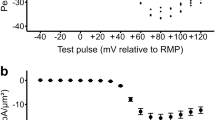
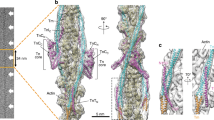
Abstract
THE Na + /Ca2 + exchanger, driven by a transmembrane Na+ gradient, plays a key role in regulating Ca2+concentration in many cells1'2. Although the exchanger influences Ca2+concentration, its activity in smooth muscle appears to be closely coupled to Ca2+ availability from intracellular stores3. This linkage might result if the exchanger were positioned close to Ca2+storage sites within the sarcoplasmic reticulum. To test this hypothesis we have developed methods to assess the relative three-dimensional distribution of proteins involved in Na+/K+ pumping, Na+/Ca2+exchange, Ca2+ storage within the sarcoplasmic reticulum, and attachment of contractile filaments to the membrane in smooth muscle. Here we report that the Na+ /Ca2 + exchanger is largely co-distributed with the Na+/K+ pump on unique regions of the plasma membrane in register with, and close to, calsequestrin-containing regions of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in sites distinct from the sites where contractile filaments attach to the membrane. This molecular organization suggests that the plasma membrane is divided into at least two functional domains, and appear to provide a mechanism for the strong linkage seen in smooth muscle between Na+/K+ pumping and Na+/Ca2+exchange, and between Na+/Ca2+ exchange and Ca2 + release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum4–7.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reuter, H. Nature 349, 567–568 (1991).
Reuter, H., Blaustein, M. P. & Haeusler, G. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B265, 87–94 (1973).
Ashida, T. & Blaustein, M. P. J. Physiol., Lond. 392, 617–635 (1987).
van Breeman, C. J. Physiol., Lond. 272, 317–329 (1977).
Bird, G.StJ. et al. Nature 352, 162–165 (1991).
Brading, A. F. & Sneddon, P. Br. J. Pharmac. 70, 229–240 (1980).
Stehno-Bittel, L. & Sturek, M. J. Physiol., Lond. 451, 49–78 (1992).
Scheid, C. R., Honeyman, T. W. & Fay, F. S. Nature 277, 32–36 (1979).
Williams, D. A. & Fay, F. S. Am. J. Physiol. 250, C779–C791 (1986).
Somlyo, A. P., Devine, C. E., Somlyo, A. V. & North, S. R. J. Cell Biol,. 51, 722–741 (1971).
Gabella, G. & Blundell, D. Cell Tiss. Res. 190, 255–271 (1978).
Fay, F. S., Carrington, W. & Fogarty, K. E. J. Microsc. 153, 133–149 (1989).
Carrington, W. A., Fogarty, K. E. & Fay, F. S. Modern Cell Biol. 9, 53–72 (1990).
Carrington, W. A. Soc. Photo-opt. Instr. Engnrs Proc. 1205, 72–83 (1990).
Etter, E. F., Jones, L. R., Fogarty, K. E. & Fay, F. S. J. Cell Biol. 109, 169a (1989).
Fambrough, D. M. Trends Neurosci. 11, 325–328 (1988).
Horowitz, B. et al. J. biol. Chem. 265, 4189–4192 (1990).
Gabella, G. Phil Trans. R. Soc. B265, 7–16 (1973).
Geiger, B. Cell 18, 193–205 (1979).
LeBlanc, L. & Hume, J. Science 248, 372–376 (1990).
Niggli, E. & Lederer, W. J. Science 250, 565–568 (1990).
Fay, F. S., McGeown, J. G., Walsh, J. V. & McCarron, J. G. Biophys. J. 61, A389 (1992).
Hilgemann, D. W., Nicoll, D. A. & Philipson, K. D. Nature 352, 715–718 (1991).
Fay, F. S., Hoffman, R., LeClair, S. & Merriam, P. Meth. Enzym. 85, 284–292 (1982).
Lynch, R. M., Fogarty, K. E. & Fay, F. S. J. Cell Biol. 112, 385–395 (1991).
Girardet, M., Geering, K., Rossier, B. C., Kraehunbuhl, J. P. & Bron, C. Biochem. J. 22, 2296–2300 (1983).
Nicoll, D. A., Longoni, S. & Philipson, K. D. Science 250, 562–565 (1990).
Mahoney, L. & Jones, L. R. J. biol. Chem. 261, 15257–15265 (1986).
Wuytack, F., Raeymaekers, L., Verbist, J., Jones, L. R. & Casteels, R. Biochim. biophys. Acta 899, 151–158 (1987).
Milner, R. E. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 7155–7165 (1991).
Lifshitz, L. M., Fogarty, K. E., Gauch, J. & Moore, E. D. W. Soc. Photo-opt. Instr. Engnrs Proc. 1808, 521–534 (1992).
Villa, A. et al. J. Cell Biol. 121, 1041–1051 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moore, E., Etter, E., Philipson, K. et al. Coupling of the Na+/Ca2+exchanger, Na+/K+ pump and sarcoplasmic reticulum in smooth muscle. Nature 365, 657–660 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/365657a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/365657a0
This article is cited by
-
Signaling pathways in vascular function and hypertension: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2023)
-
Trop-2, Na+/K+ ATPase, CD9, PKCα, cofilin assemble a membrane signaling super-complex that drives colorectal cancer growth and invasion
Oncogene (2022)
-
Modelling Human Colonic Smooth Muscle Cell Electrophysiology
Cellular and Molecular Bioengineering (2017)
-
The role of cytoplasmic nanospaces in smooth muscle cell Ca2+ signalling
Protoplasma (2012)
-
Structure and dynamics of the actin-based smooth muscle contractile and cytoskeletal apparatus
Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility (2012)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.