Abstract
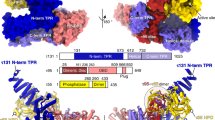
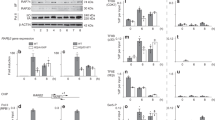
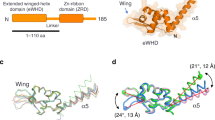
THE protein TFIIB is a general transcription initiation factor1 that interacts with a promoter complex (D·DNA) containing the TATA-binding subunit (TFIIDτ, or TBP) of TFIID to facilitate subsequent interaction with RNA polymerase II (ref. 2) through the associated TFIIF (ref. 3). The potential bridging function2,4 of TFIIB raises the possibility of two structural domains and emphasizes the importance of TFIIB structure–function studies for a further understanding of preinitiation complex assembly and function1. Here we show that human TFIIB (refs 5,6) is comprised of functionally distinct N- and C-terminal domains. The C-terminal domain, containing the direct repeats and associated basic regions, is necessary and sufficient for interaction with the D·DNA complex. By contrast, the N-terminal domain that is dispensable for formation of the TFIIDτ–TFIIB–promoter (D·B·DNA) complex is required for subsequent events leading to basal transcription initiation. On the basis of these results, we discuss structural and functional similarities between TFIIB and TFIIDτ, which have similar structural organization and motifs5.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roeder, R. G. Trends biochem. Sci. 16, 402–408 (1991).
Buratowski, S., Hahn, S., Guarente, L. & Sharp, P. Cell 56, 549–561 (1989).
Flores, O. et al. Pro. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 9999–10003 (1991).
Pinto, I., Ware, D. E. & Hampsey, M. Cell 68, 977–988 (1992).
Malik, S., Hisatake, K., Sumimoto, H., Horikoshi, M. & Roeder, R. G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 9553–9557 (1991).
Ha, I., Lane, S. & Reinberg, D. Nature 352, 689–695 (1991).
Maldonado, E., Ha, I., Cortes, P., Weiss, L. & Reinberg, D. Molec. cell. Biol. 10, 6335–6347 (1990).
Cortes, P., Flores, O. & Reinberg, D. Molec. cell. Biol. 12, 413–421 (1992).
Yamashita, S. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 2839–2843 (1992).
Hisatake, K., Malik, S., Roeder, R. G. & Horikoshi, M. Nucleic Acids Res. 19, 6639 (1991).
Colbert, T. & Hahn, S. Genes Dev. 6, 1940–1949 (1992).
Allfredo, L., Librizzi, M., Puglia, K. & Willis, I. M. Cell 71, 211–220 (1992).
Buratowski, S. & Zhou, H. Cell 71, 221–230 (1992).
Yano, R. & Nomura, M. Molec. cell. Biol. 11, 754–764 (1991).
Werner, M., Denmat, S. H.-L., Treich, I., Sentenac, A. & Thuriaux, P. Molec. cell. Biol. 12, 1087–1095 (1992).
Horikoshi, M., Yamamoto, T., Ohkuma, Y., Weil, P. A. & Roeder, R. G. Cell 61, 1171–1178 (1990).
Reddy, P. & Hahn, S. Cell 65, 349–357 (1991).
Yamamoto, T. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 2844–2848 (1992).
Nikolov, D. B. et al. Nature 360, 40–46 (1992).
Hoffmann, A. et al. Nature 346, 387–390 (1990).
Lewin, B. Cell 61, 1161–1164 (1990).
Greenblatt, J. Cell 66, 1067–1070 (1991).
Wampler, S. L. & Kadonaga, J. T. Genes Dev. 6, 1542–1552 (1992).
Horikoshi, M. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 1060–1064 (1992).
Horikoshi, M., Hai, T., Lin, Y.-S., Green, M. R. & Roeder, R. G. Cell 54, 1033–1042 (1988).
Kunkel, T. A., Roberts, L. D. & Zakour, R. A. Meth. Enzym. 154, 367–382 (1987).
Hoffmann, A. & Roeder, R. G. Nucleic Acids Res. 19, 6337–6338 (1991).
Hai, T., Horikoshi, M., Roeder, R. G. & Green, M. R. Cell 54, 1043–1051 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hisatake, K., Roeder, R. & Horikoshi, M. Functional dissection of TFIIB domains required for TFIIB–TFIID–promoter complex formation and basal transcription activity. Nature 363, 744–747 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/363744a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/363744a0
This article is cited by
-
Crystal structure of a TFIIB–TBP–TATA-element ternary complex
Nature (1995)
-
Activator-induced conformational change in general transcription factor TFIIB
Nature (1994)
-
Efficiency in activation
Nature (1993)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.