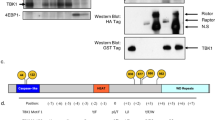
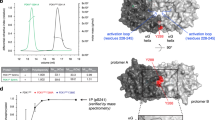
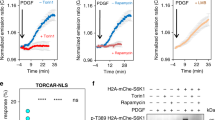
Abstract
WHEN complexed with the intracellular protein FKBP12, rapamy-cin is a potent immunosuppressant1,2 and an inhibitor of a mitogen-stimulated signalling pathway that leads to activation of p70 S6 kinase3-6 (p70S6k) and cyclin-dependent kinases7-10 (CDKs). A recently cloned FKBP12-rapamycin-associated protein (FRAP/ RAFT) is the likely mediator of these effects11,12. Using FRAP variants that do not bind FKBP12-rapamycin, we demonstrate here that FRAP is a rapamycin-sensitive regulator of p70S6k in vivo and that the kinase activity of FRAP is required for this regulation. In addition, we show that FRAP autophosphorylates in vitro. Consistent with an essential role for FRAP kinase activity in vivo, autophosphorylation of FRAP is inhibited by FKBP12-rapamycin. Deletion studies indicate that the kinase activity of FRAP alone is not sufficient for control of p70S6k and that an amino-terminal domain in FRAP is also required.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bierer, B. E. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87, 9231–9235 (1990).
Dumont, F. J., Staruch, M. J., Koprak, S. L., Melino, M. R. & Sigal, N. H. J. Immun. 144, 251–258 (1990).
Kuo, C. J. et al. Nature 358, 70–73 (1992).
Chung, J., Kuo, C. J., Crabtree, G. R. & Blenis, J. Cell 69, 1227–1236 (1992).
Price, D. J., Grove, J. R., Calvo, V., Avruch, J. & Bierer, B. E. Science 257, 973–977 (1992).
Calvo, V., Crews, C. M., Vik, T. A. & Bierer, B. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 7571–7575 (1992).
Morice, W. G., Brunn, G. J., Wiederrecht, G., Siekierka, J. J. & Abraham, R. T. J. biol. Chem. 268, 3734–3738 (1993).
Morice, W. G., Wiederrecht, G., Brunn, G. J., Siekierka, J. J. & Abraham, R. T. J. biol. Chem. 268, 22737–22745 (1993).
Albers, M. W. et al. J. biol. Chem. 268, 22825–22829 (1993).
Nourse, J. et al. Nature 372, 570–573 (1994).
Brown, E. J. et al. Nature 369, 756–758 (1994).
Sabatini, D. M., Erdjument, B. H., Lui, M., Tempst, P. & Snyder, S. H. Cell 78, 35–43 (1994).
Schu, P. V. et al. Science 260, 88–91 (1993).
Dhand, R. et al. EMBO J. 13, 522–533 (1994).
Taylor, S. S. et al. Trends biochem. Sci. 18, 84–89 (1993).
Clipstone, N. A. & Crabtree, G. R. Nature 357, 695–697 (1992).
Chen, J., Zheng, X.-F., Brown, E. J. & Schreiber, S. L. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92, 4947–4951 (1995).
Ballou, L. M., Siegmann, M. & Thomas, G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 7154–7158 (1988).
Chung, J., Grammer, T. C., Lemon, K. P., Kazlauskas, A. & Blenis, J. Nature 370, 71–75 (1994).
Zheng, X.-F., Fiorentino, D., Chen, J., Crabtree, G. R. & Schreiber, S. L. Cell 82, 121–130 (1995).
Herman, P. K. & Emr, S. D. Molec. cell. Biol. 10, 6742–6754 (1990).
Boyle, W. J., Van Der Geer, P. & Hunter, T. Meth. Enzym. 201, 110–148 (1991).
Kolodziej, P. A. & Young, R. A. Meth. Enzym. 194, 508–519 (1991).
Kozma, S. C. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87, 7365–7369 (1990).
Jeno, P., Ballou, L. M., Novak-Hofer, I. & Thomas, G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci U.S.A. 85, 406–410 (1988).
Flotow, H. & Thomas, G. J. biol. Chem. 267, 3074–3078 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brown, E., Beal, P., Keith, C. et al. Control of p70 S6 kinase by kinase activity of FRAP in vivo. Nature 377, 441–446 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/377441a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/377441a0
This article is cited by
-
Marker-free co-selection for successive rounds of prime editing in human cells
Nature Communications (2022)
-
AIMTOR, a BRET biosensor for live imaging, reveals subcellular mTOR signaling and dysfunctions
BMC Biology (2020)
-
Copper is an essential regulator of the autophagic kinases ULK1/2 to drive lung adenocarcinoma
Nature Cell Biology (2020)
-
Clinorotation-induced autophagy via HDM2-p53-mTOR pathway enhances cell migration in vascular endothelial cells
Cell Death & Disease (2018)
-
Metformin as an Adjunctive Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer: A Review of the Literature on Its Potential Therapeutic Use
Digestive Diseases and Sciences (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.