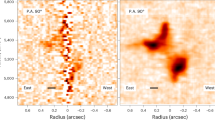
Abstract
RECENT infrared observations1 have revealed hot gas, with a temperature possibly as high as one million degrees, associated with a small cavity 2 arcseconds in diameter in one of the ionized gas streamers (the 'Bar') that orbit the Galactic Centre radio source SgrA* (ref. 2), thought to contain a massive black hole. Radio continuum observations3 show a chain of blobs of emission leading from SgrA* to the small cavity. We present here further high-resolution radio images which show that the blobs are connected to SgrA*; by a ridge of emission. We suggest that the blobs are formed by the interaction of stellar winds from the IRS16 cluster with the gravitational potential of SgrA*. The hot gas1 then results from the dissipation of the kinetic energy of the blobs as they collide with the orbiting ionized streamer. These collisions are of dynamial significance for the motion of the Bar around the Galactic Centre, and there should be detectable variability in the structure on a timescale of 10 years.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eckart, A. et al. Nature 355, 526–529 (1992).
Lo, K. Y. IAU Symp. 136, The Center of the Galaxy (ed. Morris, M.) 527–534 (Kluwer, Dordrecht, 1989).
Yusef-Zadeh, F., Morris, M. & Ekers, R. Nature 348, 45–47 (1990).
Serabyn, E., Lacy, J. H., Townes, C. H. & Bharat, R. Astrophys. J. 326, 171–185 (1988).
Lacy, J. H., Achtermann, J. M. & Serabyn, E. Astrophys. J. 380, L71–L74 (1991).
McGinn, M. T., Sellgren, K., Becklin, E. E. & Hall, D. N. B. Astrophys. J. 338, 824–840 (1989).
Sellgren, K., McGinn, N. T., Becklin, E. E. & Hall, D. N. B. Astrophys. J. 359, 112–120 (1990).
Allen, D. A., Hyland, A. R. & Hillier, D. J. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 244, 706–713 (1990).
Hall, D. N. B., Kleinmann, S. G. & Scoville, N. Z. Astrophys. J. 260, L53–L57 (1982).
Geballe, T. R., Krisciunas, K., Lee, T. J., Gatley, I. & Wade, R. Astrophys. J. 284, 118–125 (1984).
Maillard, J. P. & Gay, J. IAU Symp. 136, The Center of the Galaxy (ed. Morris, M.) 517–521 (Kluwer, Dordrecht, 1989).
Geballe, T. R., Krisciunas, K., Bailey, J. A. & Wade, R. Astrophys. J. 370, L73–L76 (1991).
Krabbe, A., Genzel, R., Drapatz, S. & Rotaciuc, V. Astrophys. J. 382, L19–L22 (1991).
Yusef-Zadeh, F. & Morris, M. Astrophys. J. 371, L59–L62 (1991).
Serabyn, E., Lacy, J. H. & Achtermann, J. M. Astrophys. J. 378, 557–564 (1991).
Yusef-Zadeh, F. & Melia, F. Astrophys. J. 385, L41–L44 (1992).
Yusef-Zadeh, F. & Wardle, M. in The Large Scale Distribution of Stars and Gas in the Milky Way (ed. Blitz, L.) (Kluwer, in the press).
Yusef-Zadeh, F., Morris, M. & Ekers, R. IAU Symp. 136, The Center of the Galaxy (ed. Morris, M.) 443–451 (Kluwer, Dordrecht, 1989).
Zhao, J.-H., Goss, W. M., Lo, K. Y. & Ekers, R. D. Nature 354, 46–48 (1991).
Ozernoy, L. M. IAU Symp. 136, The Center of the Galaxy (ed. Morris, M.) 555–566 (Kluwer, Dordrecht, 1989).
Melia, F. Astrophys. J. 387, L25–L28 (1992).
Gaetz, T. J. & Salpeter, E. E. Astrophys. J. (Suppl.) 52, 155–168 (1983).
Watson, M. G., Willingale, R., Grindlay, J. E. & Hertz, P. Astrophys. J. 250, 142–154 (1981).
Taam, R. E. & Fryxell, B. A. Astrophys. J. 327, L73–L75 (1988).
Field, G. B. Astrophys. J. 142, 531–567 (1965).
Brown, R. L. & Liszt, H. H. A. Rev. Astr. Astrophys. 22, 223–265 (1984).
Roberts, D. thesis, Univ. of Oklahoma (1992).
Tollestrup, E. V., Capps, R. W. & Becklin, E. E. Astr. J. 98, 204–216 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wardle, M., Yusef-Zadeh, F. Origin of the hot gas and radio blobs at the Galactic Centre. Nature 357, 308–310 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1038/357308a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/357308a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.