Abstract
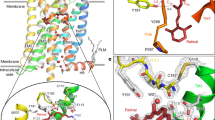
LIGHT absorption by the visual pigment rhodopsin1,2 triggers, through G-protein coupling, a cascade of events in the outer segment of the rod cell of the vertebrate retina that results in membrane hyperpolarization and nerve excitation3–5. Rhodopsin, which contains 348 amino acids6–8, has seven helices that cross the disk membrane6,9 and its amino terminus is extracellular. A wealth of biochemical data is available for rhodopsin: 11-cis retinal is bound10 to lysine 296 in helix VII; glutamic acid 113 on helix III is the counterion to the protonated Schiff's base11,12; a disulphide bridge, cystine 110–187, connects helix III to the second extracellular loop e2 (refs 13, 14); the carboxy terminus has two palmitoylated cysteines forming a cytoplasmic loop i4 (ref. 15); three intracellular loops i2, i3 and i4 mediate activation of the heterotrimeric G protein transducin16,17; glutamic acid 135 and arginine 136 at the cytoplasmic end of helix III affect binding of transducin18. But to provide a framework to interpret these data, not only for rhodopsin but for other G-protein-coupIed receptors, requires the structure to be determined. Here we present a projection map of rhodopsin showing the configuration of the helices.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hargrave, P. A. Curr. Opin. struct. Biol. 1, 575–581 (1991).
Henderson, R. & Schertler, G. F. X. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B326, 379–389 (1990).
De Grip, W. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 48, 799–810 (1988).
Chabre, M. & Deterre P. Eur. J. Biochem. 179, 255–266 (1989).
Stryer, L. J. biol. Chem. 266, 10711–10714 (1991).
Ovchinnikov, Y. A. et al. Bioorg. Khim. 8, 1424–1427 (1982).
Hargrave, P. A. et al. Biophys. struct. Mech. 9, 235–244 (1983).
Nathans, J. & Hogness, D. S. Cell 34, 807–814 (1983).
Khorana, H. G. J. biol. Chem. 267, 1–4 (1992).
Bownds, D. Nature 216, 1178–1181 (1967).
Zhukovsky, E. A. & Oprian, D. D. Science 246, 928–930 (1989).
Sakmar, T. P., Franke, R. R. & Khorana, H. G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 8309–8313 (1989).
Karnik, S. S., Sakmar, T. P., Chen, H.-B. & Khorana, H. G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 8459–8463 (1988).
Karnik, S. S. & Khorana, H. G. J. biol. Chem. 265, 17520–17524 (1990).
Ovchinnikov, Y. A., Abdulaev, N. G. & Bogachuk, A. S. FEBS Lett. 230, 1–5 (1988).
Hargrave, P. A., Hamm, H. E. & Hofmann, K. P. Bioessays (in the press).
König, B. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 6878–6882 (1989).
Franke, R. R., König, B., Sakmar, T. P., Khorana, H. G. & Hofmann, K. P. Science 250, 123–125 (1990).
De Grip, W. J. Meth. Enzym. 81, 197–207 (1982).
Kühlbrandt, W. Q. Rev. Biophys. 25, 1–49 (1992).
Corless, J. M., McCaslin, D. R. & Scott, B. L. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 1116–1120 (1982).
Dratz, E. A., Van Breemen, J. F. L., Kamps, K. M. P., Keegstra, W. & Van Bruggen, E. F. J. Biochim. biophys. Acta 832, 337–342 (1985).
Demin, V. V., Yurkova, E. V., Kuzin, A. P., Barnakov, A. N. & Abdulaev, N. G. in Retinal Proteins (ed. Ovchinnikov, Y. A.) 519–524 (VNU Science. Utrecht, 1987).
Henderson, R. et al. molec. Biol. 213, 899–929 (1990).
Baldwin, J. M., EMBO J. (in the press).
Henderson, R., Baldwin, J. M., Downing, K. H., Lepault, J. & Zemlin, F. Ultramicroscopy 19, 147–178 (1986).
Ceska T. A. & Henderson R. J. molec. Biol. 213, 539–560 (1990)
Unwin, P. N. T. & Henderson, R. J. molec. Biol. 94, 425–440 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schertler, G., Villa, C. & Henderson, R. Projection structure of rhodopsin. Nature 362, 770–772 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/362770a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/362770a0
This article is cited by
-
Earliest molecular events of vision revealed
Nature (2023)
-
Molecular pharmacology of metabotropic receptors targeted by neuropsychiatric drugs
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2019)
-
G protein-coupled receptor kinases as therapeutic targets in the heart
Nature Reviews Cardiology (2019)
-
The manipulability of what? The history of G-protein coupled receptors
Biology & Philosophy (2017)
-
Hitchhiking on the heptahelical highway: structure and function of 7TM receptor complexes
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2016)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.