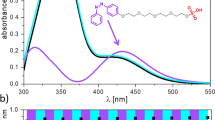
Abstract
LIPID membranes containing dye molecules that respond to light, for example by photoisomerization, may provide the basis for artificial visual systems for use in optoelectronic devices and optical transducers. Here we describe such a membrane/dye system that generates an electrical signal in response to irradiation within a specific range of wavelengths. We incorporated an amphiphilic azobenzene derivative into the planar black lipid membrane formed from egg lecithin. When a d.c. voltage is applied across the modified membrane, transient current pulses are induced by alternate irradiation with ultraviolet and visible light. We interpret this photoelectric response as the result of changes in the membrane capacitance caused by cis–trans photoisomerization of the azobenzene derivative.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, Z. F., Hashimoto, K. & Fujishima, A. Nature 347, 658–660 (1990).
Kano, K., Tanaka, Y., Ogawa, T., Shimomura, M. & Kunitake, T. Photochem. Photobiol. 34, 323–329 (1981).
Okahata, Y. Acc. chem. Res. 19, 57–63 (1986).
Tazuke, S., Kurihara, S., Yamaguchi, H., & Ikeda, T. J. phys. Chem. 91, 249–251 (1987).
Kumar, G. S., & Neckers, D. C. Chem. Rev. 89, 1915–1925 (1989).
Hanai, T., Kajiyama, S., Morita, S. & Koizumi, N. Bull. Inst. Chem. Res. Kyoto Univ. 47, 327–339 (1969).
Chapman, D. in Form and Function of Phospholipids (eds Ansell, G. B., Hawthorne, J. N. & Dawson, R. M. C.) 117–142 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1973).
Hanai, T., Haydon, D. A. & Taylor, J. Proc. R. Soc. A281, 377–391 (1964).
Mueller, P., Rudin, D. O., Ti Tien, H. & Wescott, W. C. Nature 194, 979–980 (1962).
Mueller, P., Rudin, D. O., Ti Tien, H. & Wescott, W. C. J. phys. Chem. 67, 534–535 (1963).
Parker, C. A. Proc. Roy Soc. A220, 104–116 (1953).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujiwara, H., Yonezawa, Y. Photoelectric response of a black lipid membrane containing an amphiphilic azobenzene derivative. Nature 351, 724–726 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1038/351724a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/351724a0
This article is cited by
-
Rapid and reversible optical switching of cell membrane area by an amphiphilic azobenzene
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Neuronal firing modulation by a membrane-targeted photoswitch
Nature Nanotechnology (2020)
-
Generation of Maxwell displacement current across an azobenzene monolayer by photoisomerization
Nature (1991)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.