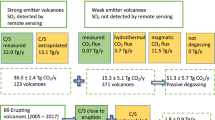
Abstract
SULPHUR dioxide from volcanic eruptions may have a significant effect on the Earth's climate and atmospheric chemistry, and it is therefore important to quantify outgassing rates for all types of volcanic activity. Non-explosive volcanoes (for example, Mount Etna) outgas at relatively constant rates, providing an annual flux of about 9 million tons (Mt) SO2 (ref. 1). By contrast, the outgassing from volcanoes prone to explosive eruptions (such as Mount Pinatubo) is sporadic and much more difficult to quantify. The total annual volcanic SO2 flux is therefore poorly constrained, with ground-based estimates1–8 ranging from 1.5 to 50 Mt–up to onequarter of the estimated current anthropogenic contribution. The Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer aboard the NASA satellite Nimbus 7 recorded SO2emissions from explosive eruptions from November 1978 to May 1993. We use these data to show that the annual flux from explosive volcanism is of the order of 4 Mt SO2, less than half of the non-explosive output. Thus it seems that the total volcanic emission of SO2 to the Earth's atmosphere is about 13 Mt yr−1, which is only 5–10% of the current anthropogenic flux.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stoiber, R. E., Williams, S. N. & Huebert, B. J. Volcan. geotherm. Res. 33, 1–8 (1987).
Kellog, W. W., Cadle, R. D., Allen, E. R., Lazrus, A. L. & Martell, E. A. Science 175, 587–596 (1972).
Friend, J. P. in Chemistry of the Lower Atmosphere (ed. I. Rasool) 177–201 (Plenum, New York, 1973).
Stoiber, R. E. & Jepsen, A. Science 182, 577–578 (1973).
Cadle, R. D. J. geophys. Res. 80, 1650–1652 (1975).
Ie Guern, F. Bull. volcan. 45-3, 197–202 (1982).
Berresheim, H. & Jaeschke, W. J. geophys. Res. 88, 3732–3740 (1983).
Lambert, G., Le Cloarec, M.-F. & Pennisi, M. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 52, 39–42 (1988).
Möller, D. Atmos. Envir. 18, 19–27 (1984).
Krueger, A. J. Science 220, 1377–1379 (1983).
Krueger, A. J., Walter, L. S., Schnetzler, C. C. & Doiron, S. D. J. volcan. geotherm. Res. 41, 7–15 (1990).
Smithsonian Institution/SEAN Global Volcanism 1975–1985 (Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, and Am. Geophys. Un., Washington DC, 1989).
Bluth, G. J. S., Doiron, S. D., Schnetzler, C. C., Krueger, A. J. & Walter, L. S. Geophys. Res. Lett. 19, 151–154 (1992).
Newhall, C. G. & Self, S. J. geophys. Res. 87, 1231–1238 (1982).
Simkin, T. A. Rev. Earth planet. Sci. 21, 427–452 (1993).
Hammer, C. U., Clausen, H. B. & Dansgaard, W. Nature 288, 230–235 (1980).
Stothers, R. B. Science 224, 1191–1198 (1984).
Legrand, M. & Delmas, R. J. Nature 327, 671–676 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bluth, G., Schnetzler, C., Krueger, A. et al. The contribution of explosive volcanism to global atmospheric sulphur dioxide concentrations. Nature 366, 327–329 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/366327a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/366327a0
This article is cited by
-
A decade of global volcanic SO2 emissions measured from space
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Thermal erosion of cratonic lithosphere as a potential trigger for mass-extinction
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Sulphur geodynamic cycle
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
Possible correlation of Oligocene climate changes with Ethiopian Oligocene ignimbrite eruptions
Arabian Journal of Geosciences (2012)
-
Satellite detection of hazardous volcanic clouds and the risk to global air traffic
Natural Hazards (2009)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.