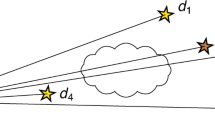
Abstract
Images obtained by the cameras on board the spacecraft encounter-ing comet Halley in March 1986 showed that the dust activity was very non-uniform. Very fine structures (filaments) were observed as well as strong jet-like features originating from active areas1. The dust particle density at large distances (R > 100 km) from the nucleus decreases proportional to 1/R2, that is, the intensity decreases proportional to 1/R as expected for free outflow. Flattening of the profile is evident within several tens of kilometres of the nucleus. As we show here, this can be explained by a model that considers the extended size and non-uniformity of the active region on the surface. A critical scale length, defined by the opening angle of a jet-like feature and the size of the source, can be introduced to describe the flattening. The model is consistent with the observations and provides the basis for studying other mechan-isms such as particle fragmentation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thomas, N. & Keller, H. U. Astr. Aslrophys. 187, 843–846 (1987).
Keller, H. U. et al. Nature 321, 320–326 (1986).
Thomas, N. & Keller, H. U. Eur. Space Ag. spec. Publ. 278, 337–342 (1987).
Toth, I., Szegö, K. & Kondor, A. Eur. Space Ag. spec. Publ. 278, 343–347 (1987).
Keller, H. U. et al. Aslr. Aslrophys. 187, 807–823 (1987).
Sagdeev, R. Z. et al. Eur. Space Ag. spec. Publ. 250, II, 317–326 (1986).
Keller et al. Nature 331, 227–231 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomas, N., Boice, D., Huebner, W. et al. Intensity profiles of dust near extended sources on comet Halley. Nature 332, 51–52 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1038/332051a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/332051a0
This article is cited by
-
Cometary Comae-Surface Links
Space Science Reviews (2020)
-
Distributed Sources in Comets
Space Science Reviews (2008)
-
OSIRIS – The Scientific Camera System Onboard Rosetta
Space Science Reviews (2007)
-
Comets
The Astronomy and Astrophysics Review (1993)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.