Abstract
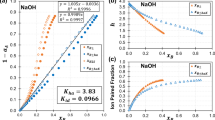
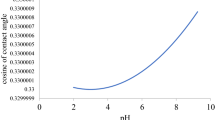
NONE of the traditional models of surface complexation of ions at oxide–water interfaces, such as the constant-capacitance, double-diffuse-layer and triple-layer models1–5, provides an explicit, quantitative treatment of ion solvation. Here I show that this process can be included quantitatively in surface-complexation theory by describing it using the Born theory of ion solvation6,7. In this way, the standard Gibbs free energy of sorption can be decomposed into three terms: the standard coulombic term, a Born solvation contribution and a term intrinsic to the ion alone. Consideration of the Born solvation term shows that the equilibrium constant for sorption depends linearly on the inverse of the dielectric constant of the solid. By this means, all three contributions to the free energy can be estimated empirically or calculated theoretically. Inclusion of this physical description of ion solvation should facilitate the application of the theory of ion sorption to complex natural oxide and silicate minerals.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schindler, P. W. & Stumm, W. in Aquatic Surface Chemistry: Chemical Processes at the Particle-Water Interface (ed. Stumm, W.) 83–110 (Wiley, New York, 1987).
Stumm, W. & Morgan, J. J. Aquatic Chemistry: An Introduction Emphasizing Chemical Equilibria in Natural Waters 1–780 (Wiley, New York, 1981).
Davis, J. A. & Kent, D. B. in Mineral-Water Interface Geochemistry (eds Hochella, M. F. Jr & White, A. F.) 177–259 (Min. Soc. Am., Washington DC, 1990).
Dzombak, D. A. & Morel, F.M.M. Surface Complexation Modelling 1–393 (Wiley, New York, 1990).
Davis, J. A. & Leckie, J. O. J. Colloid Inter. Sci. 67, 90–107 (1978).
Andersen, T. N. & Bockris, J. O. Electrochim. Acta 9, 347–371 (1964).
James, R. O. & Healy, T. W. J. Colloid Inter. Sci. 40, 65–81 (1972).
Helgeson, H. C. & Kirkham, D. H. Am. J. Sci. 276, 97–240 (1976).
Helgeson, H. C., Kirkham, D. H. & Flowers, G. C. Am. J. Sci. 281, 1241–1516 (1981).
Shock, E. L. & Helgeson, H. C. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 52, 2009–2036 (1988).
Schindler, P. W., Liechti, P. & Westall, J. C. Neth. J. agric. Sci. 35, 219–230 (1987).
Shannon, R. D. & Prewitt, C. T. Acta crystallogr. B25, (1969).
Sverjensky, D. A. & Molling, P. A. M. Nature 356, 231–234 (1992).
Sverjensky, D. A. Nature 358, 310–313 (1992).
Balistrieri, L. S. & Murray, J. W. Am. J. Sci. 281, 788–806 (1981).
Olhoeft, G. R. in Physical Properties of Rocks and Minerals (eds Touloukian, Y. S., Judd, W. R. & Roy, R. F.) 257–330 (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1981).
Shannon, R. D. & Rossman, G. R. Phys. Chem. Miner. 19, 157–165 (1992).
Ilton, E. S. & Veblen, D. R. EOS 74, 323 (1993).
Weast, R,. C. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (CRC, Boca Raton, Florida, 1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sverjensky, D. Physical surface-complexation models for sorption at the mineral–water interface. Nature 364, 776–780 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/364776a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/364776a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.