Abstract
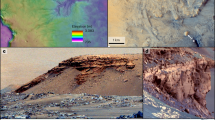
Polar processes can be sensitive indicators of global climate, and the geological features associated with polar ice caps can therefore indicate evolution of climate with time. The polar regions on Mars have distinctive morphologic and climatologic features: thick layered deposits, seasonal CO2 frost caps extending to mid latitudes, and near-polar residual frost deposits that survive the summer1,2. The relationship of the seasonal and residual frost caps to the layered deposits has been poorly constrained3,4, mainly by the limited spatial resolution of the available data. In particular, it has not been known if the residual caps represent simple thin frost cover or substantial geologic features. Here we show that the residual cap on the south pole is a distinct geologic unit with striking collapse and erosional topography; this is very different from the residual cap on the north pole, which grades into the underlying layered materials. These findings indicate that the differences between the caps are substantial (rather than reflecting short-lived differences in frost cover), and so support the idea of long-term asymmetry in the polar climates of Mars.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
James, P. B., Kieffer, H. H. & Paige, D. A. in Mars (eds Kieffer H., Jakosky, B., Snyder C. & Matthews, M.) 934–968 (Univ. Arizona Press, Tucson, 1992).
Jakosky, B. M. & Haberle, R. M. in Mars (eds Kieffer H., Jakosky, B., Snyder C. & Matthews, M.) 969–1016 (Univ. Arizona Press, Tucson, 1992).
Pollack, J. B., Colburn, D., Flasar, F. M., Kahn, R., Carlston, C. & Pidek, D. Properties and effects of dust particles suspended in the Martian atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 84, 2929–2945 (1979).
Thomas, P. C., Herkenhoff, K., Howard, A. & Murray, B. in Mars (eds H. Kieffer, H., Jakosky, B., Snyder, C. & M. Matthews) 767–795 (Univ. Arizona Press, Tucson, 1992).
Smith, D. E. et al. The global topography of Mars and implications for surface evolution. Science 284, 1495– 1503 (1999).
Farmer, C. B., Davies, D. W. & LaPorte, D. D. Mars: Northern summer ice cap—water vapor observations from Viking 2. Science 194, 1339– 1340 (1976).
Kieffer, H. H. Mars south polar spring and summer temperatures. A residual CO2 frost. J. Geophys. Res. 84, 8263– 8288 (1979).
Kieffer, H. H., Titus, T. N., Mullins, K. F. & Christiansen, P. R. Mars south polar spring and summer behavior observed by TES; seasonal cap evolution controlled by grain size. J. Geophys. Res. (submitted).
Malin, M. C. et al. Early views of the Martian surface from the Mars Orbiter Camera of Mars Global Surveyor. Science 279, 1681 –1685 (1998).
Howard, A. D., Cutts, J. A. & Blasius, K. R. Stratigraphic relationships within Martian polar cap deposits. Icarus 50, 161– 215 (1982).
Zuber, M. T. et al. Observations of the north polar region of Mars from the Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter. Science 282, 2053 –2060 (1998).
Malin, M. C. & Edgett, K. S. The nature of layered outcrop expression in the martian polar layered terrains. Lunar Planet. Sci. 34, Abstr. no. 1055 (2000).
James, P. B., Briggs, G., Barnes J. & Spruck, A. Seasonal recession of Mars’ south polar cap as seen by Viking. J. Geophys. Res. 84, 2889–2922 (1979).
Paige, D. A. & Keegan, K. D. Thermal and albedo mapping of the polar regions of Mars using Viking thermal mapper observations: 2. South polar region. J. Geophys. Res. 99, 25993 –26031 (1994).
Mellon, M. T. Small-scale polygonal features on Mars: Seasonal thermal contraction cracks in permafrost. J. Geophys. Res. 102, 25617 –25628 (1997).
Plaut, J. J., Kahn, R., Guinness, E. A. & Arvidson, R. E. Accumulation of sedimentary debris in the south polar region of Mars and implications for climate history. Icarus 76, 357– 377 (1988).
Herkenhoff, K. E. & Plaut, J. J. Surface ages and resurfacing rates of the polar layered deposits on Mars. Icarus (in the press).
Mellon, M. T. Limits on the CO2 content of the martian polar deposits. Icarus 124, 268–279 ( 1996).
Muhleman, D. O., Grossman, A. W. & Butler, B. J. Radar investigation of Mars, Mercury, and Titan. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 23, 337– 374 (1995).
Schenk, P. M. & Moore, J. M. Stereo topography of the south polar region of Mars: Volatile inventory and Mars landing site. J. Geophys. Res. (in the press).
Toon, O. B., Pollack, J. B., Ward, W., Burns, J. A. & Bilski, K. The astronomical theory of climatic change on Mars. Icarus 44, 552–607 (1980).
Kieffer, H. H. & Zent, A. P. in Mars (eds H. Kieffer, H., Jakosky, B., Snyder, C. & M. Matthews) 1180 –1220 (Univ. Arizona Press, Tucson, 1992).
Ward, W. R. in Mars (eds Kieffer, H. H., Jakosky, B., Snyder, C. & Matthews, M. S) 298–320 (Univ. Arizona Press, Tucson 1992).
Cutts, J. A. & Lewis, B. H. Models of climate cycles recorded in Martian polar layered deposits. Icarus 50, 216–244 (1982).
Acknowledgements
E. Jensen, M. Roth, M. Ryan, D. Sharman and J. Warren provided technical assistance. This work was supported in part by NASA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomas, P., Malin, M., Edgett, K. et al. North–south geological differences between the residual polar caps on Mars. Nature 404, 161–164 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/35004528
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35004528
This article is cited by
-
Geology and insolation-driven climatic history of Amazonian north polar materials on Mars
Nature (2005)
-
Albedo of the south pole on Mars determined by topographic forcing of atmosphere dynamics
Nature (2005)
-
Perennial water ice identified in the south polar cap of Mars
Nature (2004)
-
A tale of two ice caps
Nature (2000)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.