Abstract
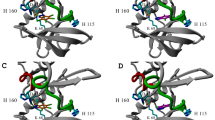
THE histidine-containing phosphocarrier protein (HPr) is a central component of the phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system that transports carbohydrates across the cell membrane of bacteria1. A typical phosphotransfer sequence is phosphoenolpyruvate → enzyme I → HPr → enzyme II/IIsugar → sugar. This is thermodynamically favourable owing to the participation of the high-energy phosphoenolpyruvate. We report here the structure of HPr from Streptococcus faecalis determined at 1.6 Å resolution. Remarkable disallowed Ramachandran torsion angles at the active centre, revealed by the X-ray structure, demonstrate a unique example of torsion-angle strain that is probably directly involved in protein function. During phosphorylation, the active-centre torsion-angle strain should facilitate the phosphotransfer reaction by lowering the activation-energy barrier. A recently reported Bacillus subtilis HPr structure2, which represents the phosphorylated state of HPr with no torsion-angle strain, provides direct evidence supporting our hypothesis that torsion-angle strain plays a direct part in the function of HPr. An HPr phosphotransfer cycling mechanism is proposed, based primarily on the structures of HPr and other phosphotransferase system proteins.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meadow, N. D., Fox, D. K. & Roseman, S. A. Rev. Biochem. 59, 495–542 (1990).
Herzberg, O. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 2499–2503 (1992).
Wang, B. C. Meth. Enzy. 115, 90–112 (1985).
Kalbitzer, H. R. et al. Biochemistry 21, 2879–2885 (1982).
Hol, W. G. J. Prog. Biophys. molec. Biol. 45, 149–195 (1985).
Aqvist, J., Luecke, H., Quiocho, F. A. & Warshel, A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 2026–2030 (1991).
Sharma, S. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 4877–4881 (1991).
Ramakrishnan, C. & Ramachandran, G. N. Biophys. J. 5, 909–933 (1965).
Jones, T. A. J. appl. Crystallogr. 11, 268–272 (1978).
Fersht, A. R. et al. Nature 314, 235–238 (1985).
van Dijk, A. A., de Lange, L. C., Bachovchin, W. W. & Robillard, G. T. Biochemistry 29, 8164–8171 (1990).
Herzberg, O. & Moult, J. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Genet. 11, 223–229 (1991).
Liao, D. et al. Biochemistry 30, 9583–9594 (1991).
Worthylake, D. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 10382–10386 (1991).
Stone, M. J. et al. Biochemistry 31, 4394–4406 (1992).
Messerschmidt, A. & Pflugrath, J. W. J. appl. Crystallogr. 20, 306–315 (1987).
Dickerson, R. E., Weinzierl, J. E. & Palmer, R. A. Acta crystallogr. B24, 997–1003 (1968).
Evans, S. V. J. molec. Graphics (in the press).
Wittekind, M. G., Reizer, J. & Klevit, R. E. Biochemistry 29, 7191–7200 (1990).
Klevit, R. E. & Waygood, E. B. Biochemistry 25, 7774–7781 (1986).
Hammen, P., Waygood, E. B. & Klevit, R. E. Biochemistry 30, 11842–11850 (1991).
Kalbitzer, H. R., Neidig, K.-P. & Hengstenberg, W. Biochemistry 30, 11186–11192 (1991).
van Nuland, N. et al. Eur. J. Biochem. 203, 483–491 (1992).
El-Kabbani, O. A. L., Waygood, E. B. & Delbaere, L. T. J. J. biol. Chem. 262, 12926–12929 (1987).
Brünger, A. T., Kuriyan, J. & Karplus, M. Science 235, 458–460 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Z., Vandonselaar, M., Quail, J. et al. Active-centre torsion-angle strain revealed in 1.6 Å-resolution structure of histidine-containing phosphocarrier protein. Nature 361, 94–97 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/361094a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/361094a0
This article is cited by
-
CcpA represses the expression of the divergent cit operons of Enterococcus faecalis through multiple cresites
BMC Microbiology (2011)
-
Recurrence of a binding motif?
Nature (1993)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.