Abstract
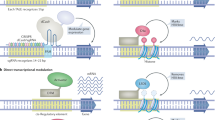
Small-molecule-regulated gene expression offers the promise of titrating the dose and duration of action of DNA-based therapies. To this end, we show that engineered zinc-finger protein transcription factors (ZFP TFs) can be coupled with a drug-inducible regulatory domain to permit small-molecule control of endogenous gene transcription. We constructed a drug-responsive ZFP TF via the fusion of a ZFP DNA-binding domain (DBD) targeting the human VEGF-A gene and an effector domain containing a truncated progesterone receptor ligand-binding domain linked to the NFκB p65 activation domain. Introduction of this engineered ZFP TF into human or murine cells allowed expression of the chromosomal VEGF-A gene to be induced upon addition of mifepristone, a synthetic steroid analog. Mifepristone-dependent VEGF-A induction was rapid, dose-dependent and reversible. Moreover, stable lines expressing the drug-responsive ZFP TF could be maintained in a state of continuous induction for at least 30 days without loss of viability. Potent VEGF-A induction was demonstrated using different engineered ZFP DBDs, thus this approach may represent a general solution to small-molecule regulation of targeted endogenous genes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jamieson AC, Miller JC, Pabo CO . Drug discovery with engineered zinc finger proteins. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2003; 2: 361–368.
Moore M, Ullman C . Recent developments in the engineering of zinc finger proteins. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic 2003; 1: 342–355.
Uil TG, Haisma HJ, Rots MG . Therapeutic modulation of endogenous gene function by agents with designed DNA-sequence specificities. Nucleic Acids Res 2003; 31: 6064–6078.
Rebar EJ . Development of pro-angiogenic engineered transcription factors for the treatment of cardiovascular disease. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2004; 13: 829–839.
Klug A . Towards therapeutic applications of engineered zinc finger proteins. FEBS Lett 2005; 579: 892–894.
Papworth M, Kolasinska P, Minczuk M . Designer zinc-finger proteins and their applications. Gene 2006; 366: 27–38.
Tan S, Guschin D, Davalos A, Lee YL, Snowden AW, Jouvenot Y et al. Zinc-finger protein-targeted gene regulation: genomewide single-gene specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 11997–12002.
Guan X, Stege J, Kim M, Dahmani Z, Fan N, Heifetz P et al. Heritable endogenous gene regulation in plants with designed polydactyl zinc finger transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 13296–13301.
Bartsevich VV, Miller JC, Case CC, Pabo CO . Engineered zinc finger proteins for controlling stem cell fate. Stem Cells 2003; 21: 632–637.
Dai Q, Huang J, Klitzman B, Dong C, Goldschmidt-Clermont PJ, March KL et al. Engineered zinc finger-activating vascular endothelial growth factor transcription factor plasmid DNA induces therapeutic angiogenesis in rabbits with hindlimb ischemia. Circulation 2004; 110: 2467–2475.
Rebar EJ, Huang Y, Hickey R, Nath AK, Meoli D, Nath S et al. Induction of angiogenesis in a mouse model using engineered transcription factors. Nat Med 2002; 8: 1427–1432.
Yu J, Lei L, Liang Y, Hinh L, Hickey RP, Huang Y et al. An engineered VEGF-activating zinc finger protein transcription factor improves blood flow and limb salvage in advanced-age mice. FASEB J 2006; 20: 479–481.
Xie D, Li Y, Reed EA, Odronic SI, Kontos CD, Annex BH . An engineered vascular endothelial growth factor-activating transcription factor induces therapeutic angiogenesis in ApoE knockout mice with hindlimb ischemia. J Vasc Surg 2006; 44: 166–175.
Price SA, Dent C, Duran-Jimenez B, Liang Y, Zhang L, Rebar EJ et al. Gene transfer of an engineered transcription factor promoting expression of VEGF-A protects against experimental diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes 2006; 55: 1847–1854.
Gossen M, Bujard H . Tight control of gene expression in mammalian cells by tetracycline-responsive promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992; 89: 5547–5551.
Burcin MM, BW OM, Tsai SY . A regulatory system for target gene expression. Front Biosci 1998; 3: c1–c7.
Graham LD . Ecdysone-controlled expression of transgenes. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2002; 2: 525–535.
No D, Yao TP, Evans RM . Ecdysone-inducible gene expression in mammalian cells and transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: 3346–3351.
Pollock R, Giel M, Linher K, Clackson T . Regulation of endogenous gene expression with a small-molecule dimerizer. Nat Biotechnol 2002; 20: 729–733.
Beerli RR, Schopfer U, Dreier B, Barbas III CF . Chemically regulated zinc finger transcription factors. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 32617–32627.
Wang Y, O'Malley Jr BW, Tsai SY, O'Malley BW . A regulatory system for use in gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994; 91: 8180–8184.
Wang Y, Xu J, Pierson T, O'Malley BW, Tsai SY . Positive and negative regulation of gene expression in eukaryotic cells with an inducible transcriptional regulator. Gene Therapy 1997; 4: 432–441.
Ye X, Schillinger K, Burcin MM, Tsai SY, O'Malley BW . Ligand-inducible transgene regulation for gene therapy. Methods Enzymol 2002; 346: 551–561.
Vegeto E, Allan GF, Schrader WT, Tsai MJ, McDonnell DP, O'Malley BW . The mechanism of RU486 antagonism is dependent on the conformation of the carboxy-terminal tail of the human progesterone receptor. Cell 1992; 69: 703–713.
Wang Y, Xu J, Pierson T, O'Malley BW, Tsai SY . Positive and negative regulation of gene expression in eukaryotic cells with an inducible transcriptional regulator. Gene Therapy 1997; 4: 432–441.
Ruben SM, Dillon PJ, Schreck R, Henkel T, Chen CH, Maher M et al. Isolation of a rel-related human cDNA that potentially encodes the 65-kD subunit of NF-kappa B. Science 1991; 251: 1490–1493.
Abruzzese RV, Godin D, Burcin M, Mehta V, French M, Li Y et al. Ligand-dependent regulation of plasmid-based transgene expression in vivo. Hum Gene Ther 1999; 10: 1499–1507.
Liu PQ, Rebar EJ, Zhang L, Liu Q, Jamieson AC, Liang Y et al. Regulation of an endogenous locus using a panel of designed zinc finger proteins targeted to accessible chromatin regions. Activation of vascular endothelial growth factor A. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 11323–11334.
Nordstrom JL . The antiprogestin-dependent GeneSwitch system for regulated gene therapy. Steroids 2003; 68: 1085–1094.
Nordstrom JL . Antiprogestin-controllable transgene regulation in vivo. Curr Opin Biotechnol 2002; 13: 453–458.
Pratt WB, Gehring U, Toft DO . Molecular chaperoning of steroid hormone receptors. EXS 1996; 77: 79–95.
Pratt WB, Toft DO . Steroid receptor interactions with heat shock protein and immunophilin chaperones. Endocr Rev 1997; 18: 306–360.
Dennis AP, Haq RU, Nawaz Z . Importance of the regulation of nuclear receptor degradation. Front Biosci 2001; 6: D954–D959.
Abruzzese RV, MacLaughlin FC, Smith LC, Nordstrom JL . Regulated expression of plasmid-based gene therapies. Methods Mol Med 2002; 69: 109–122.
Oligino T, Poliani PL, Wang Y, Tsai SY, O'Malley BW, Fink DJ et al. Drug inducible transgene expression in brain using a herpes simplex virus vector. Gene Therapy 1998; 5: 491–496.
Wang Y, DeMayo FJ, Tsai SY, O'Malley BW . Ligand-inducible and liver-specific target gene expression in transgenic mice. Nat Biotechnol 1997; 15: 239–243.
Pierson TM, Wang Y, DeMayo FJ, Matzuk MM, Tsai SY, Omalley BW . Regulable expression of inhibin A in wild-type and inhibin alpha null mice. Mol Endocrinol 2000; 14: 1075–1085.
Osterwalder T, Yoon KS, White BH, Keshishian H . A conditional tissue-specific transgene expression system using inducible GAL4. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 12596–12601.
Goverdhana S, Puntel M, Xiong W, Zirger JM, Barcia C, Curtin JF et al. Regulatable gene expression systems for gene therapy applications: progress and future challenges. Mol Ther 2005; 12: 189–211.
McCarty DM, Monahan PE, Samulski RJ . Self-complementary recombinant adeno-associated virus (scAAV) vectors promote efficient transduction independently of DNA synthesis. Gene Therapy 2001; 8: 1248–1254.
Liu Z, Auboeuf D, Wong J, Chen JD, Tsai SY, Tsai MJ et al. Coactivator/corepressor ratios modulate PR-mediated transcription by the selective receptor modulator RU486. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 7940–7944.
Gill G, Ptashne M . Negative effect of the transcriptional activator GAL4. Nature 1988; 334: 721–724.
Salghetti SE, Muratani M, Wijnen H, Futcher B, Tansey WP . Functional overlap of sequences that activate transcription and signal ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 3118–3123.
Salghetti SE, Caudy AA, Chenoweth JG, Tansey WP . Regulation of transcriptional activation domain function by ubiquitin. Science 2001; 293: 1651–1653.
Reid G, Hubner MR, Metivier R, Brand H, Denger S, Manu D et al. Cyclic, proteasome-mediated turnover of unliganded and liganded ERalpha on responsive promoters is an integral feature of estrogen signaling. Mol Cell 2003; 11: 695–707.
Zhang L, Spratt SK, Liu Q, Johnstone B, Qi H, Raschke EE et al. Synthetic zinc finger transcription factor action at an endogenous chromosomal site. Activation of the human erythropoietin gene. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 33850–33860.
Snowden AW, Zhang L, Urnov F, Dent C, Jouvenot Y, Zhong X et al. Repression of vascular endothelial growth factor A in glioblastoma cells using engineered zinc finger transcription factors. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 8968–8976.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs Trevor Collingwood, Michael Holmes, Edward Rebar and Sean Brennan for careful reading of the manuscript. We are also grateful to Edward Lanphier for encouragement and support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dent, C., Lau, G., Drake, E. et al. Regulation of endogenous gene expression using small molecule-controlled engineered zinc-finger protein transcription factors. Gene Ther 14, 1362–1369 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302985
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302985
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Aptazyme-embedded guide RNAs enable ligand-responsive genome editing and transcriptional activation
Nature Communications (2017)
-
Compact designer TALENs for efficient genome engineering
Nature Communications (2013)
-
Benzoate X receptor zinc-finger gene switches for drug-inducible regulation of transcription
Gene Therapy (2012)
-
Diabetes mellitus: new challenges and innovative therapies
EPMA Journal (2010)
-
Drug-inducible and simultaneous regulation of endogenous genes by single-chain nuclear receptor-based zinc-finger transcription factor gene switches
Gene Therapy (2008)