Abstract
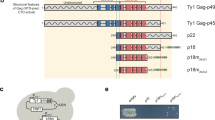
OVEREXPRESSION of dominant-negative mutants of various viral proteins can result in 'intracellular immunization' (refs 1, 2). Here we describe a new approach to interfering with viral replication in which a nuclease is fused to a capsid component so that the nuclease is encapsidated inside the virion where it can inactivate viral nucleic acid. We used Tyl, a yeast retrotransposon whose transposition closely parallels retroviral replication mechanisms and serves as an easily manipulated model for the retroviral infection process3. We constructed fusion genes consisting of the region encoding the N-terminal portion of the TYA/TYB open reading frames of retrotransposon Tyl and either of two different nuclease genes. Tyl-nuclease fusion proteins are targeted to Tyl virus-like particles, and are active in degrading nucleic acids. A Tyl-barnase fusion protein causes 98–99% reduction in the efficiency of Tyl transposition in vivo, presumably by degrading encapsidated Tyl RNA. This strategy, referred to as capsid- targeted viral inactivation, may be useful for interfering with the replication of retroviruses and other viruses.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Herskowitz, I. Nature 329, 219–222 (1987).
Baltimore, D. Nature 335, 395–396 (1988).
Boeke, J. D. in Mobile DNA (eds Berg, D. E. & Howe, M. M.) 335–374 (American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC, 1989).
Atkins, J. F., Weiss, R. B. & Gesteland, R. F. Cell 62, 413–423 (1990).
Yoshinaka, Y., Katoh, I., Copeland, T. D. & Oroszlan, S. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 1618–1622 (1985).
Yoshioka, K. et al. EMBO J. 9, 535–541 (1990).
Brierley, C. & Flavell, A. J. Nucleic Acids Res. 18, 2947–2951 (1990).
Jones, T. A., Blaug, G., Hansen, M. & Barklis, E. J. Virol. 64, 2265–2279 (1990).
Weldon, R. A., Erdie, C. R., Oliver, M. G. & Wills, J. W. J. Virol. 64, 4169–4179 (1990).
Adams, S. E., Dawson, K. M., Gull, K., Kingsman, S. M. & Kingsman, A. J. Nature 329, 68–70 (1987).
Hartley, R. W. Trends biochem. Sci. 14, 450–454 (1989).
Mariani, C., deBeuckeleer, M., Truettner, J., Leemans, J. & Goldberg, R. B. Nature 347, 737–741 (1990).
Tucker, P. W., Hazen, E. E. & Cotton, F. A. Molec. cell. Biochem. 22, 67–77 (1978).
Weber, D. J., Serpersu, E. H., Shortle, D. & Mildvan, A. S. Biochemistry 29, 8632–8642 (1990).
Mossakowska, D. E., Nyberg, K. & Fersht, A. R. Biochemistry 28, 3843–3850 (1989).
Boeke, J. D., Garfinkel, D. J., Styles, C. A. & Fink, G. R. Cell 40, 491–500 (1985).
Garfinkel, D. J., Boeke, J. D. & Fink, G. R. Cell 42, 507–517 (1985).
Mellor, J. et al. Nature 318, 583–586 (1985).
Müller, F., Brühl, K. H., Freidel, K., Kowallik, K. V. & Ciriacy, M. Molec. Gen. Genet. 207, 421–429 (1987).
Adams, S. E. et al. Cell 49, 111–119 (1987).
Youngren, S. D., Boeke, J. D., Sanders, N. J. & Garfinkel, D. J. Molec. cell. biol. 8, 1421–1431 (1988).
Eichinger, D. J. & Boeke, J. D. Cell 54, 955–966 (1988).
Eichinger, D. J. & Boeke, J. D. Genes Dev. 4, 324–330 (1990).
Boeke, J. D., Xu, H. & Fink, G. R. Science 239, 280–282 (1988).
Cuatrecasas, P., Fuchs, S. & Anfinsen, C. B. J. Biol. Chem. 242, 1541–1547 (1967).
Sikorski, R. S. & Hieter, P. Genetics 122, 19–27 (1989).
Boeke, J. D., Eichinger, D. J., Castrillon, D. & Fink, G. R. Molec. cell. Biol. 8, 1432–1442 (1988).
Hartley, R. W. J. molec. Biol. 202, 913–915 (1988).
Rose, M. D. & Fink, G. R. Cell 48, 1047–1060 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Natsoulis, G., Boeke, J. New antiviral strategy using capsid-nuclease fusion proteins. Nature 352, 632–635 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1038/352632a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/352632a0
This article is cited by
-
Structure and function of capsid protein in flavivirus infection and its applications in the development of vaccines and therapeutics
Veterinary Research (2021)
-
Capsid-targeted viral inactivation can destroy dengue 2 virus from within in vitro
Archives of Virology (2006)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.