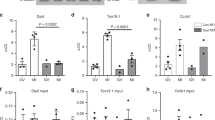
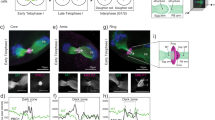
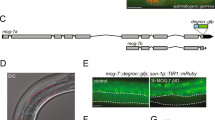
Abstract
c-mos protein, encoded by a proto-oncogene, is essential for the meiotic maturation of frog oocytes. Polyadenylation of c-mos messenger RNA is shown here to be a pivotal regulatory step in meiotic maturation. Maturation is prevented by selective amputation of polyadenylation signals from c-mos mRNA. Injection of a prosthetic RNA, which restores c-mos polyadenylation signals by base pairing to the amputated mRNA, rescues maturation and can stimulate translation in trans. Prosthetic RNAs may provide a general strategy by which to alter patterns of mRNA expression in vivo.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yew, N., Strobel, M. & Vande Woude, G. F. Curr. Opin. Gen. Dev. 3, 19–25 (1993).
Sagata, N., Daar, I., Oskarsson, M., Showalter, S. D. & Vande Woude, G. F. Science 245, 643–646 (1989).
Freeman, R. S. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 5805–5809 (1989).
Yew, M., Mellini, M. I. & Vande Woude, G. F. Nature 355, 649–652 (1992).
Colledge, W. H., Carlton, M. B. L., Udy, G. B. & Evans, M. J. Nature 370, 65–68 (1994).
Hashimoto, N. et al. Nature 370, 68–71 (1994).
Sagata, N., Oskarsson, M., Copeland, T., Brumbaugh, J. & Vande Woude, G. F. Nature 333, 519–525 (1988).
Wickens, M. Semin devl Biol. 3, 399–412 (1992).
Jackson, R. & Standart, N. Cell 62, 15–24 (1990).
Richter, J. Bioessays 13, 179–183 (1991).
Fox, C. A., Sheets, M. D. & Wickens, M. P. Genes Dev. 3, 2151–2162 (1989).
Sheets, M. D., Fox, C. A., Hunt, T., Vande Woude, G. & Wickens, M. Genes Dev. 8, 926–938 (1994).
Smith, R. C. et al. Development 110, 769–779 (1990).
Takayama, K. & Inouye, M. CRC Crit. Rev. Biochem. 25, 155–184 (1990).
Nellen, W. & Lichtenstein, C. Trends biochem. Sci. 18, 419–423 (1993).
Simons, R. W. & Kleckner, N. A. Rev. Genet. 22, 567–600 (1988).
Bilger, A., Fox, C. A., Wahle, E. & Wickens, M. Genes Dev. 8, 1106–1116 (1994).
Fox, C. A., Sheets, M., Wahle, E. & Wickens, M. EMBO J. 11, 5021–5032 (1992).
Ballantyne, S., Bilger, A., Astrom, J., Virtanen, A. & Wickens, M. RNA (in the press).
Maller, J. L. in Oogenesis Vol. 1 (ed. Browder, L. W.) 289–311 (Plenum, New York, 1985).
Bachvarova, R. in Oogenesis Vol. 1 (ed. Browder, L. W.) 453–524 (Plenum, New York, 1985).
Kobayashi, H. et al. J. Cell Biol. 114, 755–765 (1991).
Wharton, R. & Struhl, G. Cell 67, 955–967 (1991).
Ahringer, J. & Kimble, J. Nature 349, 346–348 (1991).
Bass, B. & Weintraub, H. Cell 55, 1089–1098 (1988).
Wagner, R. W., Smith, J. E., Cooperman, B. S. & Nishikura, K. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 2647–2651 (1989).
Bass, B. L. Semin. devl Biol. 3, 425–433 (1992).
Wickens, M. (ed.) Semin. devl Biol. 3, 363–424 (1992).
Wickens, M. Nature 363, 305–306 (1993).
Salles, F. J., Lieberfarb, M. E., Wreden, C., Gergen, J. P. & Strickland, S. Science 266, 1996–1998 (1994).
Gebauer, F., Xu, M., Cooper, G. M. & Richter, J. D. EMBO J. 13, 5712–5720 (1994).
Nishizawa, M., Okazaki, K., Furuno, N., Watanabe, N. & Sagata, N. EMBO J. 11, 2433–2446 (1992).
Vande Woude, G. F. Nature 370, 20–21 (1994).
Standart, N. & Jackson, R. Biochimie 76, 867–879 (1994).
Konarska, M. M., Padgett, R. A. & Sharp, P. A. Cell 42, 165–171 (1985).
Bienroth, S., Keller, W. & Wahle, E. EMBO J. 12, 585–594 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheets, M., Wu, M. & Wickens, M. Polyadenylation of c-mos mRNA as a control point in Xenopus meiotic maturation. Nature 374, 511–516 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/374511a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/374511a0
This article is cited by
-
Roles of mRNA poly(A) tails in regulation of eukaryotic gene expression
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2022)
-
Smaug assembles an ATP-dependent stable complex repressingnanosmRNA translation at multiple levels
The EMBO Journal (2011)
-
Enforcing temporal control of maternal mRNA translation during oocyte cell-cycle progression
The EMBO Journal (2010)
-
Survey of O-GlcNAc level variations in Xenopus laevis from oogenesis to early development
Glycoconjugate Journal (2009)
-
The Xenopus Cell Cycle: An Overview
Molecular Biotechnology (2008)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.