Abstract
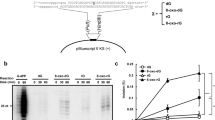
HUMANS with a defect in the XPG protein suffer from xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) resulting from an inability to perform DNA nucleotide excision repair properly1–4. Here we show that XPG makes a structure-specific endonucleolytic incision in a synthetic DNA substrate containing a duplex region and single-stranded arms. One strand of the duplex is cleaved at the border with single-stranded DNA. A cut with the same polarity is also made in a bubble structure, at the 3′ side of the centrally unpaired region. Normal cell extracts introduce a nick 3′ to a platinum – DNA lesion, but an XP-G cell extract is defective in making this incision. These data show that XPG has a direct role in making one of the incisions required to excise a damaged oligonucleotide, by cleaving 3' to DNA damage during nucleotide excision repair.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keijzer, W. et al. Mutat. Res. 62, 183–190 (1979).
Arlett, C. F. et al. Carcinogenesis 1, 745–751 (1980).
Ichihashi, M., Fujiwara, Y., Uehara, Y. & Matsumoto, A. J. invest. Dermatol. 85, 284–287 (1985).
Norris, P. G., Hawk, J. L. M., Avery, J. A. & Giannelli, F. Br. J. Dermatol. 116, 861–866 (1987).
O'Donovan, A., Scherly, D., Clarkson, S. G. & Wood, R. D. J. biol. Chem. 269, 15965–15968 (1994).
Habraken, Y., Sung, P., Prakash, L. & Prakash, S. Nature 366, 365–368 (1993).
Tomkinson, A. E., Bardwell, A. J., Bardwell, L., Tappe, N. J. & Friedberg, E. C. Nature 362, 860–862 (1993).
Sung, P., Reynolds, P., Prakash, L. & Prakash, S. J. biol. Chem. 268, 26391–26399 (1993).
Biggerstaff, M., Szymkowski, D. E. & Wood, R. D. EMBO J. 12, 3685–3692 (1993).
van Vuuren, A. J. et al. EMBO J. 12, 3693–3701 (1993).
Reardon, J. T., Thompson, L. H. & Sancar, A. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. quant. Biol. 58, 605–617 (1993).
Aboussekhra, A. & Wood, R. D. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 4, 212–220 (1994).
O'Donovan, A. & Wood, R. D. Nature 363, 185–188 (1993).
Svoboda, D. L., Taylor, J. S., Hearst, J. E. & Sancar, A. J. biol. Chem. 268, 1931–1936 (1993).
Lin, J. J., Phillips, A. M., Hearst, J. E. & Sancar, A. J. biol. Chem. 267, 17693–17700 (1992).
Scherly, D. et al. Nature 363, 182–185 (1993).
Carr, A. M. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 21, 1345–1349 (1993).
Maclnnes, M. A. et al. Molec. cell. Biol. 13, 6393–6402 (1993).
Shiomi, T. et al. Mutat. Res. 314, 167–175 (1994).
Harrington, J. J. & Lieber, M. R. Genes Dev. 8, 1344–1355 (1994).
Murray, J. M. et al. Molec. cell. Biol. 14, 4878–4888 (1994).
Vermeulen, W., Jaeken, J., Jaspers, N. G. J., Bootsma, D. & Hoeijmakers, J. H. J. Am. J. hum. Genet. 53, 185–192 (1993).
Bootsma, D. & Hoeijmakers, J. H. J. Nature 363, 114–115 (1993).
Bennett, R. J., Dunderdale, H. & West, S. Cell 74, 1021–1031 (1993).
Szymkowski, D. E., Yarema, K., Essigmann, J. E., Lippard, S. J. & Wood, R. D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 10772–10776 (1992).
Shivji, M. K. K., Kenny, M. K. & Wood, R. D. Cell 69, 367–374 (1992).
Bardwell, L. et al. Science (in the press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O'Donovan, A., Davies, A., Moggs, J. et al. XPG endonuclease makes the 3′ incision in human DNA nucleotide excision repair. Nature 371, 432–435 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/371432a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/371432a0
This article is cited by
-
Association of ERCC family mutations with prognosis and immune checkpoint inhibitors response in multiple cancers
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Pathological consequences of DNA damage in the kidney
Nature Reviews Nephrology (2023)
-
Dynamic conformational switching underlies TFIIH function in transcription and DNA repair and impacts genetic diseases
Nature Communications (2023)
-
XPG: a multitasking genome caretaker
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2022)
-
XPG in the Nucleotide Excision Repair and Beyond: a study on the different functional aspects of XPG and its associated diseases
Molecular Biology Reports (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.