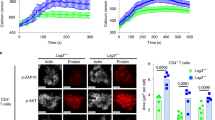
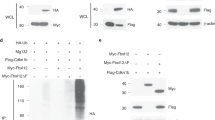
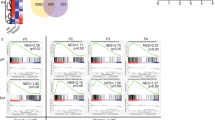
Abstract
THYMIC selection of the developing T-cell repertoire occurs in immature CD4+CD8+ double-positive thymocytes1–3 and is thought to be mediated by signals transduced by T-cell antigen receptor (TCR) molecules and possibly by CD4 and CD8 accessory molecules as well1, 4–6 It is not known, however, which signal-transduction mechanisms function in immature CD4+CD8+ thymocytes on engagement of TCR, CD4 or CD8 molecules. In mature T cells, CD4 and CD8 molecules are each associated with the src-like protein tyrosine kinase p56 lck7, 8 and signals transduced by TCR and CD4 activate tyrosine kinases that phosphory-late TCR-ε chains and other intracellular substrates9, 10. Consequently, we examined whether tyrosine kinases could be similarly activated in immature CD4+CD8+ thymocytes. Unexpectedly, we found that TCR-εchains from CD4+CD8+ thymocytes were already phosphorylated in vivo, and that dephosphorylation of this TCR subunit occurred on removal of CD4+CD8+ cells from their intrathymic environment. Rephosphorylation of TCR-ε in cultured CD4+CD8+ thymocytes occurred rapidly in vitro, either in response to cross-linking of TCR, CD4 or CD8 by specific monoclonal antibodies, or on cell–cell contact. These observations indicate that tyrosine kinases are activated in vivo in immature CD4+CD8+ thymocytes undergoing thymic differentiation and selection. They also indicate that TCR, CD4 and CD8 molecules can function in CD4+CD8+ thymocytes as signalling molecules to activate tyrosine kinases and that phosphorylated TCR-ε serves as a marker of these signalling events.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kisielow, P., Bluthmann, H., Staerz, U. D., Steinmetz, M. & von Boehmer H. Nature 333, 742–746 (1988).
Fowlkes, B. J., Schwartz, R. H. & Pardoll, D. M. Nature 334, 620–623 (1988).
Sha, W. C. et al. Nature 336, 73–76 (1988).
Eichmann, K., Jonsson, J.-I., Falk, I. & Emmrich, F. Eur. J. Immun. 17, 643–650 (1987).
Mizuochi, T., Tentori, L., Sharrow, S. O., Kruisbeek, A. M. & Singer, A. J. exp. med. 168, 437–442 (1988).
McCarthy, S. A., Kruisbeek, A. M., Uppenkamp, I. K., Sharrow, S. O. & Singer, A. Nature 336, 76–79 (1988).
Veillette, A., Bookman, M. A., Horak, E. M. & Bolen, J. B. Cell 55, 301–308 (1988).
Rudd, C. E., Trevillyan, J. M., Dasgupta, J. D., Wong, L. L. & Schlossman, S. F. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 5190–5194 (1988).
Veillette, A., Bookman, M. A., Horak, E. M., Samelson, L. E. & Bolen, J. B. Nature 338, 257–259 (1989).
Hsi, E. D. et al. J. biol. Chem. 264, 10836–10842 (1989).
Kappler, J. W., Roehm, N. & Marrack, P. Cell 49, 273–280 (1987).
Baniyash, M., Garcia-Morales, P., Luong, E., Samelson, L. E. & Klausner, R. D. J. biol. Chem. 263, 18225–18230 (1988).
Kappler, J. W. et al. Cell 49, 263–271 (1987).
Kappler, J. W., Staerz, U., White, J. & Marrack, P. C. Nature 332, 35–40 (1988).
MacDonald, H. R. et al. Nature 332, 40–45 (1988).
Pullen, A. M., Marrack, P. & Kappler, J. W. Nature 335, 796–801 (1988).
Abe, R., Vacchio, M. S., Fox, B. & Hodes, R. Nature 335, 827–830 (1988).
Havran, W. L. et al. Nature 330, 170–173 (1987).
Finkel, T. H., McDuffie, M., Kappler, J. W., Marrack, P. & Cambier, J. C. Nature 330, 179–181 (1987).
Samelson, L. E., Patel, M. D., Weissman, A. M., Harford, J. B. & Klausner, R. D. Cell 46, 1083–1090 (1986).
Staerz, U. D., Rammensee, H.-G., Benedetto, J. D. & Bevan, M. J. J. Immun. 134, 3994–4000 (1985).
Leo, O., Foo, M., Sachs, D. H., Samelson, L. E. & Bluestone, J. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 1374–1378 (1987).
Kappler, J., White, J., Weggman, D., Mustain, E. & Marrack, P. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 3604–3607 (1982).
Kubo, R. T., Born, W., Kappler, J. W., Marrack, P. & Pigeon, M. J. Immun. 142, 2736–2742 (1989).
Dialynas, D. P. et al. Immunol. Rev. 74, 29–56 (1983).
Ledbetter, J. A. & Herzenberg, L. A. Immunol. Rev. 47, 63–90 (1979).
Springer, T., Galfre, G., Secher, D. S. & Milstein, C. Eur. J. Immun. 8, 539–551 (1978).
Kanagawa, O., Palmer, E. & Bill, J. Cellular Immun. 119, 421–426 (1989).
Leo, O., Foo, M., Segal, D. M., Shevach, E., & Bluestone, J. A. J. Immun. 139, 1214–1222 (1987).
Pierres, A. et al. J. Immun. 132, 2775–2782 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakayama, T., Singer, A., Hsi, E. et al. Intrathymic signalling in immature CD4+ CD8+ thymocytes results in tyrosine phosphorylation of the T-cell receptor zeta chain. Nature 341, 651–654 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1038/341651a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/341651a0
This article is cited by
-
Insights into the initiation of TCR signaling
Nature Immunology (2014)
-
SLAP deficiency increases TCR avidity leading to altered repertoire and negative selection of cognate antigen-specific CD8+ T cells
Immunologic Research (2013)
-
Tonic ubiquitylation controls T-cell receptor:CD3 complex expression during T-cell development
The EMBO Journal (2010)
-
Maintaining the norm: T-cell homeostasis
Nature Reviews Immunology (2002)
-
CD4+ T cell survival is not directly linked to self-MHC–induced TCR signaling
Nature Immunology (2000)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.