Abstract
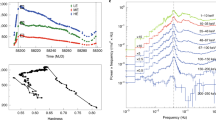
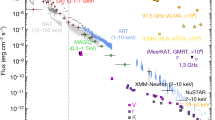
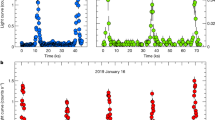
THE binary system Cygnus X-1 is thought to contain a black hole that accretes matter from an O-type supergiant companion. Gravitational energy of the matter in the accretion disk is transformed to thermal energy, resulting in the emission of X-rays. These are emitted in successive bursts ('shots')1. Here we demonstrate the existence of a time delay between X-rays in different energy ranges; this is manifest as a double-peaked structure in the phase lag between two X-ray energy ranges for Fourier periods between 0.2 and 20 s. Taken together with our analysis of the power density spectrum, this indicates that shots tend to occur with two preferred durations and that the X-ray energy spectrum becomes harder as the shot progresses. This is consistent with an accretion model in which clumps of matter in the disk have two preferred sizes, and are heated by the release of gravitational energy as they drift from the outer to the inner region of the disk before disappearing into the black hole.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Terrell, N. J. Astrophys. J. 174, L35–L41 (1972).
Oda, M. Space Sci. Rev. 20, 757–813 (1977).
Liang, E. P. & Nolan, P. L. Space Sci. Rev. 38, 353–384 (1984).
Miyamoto, S., Kitamoto, S., Mitsuda, K. & Dotani, T. Nature 336, 450–452 (1988).
Shapiro, S. L., Lightman, A. P. & Eardley, D. M. Astrophys. J. 204, 187–199 (1976).
Sunyaev, R. A. & Trumper, J. Nature 279, 506–508 (1979).
Makino, M. & Astro-C team. Astrophys. Lett. 25, 223–233 (1987).
Turner, M. J. L. et al. Publs astr. Soc. Japan 41, 345–372 (1989).
Van der Klis, M. et al. Astrophys. J. 319, L13–L18 (1987).
Nolan, P. L. et al. Astrophys. J. 246, 494–501 (1981).
Kitamoto, S., Miyamoto, S. & Yamamoto, S. Publs. astr. Soc. Japan 41, 81–95 (1989).
Bendat, J. S. & Piersol, A. G. Random Data: Analysis and Measurement Procedures (Wiley, New York, 1971).
Meekins, J. F. et al. Astrophys. J. 278, 288–297 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyamoto, S., Kitamoto, S. X-ray time variations from Cygnus X-1 and implications for the accretion process. Nature 342, 773–774 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1038/342773a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/342773a0
This article is cited by
-
The corona contracts in a black-hole transient
Nature (2019)
-
A study of the cross-correlation and time lag in black hole X-ray binary XTE J1859+226
Astrophysics and Space Science (2017)
-
Modelling Spectral and Timing Properties of Accreting Black Holes: The Hybrid Hot Flow Paradigm
Space Science Reviews (2014)
-
X-ray reverberation around accreting black holes
The Astronomy and Astrophysics Review (2014)
-
Modelling the behaviour of accretion flows in X-ray binaries
The Astronomy and Astrophysics Review (2007)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.