Abstract
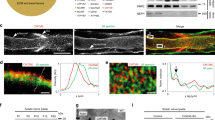
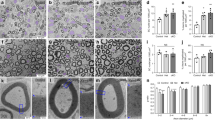
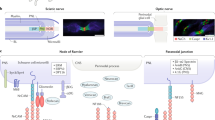
IN myelinated nerves, segregation of voltage-dependent sodium channels to nodes of Ranvier is crucial for saltatory conduction along axons1–4. As sodium channels associate5 and colocalize with ankyrin at nodes of Ranvier6, one possibility is that sodium channels are recruited and immobilized at axonal sites which are specified by the subaxolemmal cytoskeleton, independent of glial cell contact7–10. Alternatively, segregation of channels at distinct sites along the axon may depend on glial cell contact11–14. To resolve this question, we have examined the distribution of sodium channels, ankyrin and spectrin in myelination-competent co-cultures of sensory neurons and Schwann cells by immunofluores-cence, using sodium channel-, ankyrin- and spectrin-specific antibodies. In the absence of Schwann cells, sodium channels, ankyrin and spectrin are homogeneously distributed on sensory axons. When Schwann cells are introduced into these cultures, the distribution of sodium channels dramatically changes so that channel clusters on axons are abundant, but ankyrin and spectrin remain homogeneously distributed. Addition of latex beads or Schwann cell membranes does not induce channel clustering. Our results suggest that segregation of sodium channels on axons is highly dependent on interactions with active Schwann cells and that continuing axon-glial interactions are necessary to organize and maintain channel distribution during differentiation of myelinated axons.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Waxman, S. G. & Ritchie, J. M. Science 228, 1502–1507 (1985).
Black, J. A., Kocsis, J. D. & Waxman, S. G. Trends Neurosci. 13, 48–54 (1990).
Bostock, H. & Sears, T. A. J. Physiol. Lond. 280, 273–301 (1978).
Rasminsky, M. & Sears, T. A. J. Physiol., Lond. 227, 323–349 (1972).
Srinivasan, Y., Elmer, L., Davis, J., Bennett, V. & Angelides, K. J. Nature 333, 177–180 (1988).
Kordeli, E., Davis, J., Trapp, B. & Bennett, V. J. J Cell Biol. 110, 1341–1352 (1990).
Ellisman, M. H. J. Neurocytol. 8, 719–748 (1979).
LeBeau, J. M., Powell, H. C. & Ellisman, M. H. J. Neurocytol. 16, 347–358 (1987).
Wiley-Livinston, C. A. & Ellisman, M. H. Devl Biol. 79, 334–355 (1980).
Wiley, C. A. & Ellisman, M. H. J. Cell Biol 84, 261–280 (1980).
Rosenbluth, J. J. Neurocytol. 8, 655–672 (1979).
Rosenbluth, J. Int. J. devl Neurosci. 6, 3–24 (1988).
Black, J. A., Waxman, S. G. & Hildebrand, C. J. Neurocytol. 14, 887–909 (1985).
Bigbee, J. W. & Foster, R. E. Brain Res. 494, 182–186 (1989).
Eldridge, C. F., Bunge, M. B., Bunge, R. P. & Wood, P. M. J. Cell Biol 105, 1023–1034 (1987).
Eldridge, C. F., Bunge, M. B. & Bunge, R. P. J. Neurosci. 9, 625–638 (1989).
Clark, M. B. & Bunge, M. B. Devl Biol. 133, 393–404 (1989).
Brockes, J. P., Fields, K. P. & Raff, M. C. Brain Res. 165, 105–108 (1979).
Elmer, L. W., Black, J. A., Waxman, S. G. & Angelides, K. J. Brain Res. 532, 222–231 (1990).
Reiger, F. Daniloff, J. K., Pincon-Raymond, M., Crosin, K. L., Grumet, M. & Edelman, G. M. J. Cell Biol. 103, 379–391 (1986).
Waxman, S. G. & Foster, R. E. Proc. R. Soc. B209, 441–446 (1980).
Black, J. A., Foster, R. E. & Waxman, B. S. J. Neurocytol. 10, 981–993 (1981).
Smith, K. J., Bostock, H., and Hall, S. M. J. Neurol. Sci. 54, 3–31, 1982.
Black, J. A., Sims, T. J., Waxman, S. G. & Gilmore, S. A. J. Neurocytol. 14, 79–104 (1985).
Foster, R. E., Whalen, C. C. & Waxman, S. G. Science 210, 661–663 (1980).
Rosenbluth, J. & Blakemore, W. Neurosci. Lett. 48, 171–177 (1984).
Angelides, K. J., Loftus, D., Elmer, L. W. & Elson, E. L. J. Cell Biol. 106, 1911–1925 (1988).
Black, J. A., Waxman, S. G., Sims, T. J. & Gilmore, S. A. J. Neurocytol. 15, 745–761 (1986).
Ratner, N., Glaser, L. & Bunge, R. P. J. Cell Biol. 98, 1150–1155 (1984).
Ranscht, B., Wood, P. M. & Bunge, R. P. J. Neurosci. 7, 2936–2947 (1987).
Owens, G. & Bunge, R. P. Glia 2, 119–128 (1989).
Wood, P. M., Schachner, M. & Bunge, R. P. J. Neurosci. 10, 3635–3645 (1990).
Froehner, S. C. J. Cell Biol. 113, 1133–1144 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joe, Eh., Angelides, K. Clustering of voltage-dependent sodium channels on axons depends on Schwann cell contact. Nature 356, 333–335 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1038/356333a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/356333a0
This article is cited by
-
KATP Channel Subunits in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglia: Alterations by Painful Axotomy
Molecular Pain (2010)
-
Distribution of sodium channels during nerve elongation in rat peripheral nerve
Journal of Orthopaedic Science (2005)
-
Functional localization of single active ion channels on the surface of a living cell
Nature Cell Biology (2000)
-
Induction of sodium channel clustering by oligodendrocytes
Nature (1997)
-
Heteromultimeric K+ channels in terminal and juxtaparanodal regions of neurons
Nature (1993)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.