Abstract
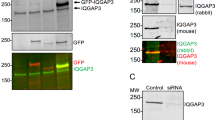
APOPTOSIS is an important but poorly understood mechanism of cell regulation. Growth factor deprivation can trigger apoptosis in a variety of cells1–3, suggesting the existence of a signal transduction pathway responding to external signals and leading to apoptosis. Overexpression of the proto-oncogene bcl-2 can override these signals and block apoptosis4–14, indicating that the bcl-2protein (Bcl-2) is an important component of the apoptotic response. The identification of Bcl-2-binding proteins might help explain how Bcl-2 acts to regulate apoptosis. Here we use the yeast two-hybrid system15 to show that the human ras-related protein R-rasp23 (refs 16-18) binds to Bcl-2. This association is also detected in immunoprecipitates from human cell extracts. The association requires full-length Bcl-2 but the C-terminal 60 amino acids of R-ras p23 are sufficient for the interaction. These results provide evidence of a putative component of a signal transduction pathway involved in the regulation of apoptosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nunez, G. et al. J. Immun. 144, 3602–3610 (1990).
Lee, S., Christakos, S. & Small, M. B. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 5, 286–291 (1993).
Vaux, D. L. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 786–789 (1993).
McDonnell, T. J. et al. Cell 57, 79–88 (1989).
Hockenbery, D., Nun̄ez, G., Milliman, C., Schreiber, R. D. & Korsmeyer, S. J. Nature 348, 334–336 (1990).
Sentman, C. L., Shutter, J. R., Hockenbery, D., Kanagawa, O. & Korsmeyer, S. J. Cell 67, 879–888 (1991).
Strasser, A., Harris, A. W. & Cory, S. Cell 67, 889–899 (1991).
Alnemri, E. S., Robertson, N. M., Fernandes, T. F., Croce, C. M. & Litwack, G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 7295–7299 (1992).
Bissonnette, R. P., Echeverri, F., Mahboubi, A. & Green, D. R. Nature 359, 552–556 (1992).
Fanidi, A., Harrington, E. A. & Evan, G. I. Nature 359, 554–556 (1992).
Garcia, I., Martinou, I., Tsujimoto, Y. & Martinou, J.-C. Science 258, 302–304 (1992).
Seigel, R. M. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 7003–7007 (1992).
Vaux, D. L., Weissman, I. L. & Kim, S. K. Science 258, 1955–1957 (1992).
Wagner, A. J., Small, M. B. & Hay, N. Molec. cell. Biol. 13, 2432–2440 (1993).
Chien, C.-T., Bartel, P. L., Sternglanz, R. & Fields, S. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 9578–9582 (1991).
Lowe, D. G. et al. Cell 48, 137–146 (1987).
Lowe, D. G. & Goeddel, D. V. Molec. cell. Biol. 7, 2845–2856 (1987).
Lowe, D. G., Rickets, M., Levinson, A. D. & Goeddel, D. V. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 1015–1019 (1988).
Haldar, S., Beatty, C., Tsujimoto, Y. & Croce, C. M. Nature 342, 195–200 (1989).
Monica, K., Zehava, C.-L. & Cleary, M. L. Nature 346, 189–191 (1990).
Chen-Levy, Z., Nouse, J. & Cleary, M. L. Molec. cell. Biol. 9, 701–710 (1989).
Jacobson, M. D. et al. Nature 361, 365–369 (1993).
Tanaka, S., Saito, K. & Reed, J. C. J. biol. Chem. 268, 10920–10926 (1993).
Lerosey, I., Chardin, P., de Gunzburg, J. & Tavitian, A. J. biol. Chem. 266, 4315–4321 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
fernandez-Sarabia, M., Bischoff, J. Bcl-2 associates with the ras-related protein R-rasp23. Nature 366, 274–275 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/366274a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/366274a0
This article is cited by
-
Targeting inhibition of K-ras enhances Ad.mda-7-induced growth suppression and apoptosis in mutant K-ras colorectal cancer cells
Oncogene (2007)
-
Transformed immortalized gastric epithelial cells by virulence factor CagA of Helicobacter pylori through Erk mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway
Oncogene (2005)
-
Bcl-2 differentially targets K-, N-, and H-Ras to mitochondria in IL-2 supplemented or deprived cells: Implications in prevention of apoptosis
Oncogene (1999)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.