Abstract
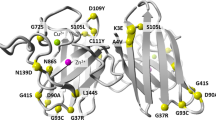
AMYOTROPHIC lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a degenerative disorder of motor neurons in the cortex, brainstem and spinal cord1,2. Its cause is unknown and it is uniformly fatal, typically within five years3. About 10% of cases are inherited as an autosomal dominant trait, with high penetrance after the sixth decade4,5. In most instances, sporadic and autosomal dominant familial ALS (FALS) are clinically similar4,6,7. We have previously shown that in some but not all FALS pedigrees the disease is linked to a genetic defect on chromosome 21q (refs 8,9). Here we report tight genetic linkage between FALS and a gene that encodes a cytosolic, Cu/Zn-binding superoxide dismutase (SOD1), a homodimeric metalloenzyme that catalyzes the dismutation of the toxic superoxide anion O–2 to O2 and H2O2 (ref. 10). Given this linkage and the potential role of free radical toxicity in other neurodenegerative disorders11, we investigated SOD1 as a candidate gene in FALS. We identified 11 different SOD1 missense mutations in 13 different FALS families.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tandan, R. & Bradley, W. G. Ann. Neurol. 18, 271–280 (1985).
Tandan, R. & Bradley, W. G. Ann. Neurol. 18, 419–431 (1985).
Kurland, L. T. Proc. Staff Meet Mayo Clin. 32, 449–462 (1957).
Mulder, D. W. et al. Neurology 36, 511–517 (1986).
Horton, W. A., Eldridge, R. & Brody, J. A. Neurology 26, 460–464 (1976).
Swerts, L. & Van Den Bergh, R. J. J. genet. Hum. 24, 247–255 (1976).
Huisquinet, H. & Franck, G. Clin. Genet. 18, 109–115 (1980).
Siddique, T. et al. New Engl. J. Med. 324, 1381–1384 (1991).
Siddique, T. et al. Neurology 39, 919–925 (1989).
Fridovich, I. Adv. Enzym. 58, 61–97 (1986).
Olanow, C. W. Ann. Neurol. 32, S2–9 (1992).
Rosen, D. R. et al. Hum. molec. Genet. 1, 547 (1992).
Ott, J. Am. hum. Genet. 28, 528–529 (1976).
Ott, J. Analysis of Human Genetics 203–216 (Johns Hopkins Univ. Press, Baltimore, 1991).
Levanon, D. et al. EMBO J. 77–84 (1985).
Hallewell, R. A. et al. in Superoxide Dismutase in Chemistry, Biology and Medicine (ed. Rotilio, G.) 249–256 (Elsevier, 1986).
Orita, M. et al. Genomics 5, 874–879 (1989).
Dausset, J. et al. Genomics 6, 575–577 (1990).
Beckman, J. S. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87, 1620–1624 (1990).
Imlay, J. A. & Linns, S. Science 240, 1302–1309 (1988).
Philips, J. P. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 2761–2765 (1989).
Carlioz, A. & Touati, D. EMBO J. 5, 623–630 (1986).
Farr, S. B., D'Ari, R. & Touati, D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 8268–8272 (1986).
Chang, E. C. et al. J. biol. Chem. 266, 4417–4424 (1991).
Minotti, G. & Aust, S. D. Chem. phys. Lipids 44, 191–208 (1987).
Crapo, J. D. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 10405–10409 (1992).
Avraham, K. B. et al. Cell 54, 823–829 (1988).
Yarom, R. et al. J. neurol. Sci. 88, 41–53 (1988).
Avraham, K. B. et al. J. Neurocytol. 20, 208–215 (1991).
Wisnieski, K. et al. Clin. Genet 23, 102–110 (1983).
Ackerman, A. D. et al. New Engl. J. Med. 318, 1666–1669 (1988).
Reynolds, J. F., Wyandt, H. E. & Kelley, T. E. Am. J. hum. Genet. 20, 173–180 (1985).
Hjalmarsson, K. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 6340–6344 (1987).
Bewley, G. C. Nucleic Acids Res. 16, 2728 (1988).
Henkle, K. J. et al. Infect. Immun. 59, 2063–2069 (1991).
Perl-Treves, R. et al. Plant molec. Biol. 11, 609–623 (1988).
Bermingham-McDonogh, O. et al. Proc. natn. Acad Sci. U.S.A. 85, 4789–4793 (1988).
Muller, H. in Sixth internat. Congr. Genetics (ed. Jones, D.) 213–255 (Brooklyn Botanic Gardens, Menasha, 1932).
Park, E. & Horvitz, H. R. Genetics 113, 821–852 (1986).
Dryja, T. P. et al. Nature 339, 556–558 (1989).
Herskowitz, I. Nature 329, 219–222 (1987).
Parge, H. E., Hallewell, R. A. & Tainer, J. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 6109–6113 (1992).
Kitagawa, Y. et al. J. Biochem. 109, 477–485 (1991).
Richardson, J. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 72, 1349–1353 (1975).
Creagan, R. et al. Humangenetik 20, 203–209 (1973).
Hendrickson, D. et al. Genomics 8, 736–738 (1990).
Shoulson, I. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 648, 37–41 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosen, D., Siddique, T., Patterson, D. et al. Mutations in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene are associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature 362, 59–62 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/362059a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/362059a0
This article is cited by
-
CD4 T-cell aging exacerbates neuroinflammation in a late-onset mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2024)
-
Beyond C9orf72: repeat expansions and copy number variations as risk factors of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis across various populations
BMC Medical Genomics (2024)
-
The multifaceted functions of β-arrestins and their therapeutic potential in neurodegenerative diseases
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2024)
-
Molecular hallmarks of ageing in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2024)
-
Gut-Brain Axis Deregulation and Its Possible Contribution to Neurodegenerative Disorders
Neurotoxicity Research (2024)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.