Abstract
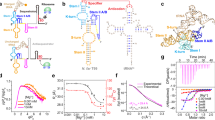
THE catalytic properties of RNA1,2 and its well known role in gene expression and regulation are the consequence of its unique solution structures. Identification of the structural determinants of ligand recognition by RNA molecules is of fundamental importance for understanding the biological functions of RNA, as well as for the rational design of RNA sequences with specific catalytic activities3–6. Towards this latter end, Szostak et al.7,8 used in vitro selection techniques to isolate RNA sequences ('aptamers') containing a high-affinity binding site for ATP, the universal currency of cellular energy, and then used this motif to engineer ribozymes with polynucleotide kinase activity. Here we present the solution structure, as determined by multidimensional NMR spectroscopy and molecular dynamics calculations, of both uniformly and specifically 13C-, 15N-labelled 40-mer RNA containing the ATP-binding motif complexed with AMP. The aptamer adopts an L-shaped structure with two nearly orthogonal stems, each capped proximally by a G·G mismatch pair, binding the AMP ligand at their junction in a GNRA-like motif.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cech, T. R., Zaug, A. J. & Grabowski, P. J. Cell 27, 487–496 (1981).
Kole, R. & Altman, S. Biochemistry 20, 1902–1906 (1981).
Joyce, G. F. Gene 82, 83–87 (1989).
Robertson, D. L. & Joyce, G. F. Nature 344, 467–468 (1990).
Ellington, A. & Szostak, J. W. Nature 346, 812–822 (1990).
Tuerk, C. & Gold, L. Science 249, 505–510 (1990).
Sassanfar, M. & Szostak, J. W. Nature 364, 550–553 (1993).
Lorsch, J. R. & Szostak, J. W. Nature 371, 31–36 (1994).
Woese, C. R., Winker, S. & Gutell, R. R. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87, 8467–8471 (1990).
Heus, H. A. & Pardi, A. Science 253, 191–194 (1991).
Varani, G., Cheong, C. & Tinoco, I. Jr Biochemistry 30, 3280–3289 (1991).
Orita, M. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 21, 5670–5678 (1993).
Pley, H. W., Flaherty, K. M. & McKay, D. B. Nature 372, 68–74 (1994).
Scott, W. G., Finch, J. T. & Klug, A. Cell 81, 991–1002 (1995).
Puglisi, J. D. et al. Science 257, 76–80 (1992).
Aboul-ela, F., Karn, J. & Varani, G. J. molec. Biol. 253, 313–332 (1995).
Battiste, J. L., Tan, R., Frankel, A. D. & Williamson, J. R. J. Biomol. NMR 6, 375–389 (1995).
Puglisi, J. D., Chen, L., Blanchard, S. & Frankel, A. D. Science 270, 1200–1203 (1995).
Ye, X., Kumar, R. A. & Patel, D. J. Chem. Biol. 2, 827–840 (1995).
Fan, P. et al. J. molec. Biol. 258, 480–500 (1996).
Allain, F. H. T. et al. Nature 380, 646–650 (1996).
Koshland, D. E. Jr Harvey Lect. 65, 33–57 (1971).
Brünger, A. T. X-PLOR, A System for X-ray Crystallography and NMR (Yale University Press, New Haven, Connecticut, 1992).
Nikonowicz, E. P. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 20, 4508–4513 (1992).
Pardi, A. Meth. Enzym. 261, 350–380 (Academic, New York, 1995).
Delaglio, F. et al. J. Biomol. NMR 6, 277–293 (1995).
Lavery, R. & Sklenar, H. J. biomolec. Struct. Dyn. 6, 63–91 (1988).
Nicholls, A., Sharp, K. A. & Honig, B. Proteins Struct. Func. Genet. 11, 281–296 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, F., Kumar, R., Jones, R. et al. Structural basis of RNA folding and recognition in an AMP–RNA aptamer complex. Nature 382, 183–186 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/382183a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/382183a0
This article is cited by
-
Computational design of three-dimensional RNA structure and function
Nature Nanotechnology (2019)
-
Comprehensive profiling of the ligand binding landscapes of duplexed aptamer families reveals widespread induced fit
Nature Communications (2018)
-
NMR resonance assignments for the tetramethylrhodamine binding RNA aptamer 3 in complex with the ligand 5-carboxy-tetramethylrhodamine
Biomolecular NMR Assignments (2017)
-
NMR resonance assignments for the class II GTP binding RNA aptamer in complex with GTP
Biomolecular NMR Assignments (2016)
-
Nucleic Acid Ligands With Protein-like Side Chains: Modified Aptamers and Their Use as Diagnostic and Therapeutic Agents
Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids (2014)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.