Abstract
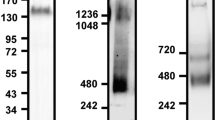
THE leukocyte adhesion molecule LFA-1 mediates a wide range of lymphocyte, monocyte, natural killer cell, and granulocyte interactions with other cells in immunity and inflammation1,2. LFA-1 (CD 1 la/CD 18) is a receptor for intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1, CD54), a surface molecule which is constitu-tively expressed on some tissues and induced on others in inflammation3–5. Induction of ICAM-1 on epithelial cells, endothelial cells and fibroblasts mediates LFA-1-dependent adhesion of lymphocytes4,6,7. Several lines of evidence have suggested the existence of a second LFA-1 ligand: homotypic adhesion of one cell line was inhibited by a monoclonal antibody to LFA-1, but not by one to ICAM-18; there exists an LFA-1-dependent, ICAM-1-indepen-dent pathway of adhesion to endothelial cells6; and also, there are some types of target cells in which LFA-1-dependent T-lymphocyte adhesion and lysis are independent of ICAM-19. We have cloned this second ligand, designated ICAM-2, using a novel method for identifying ligands of adhesion molecules. ICAM-2 is an integral membrane protein with two immunoglobulin-like domains, whereas ICAM-1 has five10,11. Remarkably, ICAM-2 is much more closely related to the two most N-terminal domains of ICAM-1 (34% identity) than either ICAM-1 or ICAM-2 is to other members of the immunoglobulin superfamily, demonstrating the existence of a subfamily of immunoglobulin-like ligands that bind the same integrin receptor.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Springer, T. A., Dustin, M. L., Kishimoto, T. K. & Marlin, S. D. A Rev. Immun. 5, 223–252 (1987).
Kishimoto, T. K. et al. Adv. Immun. (in the press).
Marlin, S. D. & Springer, T. A. Cell 51, 813–819 (1987).
Dustin, M. L., Rothlein, R., Bhan, A. K., Dinarello, C. A. & Springer, T. A. J. Immun. 137, 245–254 (1986).
Dustin, M. L., Staunton, D. E. & Springer, T. A. Immun. Today, 9, 213–215 (1988).
Dustin, M. L. & Springer, T. A. J. Cell Biol. 107, 321–331 (1988).
Dustin, M. L., Singer, K. H., Tuck, D. T. & Springer, T. A. J. exp. Med. 167, 1323–1340 (1988).
Rothlein, R., Dustin, M. L., Marlin, S. D. & Springer, T. A. J. Immun. 137, 1270–1274 (1986).
Makgoba, M. W. et al. Eur. J. Immun. 18, 637–640 (1988).
Staunton, D. E., Marlin, S. D., Stratowa, C., Dustin, M. L. & Springer, T. A. Cell 52, 925–933 (1988).
Simmons, D., Makgoba, M. W. & Seed, N. Nature 331, 624–627 (1988).
Seed, B. & Aruffo, A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 3365–3369 (1987).
Wickens, M. & Stephenson, P. Science 226, 1045–1051 (1984).
Kyte, J. & Doolittle, R. F. J. molec. Biol. 157, 105–132 (1982).
von Heijne, G. Nucleic Acids Res. 14, 4683–4690 (1986).
Cunningham, B. A. et al. Science 236, 799–806 (1987).
Salzer, J. L., Holmes, W. P. & Colman, D. R. J. cell. Biol. 104, 957–965 (1987).
Davignon, D., Martz, E., Reynolds, T., Kurzinger, K. & Springer, T. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 4535–4539 (1981).
Hynes, R. O. Cell 48, 549–554 (1987).
Ruoslahti, E. & Pierschbacher, M. D. Science 238, 491–497 (1987).
Staunton, D. E. et al. Cell 56, 849–853 (1989).
Greve, J. M. et al. Cell 56, 839–847 (1989).
Makgoba, M. W. et al. Nature 331, 86–88 (1988).
Larson, R. S., Corbi, A. L., Berman, L. & Springer, T. A. J. Cell Biol. 108, 703–712 (1989).
Seed, B. Nature 329, 840–842 (1987).
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E. F. & Sambrook, J. in Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, 1982).
Kingston, R. E. in Current Protocols in Molecular Biology 901–996 (Greene Publishing Associates, 1987).
Hirt, B. J. molec. Biol. 26, 365–369 (1967).
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S. & Coulson, A. R. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 5463–5467 (1977).
Dayhoff, M. O., Barker, W. C. & Hunt, L. T. Meth. Enzym. 91, 524–545 (1983).
Chou, P. Y. & Fasman, G. D. Biochemistry 13, 211–245 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Staunton, D., Dustin, M. & Springer, T. Functional cloning of ICAM-2, a cell adhesion ligand for LFA-1 homologous to ICAM-1. Nature 339, 61–64 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1038/339061a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/339061a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.