Abstract
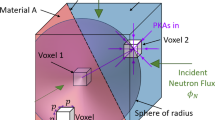
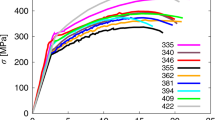
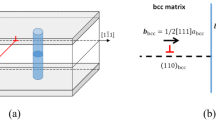
The irradiation of metals by energetic particles causes significant degradation of the mechanical properties1,2, most notably an increased yield stress and decreased ductility, often accompanied by plastic flow localization. Such effects limit the lifetime of pressure vessels in nuclear power plants3, and constrain the choice of materials for fusion-based alternative energy sources4. Although these phenomena have been known for many years1, the underlying fundamental mechanisms and their relation to the irradiation field have not been clearly demonstrated. Here we use three-dimensional multiscale simulations of irradiated metals to reveal the mechanisms underlying plastic flow localization in defect-free channels. We observe dislocation pinning by irradiation-induced clusters of defects, subsequent unpinning as defects are absorbed by the dislocations, and cross-slip of the latter as the stress is increased. The width of the plastic flow channels is limited by the interaction among opposing dislocation dipole segments and the remaining defect clusters.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eyre, B. L. & Barlett, A. F. An electron microscope study of neutron irradiation damage on α-iron. Phil. Mag. 12, 261–271 (1965).
Victoria, M. et al. The microstructure and associated tensile properties of irradiated fcc and bcc metals. J. Nucl. Mater. 276, 114–122 (2000).
Odette, G. R. & Lucas, G. E. Recent progress in understanding reactor pressure vessel steel embrittlement. Radiat. Effects Defects Solids 144, 189–231 ( 1998).
Bloom, E. E. The challenge of developing structural materials for fusion power systems. J. Nucl. Mater. 258–263, 7– 17 (1998).
Averback, R. S. & Diaz de la Rubia, T. in Solid State Physics Vol. 51 (eds Spaepen, F. et al. & Ehrenreich, H.) 281–402 (Academic, New York, 1998).
Dai, Y. & Victoria, M. Defect cluster structure and tensile properties of Cu single crystals irradiated with 600 MeV protons. MRS Symp. Proc. 439, 319–324 (1997).
Friedel, J. Dislocations (Pergamon, Oxford, 1964).
Bement, A. L. Fundamental materials problems in nuclear reactors. In Proc. 2nd Int. Conf. Strength of Metals Alloys Vol. II, 693– 728 (The American Society for Metals, 1970).
Trinkaus, H., Singh, B. N. & Foreman, A. J. E. Segregation of cascade induced interstitial loops at dislocations: possible effect on initiation of plastic deformation. J. Nucl. Mater. 251, 172–187 (1997).
Singh, B. N., Foreman, A. J. E. & Trinkaus, H. Radiation hardening revisited: role of intracascade clustering. J. Nucl. Mater. 249, 103– 115 (1997).
Diaz de la Rubia, T. & Guinan, M. W. New mechanism of defect production in metals: A molecular-dynamics study of interstitial-dislocation-loop formation in high-energy displacement cascades. Phys. Rev. Lett. 66, 2766–2769 ( 1991).
Foreman, A. J. E., Phythian, W. J. & English, C. A. The molecular dynamics simulation of irradiation damage cascades in copper using a many-body potential. Phil. Mag. A 66, 671–695 ( 1992).
Wirth, B. D., Odette, G. R., Maroudas, D. & Lucas, G. E. J. Nucl. Mater. 244, 185–194 (1997).
Osetsky, Y. N., Bacon, D. J. & Serra, A. Thermally activated glide of small dislocation loops in metals. Phil. Mag. Lett. 79, 273– 282 (1999).
Wirth, B. D., Bulatov, V. & Diaz de la Rubia, T. Atomistic simulation of stacking fault tetrahedra formation in Cu. Proc. Int. Conf. Fusion Reactor Materials ICFRM-9, J. Nucl. Mater. (in the press).
Heinisch, H. L. Computer simulation of high energy displacement cascades. Radiat. Effects Defects Solids 113, 53–73 (1990).
Caturla, M. J. et al. Comparative study of radiation damage accumulation in Cu and Fe. J. Nucl. Mater. 276, 13– 21 (2000).
Soneda, N. & Diaz de la Rubia, T. Defect production, annealing kinetics and damage evolution in alpha-Fe: an atomic-scale computer simulation. Phil. Mag. A 78, 995–1019 (1998).
Singh, B. N. & Zinkle, S. J. Defect accumulation in pure fcc metals in the transient regime: a review. J. Nucl. Mater. 206, 212–229 (1993).
Baluc, N., Dai, Y. & Victoria, M. Plasticity and microstructure of irradiated Pd. MRS Symp. Proc. 540, 555–560 (1999).
Baluc, N., Bailat, C., Luppo, M.-I., Schaublin, R. & Victoria, M. Comparison of the microstructure and tensile behavior irradiated fcc and bcc metals. MRS Symp. Proc. 540, 539–548 (1999).
Zbib, H. M., Rhee, M. & Hirth, J. P. On plastic deformation and the dynamics of 3D dislocations. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 40, 113– 127 (1998).
Rhee, M., Zbib, H. M., Hirth, J. P., Huang, H. & Diaz de la Rubia, T. Models for long/short range interactions in 3D dislocation simulation. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 6, 467–492 ( 1998).
Zbib, H. M., Diaz de la Rubia, T., Rhee, M. & Hirth, J. P. 3D dislocation dynamics: stress-strain behavior and hardening mechanisms in fcc and bcc metals. J. Nucl. Mater. 276, 154–165 (2000).
Rhee, M., Lassila, D. H., Bulatov, V. V., Hshuing, L. & Diaz de la Rubia, T. Dislocation multiplication and the early stages of plastic deformation in bcc molybdenum: a dislocation dynamics numerical simulation. Phys. Rev. Lett. (submitted).
Khraishi, T. A., Zbib, H. M., Hirth, J. P. & Diaz de la Rubia, T. The stress field of a general circular Volterra dislocation loop: analytical and numerical approaches. Phil. Mag. Lett. 80, 95–105 (2000).
Ghoniem, N. M., Singh, B. N., Sun, L. Z. & Diaz de la Rubia, T. Interaction and accumulation of glissile defect clusters near dislocations. J. Nucl. Mater. 276, 166–177 (2000).
Rodney, D. & Martin, G. Dislocation pinning by small interstitial loops: a molecular dynamics study. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 3272–3275 (1999).
Khraishi, T. A., Zbib, H. M., Diaz de la Rubia, T. & Victoria, M. Localized deformation and hardening in irradiated metals: 3D discrete dislocation dynamics simulations. Acta Metall. Mater. (submitted).
Acknowledgements
This work was performed in part under the auspices of the US Department of Energy by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. Work by M.V. was performed under a contract of the Swiss National Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diaz de la Rubia, T., Zbib, H., Khraishi, T. et al. Multiscale modelling of plastic flow localization in irradiated materials . Nature 406, 871–874 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/35022544
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35022544
This article is cited by
-
Machine learning potential assisted exploration of complex defect potential energy surfaces
npj Computational Materials (2024)
-
Structural mechanisms of enhanced mechanical properties in amorphous–nanocrystalline ZrCu alloys under irradiation
Journal of Materials Science (2023)
-
Direct imaging of the disconnection climb mediated point defects absorption by a grain boundary
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Multiscale simulation of the focused electron beam induced deposition process
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Revealing the Dynamics of Helium Bubbles Using In Situ Techniques
JOM (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.