian, R. & Rudnick, I. Phys. Rev. Lett. 52, 1421–1424 (1984).
Osborne, A. R. & Burch, T. L. Science 208, 451–460 (1980).
Mollenauer, L. F., Stolen, R. H. & Gordon, J. P. Phys. Rev. Lett. 45, 1095–1098 (1980).
Melo, F. & Douady, S. Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 3283–3286 (1993).
Balmforth, N. J. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 27, 337–373 (1995).
Dennin, M., Ahlers, G. & Cannell, D. S. Science 272, 388–390 (1996).
Joets, A. & Ribotta, R. Phys. Rev. Lett. 21, 2164–2167 (1988).
Lerman, K., Bodenschatz, E., Cannell, D. S. & Ahlers, G. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 3572–3575 (1993).
Lioubashevski, O., Arbell, H. & Fineberg, J. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 3959–3962 (1996).
Thual, O. & Fauve, S. J. Phys., Paris 49, 1829–1833 (1988).
Deissler, R. J. & Brand, H. R. Phys. Rev. A 44, R3411–R3414 (1991).
Aranson, I. S., Gorshkov, K. A., Lomov, A. S. & Rabinovich, M. I. Physica D 43, 435–453 (1990).
Jaeger, H. M., Nagel, S. R. & Behringer, R. P. Physics Today 49(4), 32–38 (1996).
Evesque, P. & Rajchenbach, J. Phys. Rev. Lett. 50, 44–47 (1989).
Laroche, C., Douady, S. & Fauve, S. J. Phys., Paris 50, 699–702 (1989).
Knight, J. B., Jaeger, H. M. & Nagel, S. R. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 3728–3730 (1993).
Pak, H. K. & Behringer, R. P. Nature 371, 231–233 (1994).
Fauve, S., Douady, S. & Laroche, C. J. Phys. Colloque, Paris 50 C3, 187–191 (1989).
Melo, F., Umbanhowar, P. & Swinney, H. L. Phys. Rev. Lett. 72, 172–175 (1994).
Melo, F., Umbanhowar, P. & Swinney, H. L. Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 3838–3841 (1995).
Pak, H. K., Van Doorn, E. & Behringer, R. P. Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 4643–4646 (1995).
Reynolds, O. Phil. Mag. 20, 469–481 (1885).
Edwards, W. S. & Fauve, S. J. Fluid Mech. 278, 123–148 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Umbanhowar, P., Melo, F. & Swinney, H. Localized excitations in a vertically vibrated granular layer. Nature 382, 793–796 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/382793a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/382793a0
This article is cited by
-
Front Selection in Reaction–Diffusion Systems via Diffusive Normal Forms
Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis (2024)
-
Arbitrarily weak head-on collision can induce annihilation: the role of hidden instabilities
Japan Journal of Industrial and Applied Mathematics (2023)
-
Geometry-controlled phase transition in vibrated granular media
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Influence of interactions between multiple point defects on wave scattering in granular media
Granular Matter (2022)
-
Moulding hydrodynamic 2D-crystals upon parametric Faraday waves in shear-functionalized water surfaces
Nature Communications (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.