Abstract
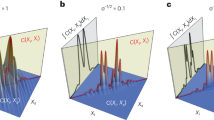
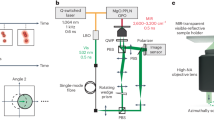
LOW-ENERGY electron diffraction (LEED) has become the most successful technique in surface crystallography1, but because of the complexity of the surface-electron scattering interactions, analyses of LEED data are still conducted on a trial-and-error basis: a direct-inversion method for treating LEED intensity data remains an attractive goal2. Building on recent theoretical and experimental developments in electron holography from surface structures3–16, we show here that three-dimensional images with atomic resolution can be obtained by a direct transform of conventional LEED intensity spectra.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pendry, J. B. Low Energy Electron Diffraction (Academic, London, 1974).
Pendry, J. B., Heinz, K. & Oed, W. Phys. Rev. Lett. 61, 2953–2956 (1988).
Szöke, A. in Short Wavelength Coherent Radiation: Generation and Application (eds Attwood, D. T. & Boker, J.) AIP Conf. No. 147 (American Institute of Physics, New York, 1986).
Barton, J. J. Phys. Rev. Lett. 61, 1356–1359 (1988).
Saldin, D. K. & de Andres, P. L. Phys. Rev. Lett. 64, 1270–1273 (1990).
Harp, G. R., Saldin, D. K. & Tonner, B. P. Phys. Rev. Lett. 65, 1012–1015 (1990).
Tong, S. Y., Wei, C. M., Zhao, T. C., Huang, H. & Li, H. Phys. Rev. Lett. 66, 60–63 (1991).
Hu, P., Barnes, C. J. & King, D. A. Chem. Phys. Lett. 183, 521–528 (1991).
Hu, P. & King, D. A. Nature 353, 831–833 (1991).
Hu, P. & King, D. A. Phys. Rev. B (in the press).
Tonner, B. P., Han, Z.-L., Harp, G. R. & Saldin, D. K. Phys. Rev. B43, 14423–14433 (1991).
Saldin, D. K., Harp, G. R., Chen, B. L. & Tonner, B. P. Phys. Rev. B44, 2480–2494 (1991).
Wei, C. M., Zhao, T. C. & Tong, S. Y. Phys. Rev. Lett. 65, 2278–2280 (1990).
Barton, J. J. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 3106–3109 (1991).
Tong, S. Y. Li, H. & Huang, H. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 3102–3105 (1991).
Mendez, M. A., Gluck, C. & Heinz, K. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 4, 999 (1992).
Landman, U. & Adams, D. L. Surf. Sci. 51, 149–173 (1975).
Marsh, F. S. & King, D. A. Surf. Sci. 79, 445–460 (1979).
Woodruff, D. P. Faraday Disc. 60, 218–229 (1975).
Barton, J. J., Xu, M.-L. & Van Hove, M. A. Phys. Rev. B37, 10475–10486 (1988).
Barton, J. J. & Shirley, D. A., Phys. Rev. B32, 1906–1920 (1985).
Hu, P., Barnes, C. J. & King, D. A. Phys. Rev. B45, 13595–13598 (1992).
Van Hove, M. A. & Tong, S. Y. Surface Crystallography by LEED (Springer, Berlin 1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, P., King, D. A direct inversion method for surface structure determination from LEED intensities . Nature 360, 655–658 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1038/360655a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/360655a0
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.