Abstract
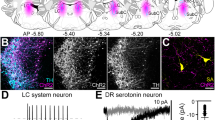
IN addition to its diverse functions inside cells, ATP can act at several types of cell-surface receptor1–3. One of these (P2x-purinoceptor) is believed to be a ligand-gated cation channel1–6. The presence of P2x receptors on autonomic, sensory and central neurons suggests that ATP might be released to act as a fast excitatory synaptic transmitter. Here we record excitatory synaptic potentials and currents from cultured coeliac ganglion neurons which are mimicked by ATP, blocked by the P2-purinoceptor antagonist suramin, desensitized by α,β-methylene-ATP and unaffected by antagonists acting at nicotine, 5-hydroxytryptamine, N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA), non-NMDA glutamate, γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), noradrenaline or adenosine receptors. We conclude that ATP is the neurotransmitter at this neuro–neuronal synapse.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burnstock, G. Nucleosides and Nucleotides 10, 917–930 (1991).
Jahr, C. E. & Jessel, T. M. Nature 304, 730–733 (1983).
Benham, C. D. et al. J. Physiol. 387, 473–488 (1987).
Bean, B. P. J. Neurosci. 10, 1–10 (1990).
Bean, B. P., Williams, C. A. & Ceelen, P. W. J. Neurosci. 10, 11–19 (1991).
Fieber, L. A. & Adams, D. J. J. Physiol. 434, 239–256 (1991).
Dunn, P. M. & Blakeley, A. G. H. Br. J. Pharmac. 93, 243–245 (1988).
Nakazawa, K. et al. Br. J. Pharmac. 101, 224–226 (1990).
von Kugelgen, I., Bultmann, R. & Starke, K. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archs Pharmak. 340, 760–763 (1989).
Hoyle, C. H. V., Knight, G. E. & Burnstock, G. Br. J. Pharmac. 99, 617–621 (1990).
von Kugelgen, I., Bultmann, R. & Starke, K. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archs Pharmak. 342, 198–205 (1990).
Evans, R. J. & Surprenant, A. Br. J. Pharmac. (in the press).
Burnstock, G. Neurochem. Int. 2, 357–368 (1990).
Starke, K. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmac. 107, 73–146 (1987).
Starke, K., Gothert, M. & Kilbinger, H. Physiol. Rev. 69, 864–969 (1989).
Burnstock, G. Acta Physiol. Scand. 126, 67–91 (1986).
White, T. D. Pharmac. Ther. 38, 129–168 (1988).
Volknandt, W. & Zimmermann, H. J. Neurochem. 47, 1449–1462 (1986).
Lagercrantz, H. Neuroscience 1, 81–92 (1976).
Fried, G. Acta. physiol. scand. 493, 546–559 (1980).
Coggan, J. S. & Kreulen, D. L. J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 34, 147–156 (1991).
Alm, P. et al. Neuroscience 4, 145–158 (1979).
Hamill, O. P. et al. Pflugers Arch. 391, 85–100 (1981).
Shen, K.-Z. et al. J. Physiol. 431, 585–608 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Evans, R., Derkach, V. & Surprenant, A. ATP mediates fast synaptic transmission in mammalian neurons. Nature 357, 503–505 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1038/357503a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/357503a0
This article is cited by
-
Glial ATP and Large Pore Channels Modulate Synaptic Strength in Response to Chronic Inactivity
Molecular Neurobiology (2020)
-
Extracellular ATP and P2 purinergic signalling in the tumour microenvironment
Nature Reviews Cancer (2018)
-
Roles of the lateral fenestration residues of the P2X4 receptor that contribute to the channel function and the deactivation effect of ivermectin
Purinergic Signalling (2015)
-
CALHM1 ion channel mediates purinergic neurotransmission of sweet, bitter and umami tastes
Nature (2013)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.