Abstract
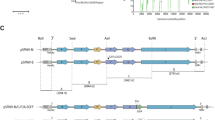
THE PBJ14 isolate of simian immunodeficiency virus from sooty mangabey monkeys (SIVSMM-PBj14) is the most acutely pathogenic primate lentivirus so far described, always causing fatal disease in pig-tailed macaques (Macaco nemestrina) within 8 days of inoculation1. As a first step in identifying viral genes and gene products that influence pathogenicity, the SIVSMM-PBjl4 genome was amplified by the polymerase chain reaction as 5´ and 3´ genomic halves of 5.1 and 5.8 kilobases, respectively, and molecularly cloned. DNA sequence analysis revealed a high degree of conservation with other SIVs, except for a 22-base-pair duplication in the enhancer region of the viral long terminal repeat which included a second binding site for the transcription factor NF-κB. Of six genomic halves examined, four contributed to the formation of infectious virus that induced acute disease and death in pig-tailed macaques as early as 6 days post-inoculation, with pathology, disease syndromes and kinetics indistinguishable from those induced by the uncloned isolate. To our knowledge this is the first example of acute immunodeficiency disease induced by a molecularly defined lentivirus. Furthermore, the molecularly cloned SIVSMM-PBjl4 viruses share with the uncloned virus cytopathicity for mangabey CD4+ cells, a property that may correlate with their observed pathogenicity in vivo.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fultz, P. N., McClure, H. M., Anderson, D. C. & Switzer, W. M. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 5, 397–409 (1989).
Hirsch, V. M., Olmsted, R. A., Murphey-Corb, M., Purcell, R. H. & Johnson, P. R. Nature 339, 389–392 (1989).
Fukasawa, M. et al. Nature 333, 457–461 (1988).
Hirsch, V. M. et al. Nature 341, 573–574 (1989).
Kodama, T. et al. J. Virol. 63, 4709–4714 (1989).
Meyerhans, A. et al. Cell 58, 901–910 (1989).
Lasky, L. A. et al. Cell 50, 975–985 (1987).
Bosch, M. et al. Science 244, 694–697 (1989).
Chakrabarti, L., Emerman, M., Tiollais, P. & Sonigo, P. J. Virol. 63, 4395–4403 (1989).
Naidu, Y. M. et al. J. Virol. 62, 4691–4696 (1988).
Baier, M. et al. J. Virol. 63, 5119–5123 (1989).
Overbaugh, J., Donahue, P. R., Hoover, E. A., Quackenbush, S. L. & Mullins, J. I. Science 239, 906–910 (1988).
Fultz, P. N. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 5286–5290 (1986).
Clark, S. P., Kaufhold, R., Chan, A. & Mak, T. W. Virology 144, 481–494 (1985).
Li, Y., Golemis, E., Hartley, J. W. & Hopkins, N. J. Virol. 61, 693–700 (1987).
Chattopadhyay, S. K. et al. Virology 168, 90–100 (1989).
Holland, C. A., Thomas, C. Y., Chattopadhyay, S. K., Koehne, C. & O'Donnell, P. V. J. Virol. 63, 1284–1292 (1989).
Fulton, R., Plumb, M., Shield, L. & Neil, J. C. J. Virol. 64, 1675–1682 (1990).
Brutlag, D. L., Dautricourt, J.-P., Maulik, S. & Relph, J. Comput. appl. Biosci. (in the press).
Dorsett, D. L., liana, K. & Winocour, E. J. Virol. 48, 218–228 (1983).
Goff, S. P., Tracktman, P. & Baltimore, D. J. Virol. 38, 239–248 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dewhurst, S., Embretson, J., Anderson, D. et al. Sequence analysis and acute pathogenicity of molecularly cloned SIVSMM-PBj14. Nature 345, 636–640 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1038/345636a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/345636a0
This article is cited by
-
In vitro inhibitory effect of maraviroc on the association of the simian immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein with CCR5
Virus Genes (2021)
-
Interaction between Nef and INI1/SMARCB1 augments replicability of HIV-1 in resting human peripheral blood mononuclear cells
Archives of Virology (2015)
-
HIV-1 Nef-mediated T-cell activation and chemotaxis are decoupled using a HIV-1/SIVpbj1.9. chimeric nef variant
Archives of Virology (2013)
-
Mutation of a diacidic motif in SIV-PBj Nef impairs T-cell activation and enteropathic disease
Retrovirology (2011)
-
Pathogenic infection of Macaca nemestrinawith a CCR5-tropic subtype-C simian-human immunodeficiency virus
Retrovirology (2009)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.