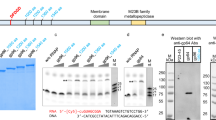
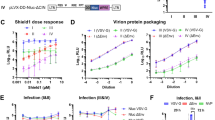
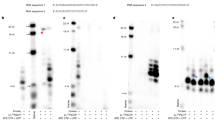
Abstract
Retroviruses and many other types of genetic elements replicate by reverse transcription of RNA (for reviews, see refs 1 and 2). Although structurally and biologically very diverse, such elements carry conserved polymerase genes (pol) that encode proteins required for reverse transcription3. In most cases, the pol gene is preceded by an overlapping gene encoding one or more nucleocapsid proteins4, in a different reading frame. Because both coding regions are represented in a single mRNA, the question arises of how the reverse transcriptase in the alternative reading frame is expressed. In retroviruses and retrotransposons it is expressed as a nucleocapsid-polymerase fusion protein by ribosomal frameshift-ing during translation of the overlapping region5–8. We have examined the mechanism of polymerase biosynthesis in another family of animal viruses that use reverse transcription, the hepatitis B viruses. Genetic and biochemical studies reveal that these viruses do not use ribosomal frameshifting to generate this enzyme, but instead direct translation initiation at an internal initiation (AUG) codon in the polymerase gene.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Varmus, H. E. Nature 314, 583–584 (1985).
Varmus, H. E. Scient. Am. 255, 56–64 (1987).
Toh, H., Hayashida, H. & Miyata, T. Nature 305, 827–829 (1983).
Fuetterer, J. & Hohn, T. Trends biochem. Sci. 12, 92–95 (1987).
Jacks, T. & Varmus, H. E. Science 230, 1237–1242 (1985).
Jacks, T., Townsley, K., Varmus, H. E. & Majors, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 4298–4302 (1987).
Jacks, T. et al. Nature 331, 280–283 (1988).
Clare, J., Belcourt, M. & Farabaugh, P. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 6816–6820 (1988).
Summers, J. & Mason, W. S. Cell 29, 403–415 (1982).
Sprengel, R., Kuhn, C., Will, H. & Schaller, H. J. med. Virol. 15, 323–333 (1985).
Buscher, M., Reiser, W., Will, H. & Schaller, H. Cell 40, 717–724 (1985).
Enders, G. H., Ganem, D. & Varmus, H. E. Cell 42, 297–308 (1985).
Moroy, T. et al. EMBO J. 4, 1507–1514 (1985).
Cattaneo, R., Will, H. & Schaller, H. EMBO J. 3, 2191–2196 (1984).
Will, H. et al Science 231, 594–596 (1986).
Bavand, M. R. & Laub, O. J. Virol. 62, 626–628 (1988).
Mack, D. H., Bloch, W., Nath, N. & Sninsky, J. J. J. Virol. 62, 4786–4790 (1988).
Will, H., Cattaneo, R., Koch, H.-G., Darai, G. & Schaller, H. Nature 299, 740–742 (1982).
Seeger, C., Ganem, D. & Varmus, H. E. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 5849–5852 (1984).
Sprengel, R., Kuhn, C., Manso, C. & Will, H. J. Virol 52, 932–937 (1984).
Aden, D. P., Fogel, A., Plotkin, S., Damjanov, I. & Knowles, B. B. Nature 282, 615–616 (1979).
Nakabayashi, H., Taketa, K., Miyano, K., Yamane, T. & Sato, J. Cancer Res. 42, 3835–3863 (1982).
Galle, P. R., Schlicht, H. J., Fischer, M. & Schaller, H. J. Virol. 62, 1736–1740 (1988).
Hirsch, R., Colgrove, R. & Ganem, D. Virology 167, 136–142 (1988).
Radziwill, G., Zentgraf, H., Schaller, H. & Bosch, V. Virology 163, 123–132 (1988).
Kunkel, T. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 488–492 (1985).
Penswick, J., Hubler, R. & Hohn, T. J. Virol 62, 1460–1463 (1988).
Weiss, R., Teich, N., Varmus, H. & Coffin, J. (eds) RNA Tumor Viruses (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, 1982).
Kozak, M. Cell 47, 481–483 (1986).
Peabody, D. S., Subramani, S. & Berg, P. Molec. cell. Biol. 6, 2704–2711 (1986).
Pelletier, J. & Sonenberg, N. Nature 334, 320–325 (1988).
Felsenstein, K. M. & Goff, S. P. J. Virol. 62, 2179–2182 (1988).
Bernards, A., Rubin, C. M., Westbrook, C. A., Paskind, M. & Baltimore, D. Molec. cell. Biol. 7, 3231–3236 (1987).
Stroehrer, V. L., Jorgensen, E. M. & Garber, R. L. Molec. cell. Biol. 6, 4667–4675 (1986).
Gerlich, W. H. & Robinson, W. S. Cell 21, 801–809 (1980).
Ganem, D. & Varmus, H. E. A. Rev. Biochem. 56, 651–693 (1987).
Bond, V. C. & Wold, B. Molec. cell. Biol. 7, 2286–2293 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, LJ., Pryciak, P., Ganem, D. et al. Biosynthesis of the reverse transcriptase of hepatitis B viruses involves de novo translational initiation not ribosomal frameshifting. Nature 337, 364–368 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1038/337364a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/337364a0
This article is cited by
-
Regulatory mechanisms of viral hepatitis B and C
Journal of Biosciences (2003)
-
Factor VIII, HIV and AIDS in haemophiliacs: An analysis of their relationship
Genetica (1995)
-
Structural features of mag, a gypsy-like retrotransposon ofBombyx mori, with unusual short terminal repeats
Genetica (1994)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.