Abstract
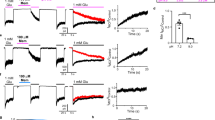
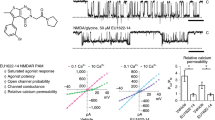
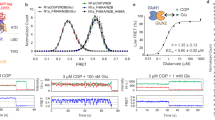
THE N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor channel is highly permeable to Ca2+ but is blocked by Mg2+ in a voltage-dependent manner1–4. These characteristics are essential for the NMDA receptor channel to mediate the induction of long-term potentiation of synaptic efficacy, a form of activity-dependent synaptic plasticity thought to underlie memory, learning and development5–8. Recent studies have revealed the molecular and functional diversity of the NMDA receptor channel subunits, which are classified into the ɛ and ζ families according to the amino-acid sequence homology9–12. Here we report that replacement by glutamine of asparagine 598 in putative transmembrane segment M2 of the ζ1 subunit, strongly reduces the sensitivity of the heteromeric ɛ 2/ζ1 NMDA receptor channel to Mg2+ block. The corresponding mutation of the ɛ2 subunit has a similar effect. Furthermore, the heteromeric ɛ 2/ζl NMDA receptor channel with the mutation on both subunits shows greatly reduced sensitivity to MK-801, a channel blocker of the NMDA receptor channel13,14, but is still susceptible to inhibition by Zn2+15,16. These findings suggest that the conserved asparagine residue in segment M2 constitutes a Mg2+-block site of the NMDA receptor channel, and that the MK-801 site overlaps the Mg2+ site.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nowak, L., Bregestovski, P., Ascher, P., Herbet, A. & Prochiantz, A. Nature 307, 462–465 (1984).
Mayer, M. L., Westbrook, G. L. & Guthrie, P. B. Nature 309, 261–263 (1984).
Ascher, P. & Nowak, L. J. Physiol., Lond. 377, 35P (1986).
MacDermott, A. B., Mayer, M. L., Westbrook, G. L., Smith, S. J. & Barker, J. L. Nature 321, 519–522 (1986).
Collingridge, G. L., Kehl, S. J. & McLennan, H. J. Physiol., Lond. 334, 33–46 (1983).
Herron, C. E., Lester, R. A. J., Coan, E. J. & Collingridge, G. L. Nature 322, 265–268 (1986).
Collingridge, G. L. & Bliss, T. V. P. Trends Neurosci. 10, 288–293 (1987).
McDonald, J. W. & Johnson, M. V. Brain Res. Rev. 15, 41–70 (1990).
Moriyoshi, K. et al. Nature 354, 31–37 (1991).
Yamazaki, M., Mori, H., Araki, K., Mori, K. J. & Mishina, M. FEBS Lett 300, 39–45 (1992).
Meguro, H. et al. Nature 357, 70–74 (1992).
Kutsuwada, T. et al. Nature 358, 36–41 (1992).
Wong, E. H. F. et al. Proc. natn. Acad Sci. U.S.A. 83, 7104–7108 (1986).
Huettner, J. E. & Bean, B. P. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 1307–1311 (1988).
Peters, S., Koh, J. & Choi, D. W. Science 236, 589–593 (1987).
Westbrook, G. L. & Mayer, M. L. Nature 328, 640–643 (1987).
Hume, R. I., Dingledine, R. & Heinemann, S. Science 253, 1028–1031 (1991).
Mishina, M. et al. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 180, 813–821 (1991).
Burnashev, N., Monyer, H., Seeburg, P. H. & Sakmann, B. Neuron 8, 189–198 (1992).
Sakimura et al. FEBS Lett. 272, 73–80 (1990).
Leonard, J. P. & Kelso, S. R. Neuron 4, 53–60 (1990).
Ascher, P. & Nowak, L. J. Physiol., Lond. 399, 247–266 (1988).
Christine, C. W. & Choi, D. W. J. Neurosci. 10, 108–116 (1990).
Legendre, P. & Westbrook, G. L. J. Physiol., Lond. 429, 429–449 (1990).
Ho, S. N., Hunt, H. D., Horton, R. M., Pullen, J. K. & Pease, L. R. Gene 77, 51–59 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mori, H., Masaki, H., Yamakura, T. et al. Identification by mutagenesis of a Mg2+ -block site of the NMDA receptor channel. Nature 358, 673–675 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1038/358673a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/358673a0
This article is cited by
-
Convergent NMDA receptor—Pannexin1 signaling pathways regulate the interaction of CaMKII with Connexin-36
Communications Biology (2021)
-
Disease-associated missense mutations in GluN2B subunit alter NMDA receptor ligand binding and ion channel properties
Nature Communications (2018)
-
GRIN1 mutation associated with intellectual disability alters NMDA receptor trafficking and function
Journal of Human Genetics (2017)
-
Enhanced stability of hippocampal place representation caused by reduced magnesium block of NMDA receptors in the dentate gyrus
Molecular Brain (2014)
-
Investigational Therapies for Ischemic Stroke: Neuroprotection and Neurorecovery
Neurotherapeutics (2011)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.