Abstract
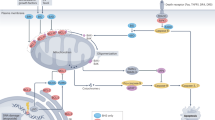
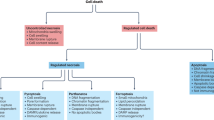
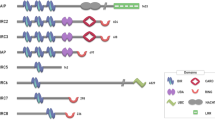
Controlling the activity of caspases is essential for the appropriate execution of cell death and the regulation of cell survival. One cellular inhibitor of apoptosis, XIAP, has emerged as a crucial regulator of caspases, and is itself subject to complex negative regulation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nicholson, D. W. Caspase structure, proteolytic substrates, and function during apoptotic cell death. Cell Death Differ. 6, 1028–1042 (1999).
Holcik, M., Gibson, H. & Korneluk, R. G. XIAP: Apoptotic brake and promising therapeutic target. Apoptosis 6, 251–259 (2001).
Takahashi, R. et al. A single BIR domain of XIAP is sufficient for inhibiting caspases. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 7787–7790 (1998).
Deveraux, Q. L. & Reed, J. C. IAP family proteins — suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev. 13, 239–252 (1999).
Sun, C. et al. NMR structure and mutagenesis of the third BIR domain of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein XIAP. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 33777–33781 (2000).
Srinivasula, S. M. et al. A conserved XIAP-interaction motif in caspase-9 and Smac/DIABLO regulates caspase activity and apoptosis. Nature 410, 112–116 (2001).
Riedl, S. J. et al. Structural basis for the inhibition of caspase-3 by XIAP. Cell 104, 791–800 (2001).
Huang, Y. et al. Structural basis of caspase inhibition by XIAP. Differential roles of the linker versus the BIR domain. Cell 104, 781–790 (2001).
Chai, J. et al. Structural basis of caspase-7 inhibition by XIAP. Cell 104, 769–780 (2001).
Roy, N., Deveraux, Q. L., Takahashi, R., Salvesen, G. S. & Reed, J. C. The c-IAP-1 and c-IAP-2 proteins are direct inhibitors of specific caspases. EMBO J. 16, 6914–6925 (1997).
Deveraux, Q. L. et al. Cleavage of human inhibitor of apoptosis protein XIAP results in fragments with distinct specificities for caspases. EMBO J. 18, 5242–5251 (1999).
Bratton, S. B. et al. Recruitment, activation and retention of caspases-9 and -3 by Apaf-1 apoptosome and associated XIAP complexes. EMBO J. 20, 998–1009 (2001).
Zeuner, A., Eramo, A., Peschle, C. & De Maria, R. Caspase activation without death. Cell Death Differ. 6, 1075–1080 (1999).
Zhou, Q. et al. Interaction of the baculovirus anti-apoptotic protein p35 with caspases. Specificity, kinetics, and characterization of the caspase/p35 complex. Biochemistry 37, 10757–10765 (1998).
Xu, G. et al. Covalent inhibition revealed by the crystal structure of the caspase-8/p35 complex. Nature 410, 494–497 (2001).
Du, C., Fang, M., Li, Y., Li, L. & Wang, X. Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell 102, 33–42 (2000).
Verhagen, A. M. et al. Identification of DIABLO, a mammalian protein that promotes apoptosis by binding to and antagonizing IAP proteins. Cell 102, 43–53 (2000).
Chai, J. et al. Structural and biochemical basis of apoptotic activation by Smac/DIABLO. Nature 406, 855–862 (2000).
Wu, G. et al. Structural basis of IAP recognition by Smac/DIABLO. Nature 408, 1008–1012 (2000).
Liu, Z. et al. Structural basis for binding of Smac/DIABLO to the XIAP BIR3 domain. Nature 408, 1004–1008 (2000).
Bangs, P. & White, K. Regulation and execution of apoptosis during Drosophila development. Dev. Dyn. 218, 68–79 (2000).
Srinivasula, S. M. et al. Molecular determinants of the caspase-promoting activity of Smac/DIABLO and its role in the death receptor pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 36152–36157 (2000).
Roberts, D. L., Merrison, W., MacFarlane, M. & Cohen, G. M. The inhibitor of apoptosis protein-binding domain of Smac is not essential for its proapoptotic activity. J. Cell Biol. 153, 221–228 (2001).
Liston, P. et al. Identification of XAF1 as an antagonist of XIAP anti-caspase activity. Nature Cell Biol. 3, 128–133 (2001).
Lazebnik, Y. A. et al. Studies of the lamin proteinase reveal multiple parallel biochemical pathways during apoptotic execution. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92, 9042–9046 (1995).
Takahashi, A. et al. Cleavage of lamin A by Mch2α but not CPP32: multiple interleukin 1β-converting enzyme-related proteases with distinct substrate recognition properties are active in apoptosis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 8395–8400 (1996).
Faleiro, L. & Lazebnik, Y. Caspases disrupt the nuclear–cytoplasmic barrier. J. Cell Biol. 151, 951–959 (2000).
Levkau, B. et al. XIAP induces cell-cycle arrest and activates nuclear factor-κB: new survival pathways disabled by caspase-mediated cleavage during apoptosis of human endothelial cells. Circ. Res. 88, 282–290 (2001).
Harlin, H., Reffey, S. B., Duckett, C. S., Lindsten, T. & Thompson, C. B. Characterization of XIAP-deficient mice. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 3604–3608 (2001).
Fong, W. G. et al. Expression and genetic analysis of XIAP-associated Factor 1 (XAF1) in cancer cell lines. Genomics 70, 113–122 (2000).
Yang, Y., Fang, S., Jensen, J. P., Weissman, A. M. & Ashwell, J. D. Ubiquitin protein ligase activity of IAPs and their degradation in proteasomes in response to apoptotic stimuli. Science 288, 874–877 (2000).
Hengartner, M. O. Apoptosis. CED-4 is a stranger no more. Nature 388, 714–715 (1997).
Ekert, P. G., Silke, J. & Vaux, D. L. Caspase inhibitors. Cell Death Differ. 6, 1081–1086 (1999).
Shin, S. et al. An anti-apoptotic protein human survivin is a direct inhibitor of caspase-3 and -7. Biochemistry 40, 1117–1123 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holcik, M., Korneluk, R. XIAP, the guardian angel. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2, 550–556 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/35080103
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35080103
This article is cited by
-
XIAP gene therapy effects on retinal ganglion cell structure and function in a mouse model of glaucoma
Gene Therapy (2022)
-
Identification of hub genes associated with RNAi-induced silencing of XIAP through targeted proteomics approach in MCF7 cells
Cell & Bioscience (2020)
-
Convergence of pathway analysis and pattern recognition predicts sensitization to latest generation TRAIL therapeutics by IAP antagonism
Cell Death & Differentiation (2020)
-
Effect of Enterococcus faecalis 2001 on colitis and depressive-like behavior in dextran sulfate sodium-treated mice: involvement of the brain–gut axis
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2019)
-
XIAP facilitates breast and colon carcinoma growth via promotion of p62 depletion through ubiquitination-dependent proteasomal degradation
Oncogene (2019)