Abstract
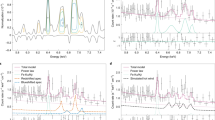
ACTIVE galactic nuclei and quasars are probably powered by the accretion of gas onto a supermassive black hole at the centre of the host galaxy1, but direct confirmation of the presence of a black hole is hard to obtain. As the gas nears the event horizon, its velocity should approach the speed of light; the resulting relativistic effects, and a gravitational redshift arising from the proximity to the black hole, should be observable, allowing us to test specific predictions of the models with the observations. Here we report the detection of these relativistic effects in an X-ray emission line (the Kα line) from ionized iron in the galaxy MCG–6–30–15. The line is extremely broad, corresponding to a velocity of ∼100,000 km s−1, and asymmetric, with most of the line flux being redshifted. These features indicate that the line most probably arises in a region between three and ten Schwarzschild radii from the centre, so that we are observing the innermost region of the accretion disk.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rees, M. J. A. Rev. Astr. Astrophys. 22, 471–506 (1984).
Ford, H. C. et al. Astrophys. J. L27–L30 (1994).
Harmes, R. J. et al. Astrophys. J. L35–L38 (1994).
Miyoshi, M. et al. Nature 373, 127–129 (1995).
Pounds, K. A., Nandra, K., Stewart, G. C., George, I. M. & Fabian, A. C. Nature 344, 132–133 (1990).
Nandra, K. & Pounds, K. A. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 268, 405–429 (1994).
Guilbert, P. W. & Rees, M. J. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 233, 475–484 (1994).
Lightman, A. P. & White, T. R. Astrophys. J. 335, 57–66 (1988).
Fabian, A. C., Rees, M. J., Stella, L. & White, N. E. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 238, 729–736 (1989).
George, I. M. & Fabian, A. C. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 249, 352–367 (1991).
Matt, G., Perola, G. C. & Piro, L. Astr. Astrophys. 245, 75 (1991).
Matt, G., Perola, G. C., Piro, L. & Stella, L. Astr. Astrophys. 257, 63 (1992).
Laor, A. Astrophys. J. 376, 90–94 (1991).
Fabian, A. C. et al. Publs astr. Soc. Japan 46, L59–L64 (1994).
Mushotzky, R. F. et al. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 272, L9–L12 (1995).
Chen, K., Halpern, J. P. & Filippenko, A. V. Astrophys. J. 339, 742–751 (1989).
Tanaka, Y., Inoue, H. & Holt, S. S. Publs astr. Soc. Japan 46, L37–L41 (1994).
Halpern, J. P. Astrophys. J. 281, 90–94 (1984).
Nandra, K., Pounds, K. A. & Stewart, G. C. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 242, 660–668 (1990).
Nandra, K. & Pounds, K. A. Nature 359, 215–216 (1992).
Czerny, B., Zbyszewska, M. & Raine, D. J. in Iron Line Diagnostics in X-ray Sources (ed. Treves, A.) 226–229 (Springer, Berlin, 1991).
Zdziarski, A. A., Johnson, W. N., Done, C., Smith, D. & McNaron-Brown, K. Astrophys. J. 438, L63–L66 (1995).
Reynolds, C. S., Fabian, A. C. & Inoue, H. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. (submitted).
Krolik, J. H. & Kallman, T. R. Astrophys. J. 320, L5–L8 (1987).
Ghisellini, G., Haardt, F. & Matt, G. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 267, 743–754 (1994).
Krolik, J. H., Madau, P. & Zycki, P. Astrophys. J. 420, L57–L61 (1994).
Ross, R. R. & Fabian, A. C. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 261, 74–82 (1993).
Matt, G., Fabian, A. C. & Ross, R. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 262, 179–186 (1993).
Stella, L. Nature 344, 747–749 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, Y., Nandra, K., Fabian, A. et al. Gravitationally redshifted emission implying an accretion disk and massive black hole in the active galaxy MCG–6–30–15. Nature 375, 659–661 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/375659a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/375659a0
This article is cited by
-
Reflecting on accretion in neutron star low-mass X-ray binaries
Astrophysics and Space Science (2024)
-
Frontiers in accretion physics at high X-ray spectral resolution
Nature Astronomy (2022)
-
XMM-Newton and Swift observations of the Seyfert 1 AGN NGC 5940
Astrophysics and Space Science (2022)
-
Towards Precision Measurements of Accreting Black Holes Using X-Ray Reflection Spectroscopy
Space Science Reviews (2021)
-
High-resolution X-ray spectroscopy of astrophysical plasmas with X-ray microcalorimeters
Reviews of Modern Plasma Physics (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.