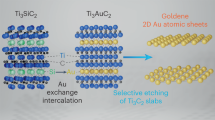
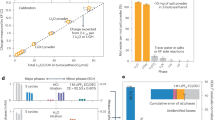
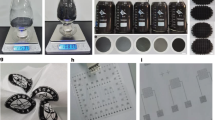
Abstract
LAYERED molybdenum and tungsten dichalcogenides have stimulated considerable interest as lubricants1,2, battery cathodes3–5, and catalysts6–8. Pure, crystalline group VI transition-metal dichalcogenides are normally prepared by intermittently grinding and heating the elements at >900 °C for several days. Low-temperature solution routes to these materials have also been explored9–11. In those studies, exchange (metathesis) reactions between transition-metal halides and alkali-metal sulphides or covalent sulphiding agents in polar organic solvents were found generally to yield finely divided products at close to ambient conditions. Here, in contrast, we consider the factors that influence reactions between transition-metal halides and alkali-metal chalcogenides in the solid state. These highly energetic reactions, driven by the formation of very stable product species, provide a powerful method for the rapid synthesis of materials normally prepared at high temperatures over long periods of time. Other advantages of these solid-state reactions include control of reaction conditions and of product particle sizes. Although our study focuses on group VI transition-metal dichalcogenides, analogous metathesis reactions can be used for rapid syntheses, initiated at low temperatures, of many other technologically important materials.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clauss, F. L. Solid Lubricants and Self-Lubricating Solids (Academic, New York, 1972).
Lince, J. R. & Fleischauer, P. D. J. Mater. Res. 2, 827–838 (1987).
Rouxel, J. & Brec, R. A. Rev. Mater. Sci. 16, 137–162 (1986).
Auborn, J. J., Barberio, Y. L., Hansen, K. J., Schleich, D. M. & Martin, M. J. J. electrochem. Soc. 134, 580–586 (1987).
Jacobson, A. J., Chianelli, R. R. & Whittingham, M. S. J. electrochem. Soc. 126, 2277–2278 (1979).
Chianelli, R. R. Catal. Rev. Sci. Engng 26, 361–393 (1984).
Pecoraro, T. A. & Chianelli, R. R. J. Catal. 67, 430–445 (1981).
Gobolos, S., Wu, Q., Delannay, F., Grange, P. & Delmon, B. Polyhedron 5, 219–224 (1986).
Chianelli, R. R. & Dines, M. B. Inorg. Chem. 17, 2758–2762 (1978).
Schleich, D. M. & Martin, M. J. J. Solid St. Chem. 64, 359–364 (1986).
Martin, M. J., Qiang, G. & Schleich, D. M. Inorg. Chem. 27, 2804–2808 (1988).
Chianelli, R. R. Int. Rev. phys. Chem. 2, 127–165 (1982).
JANAF Thermochemical Tables, 3rd Edn (ed. Lide, D.R. Jr) (American Chemical Society and American Institute of Physics, Inc., New York, 1985).
Wells, A. F. Structural Inorganic Chemistry 5th Edn (Clarendon, Oxford, 1986).
Bonneau, P. R., Shibao, R. K. & Kaner, R. B. Inorg. Chem. 29, 2511–2514 (1990).
Chakurov, Chr., Rusanov, V. & Koichev, J. J. Solid St. Chem. 71, 522–529 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonneau, P., Jarvis, R. & Kaner, R. Rapid solid-state synthesis of materials from molybdenum disulphide to refractories. Nature 349, 510–512 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1038/349510a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/349510a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.