Abstract
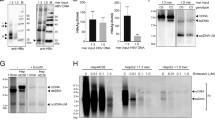
RNA interference (RNAi) was reported to block hepatitis B virus (HBV) gene expression and replication in vitro and in vivo. However, it remains a technical challenge for RNAi-based therapy to achieve long-term and complete inhibition effects in chronic HBV infection, which presumably requires more extensive and uniform transduction of the whole infected hepatocytes. To increase the in vivo transfection efficiency in liver, we used a double-stranded adeno-associated virus 8-pseudotyped vector (dsAAV2/8) to deliver shRNA. HBV transgenic mice were used as an animal model to evaluate the inhibition effects of the RNAi-based gene therapy. A single administration of dsAAV2/8 vector, carrying HBV-specific shRNA, effectively suppressed the steady level of HBV protein, mRNA and replicative DNA in liver of HBV transgenic mice, leading to up to 2–3 log10 decrease in HBV load in the circulation. Significant HBV suppression sustained for at least 120 days after vector administration. The therapeutic effect of shRNA was target sequence dependent and did not involve activation of interferon. These results underscore the potential for developing RNAi-based therapy by dsAAV2/8 vector to treat HBV chronic infection, and possibly other persistent liver infections as well.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ganem D, Prince AM . Hepatitis B virus infection – natural history and clinical consequences. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: 1118–1129.
Dienstag JL, Perrillo RP, Schiff ER, Bartholomew M, Vicary C, Rubin M . A preliminary trial of lamivudine for chronic hepatitis B infection. N Engl J Med 1995; 333: 1657–1661.
Hadziyannis SJ, Tassopoulos NC, Heathcote EJ, Chang TT, Kitis G, Rizzetto M et al. Long-term therapy with adefovir dipivoxil for HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 2673–2681.
Liaw YF, Sung JJ, Chow WC, Farrell G, Lee CZ, Yuen H et al. Lamivudine for patients with chronic hepatitis B and advanced liver disease. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 1521–1531.
Marcellin P, Lau GK, Bonino F, Farci P, Hadziyannis S, Jin R et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a alone, lamivudine alone, and the two in combination in patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 1206–1217.
Manesis EK, Hadziyannis SJ . Interferon alpha treatment and retreatment of hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2001; 121: 101–109.
Hannon GJ . RNA interference. Nature 2002; 418: 244–251.
Sharp PA . RNAi and double-strand RNA. Genes Dev 1999; 13: 139–141.
Waterhouse PM, Wang MB, Lough T . Gene silencing as an adaptive defence against viruses. Nature 2001; 411: 834–842.
Lu R, Maduro M, Li F, Li HW, Broitman-Maduro G, Li WX et al. Animal virus replication and RNAi-mediated antiviral silencing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 2005; 436: 1040–1043.
Wilkins C, Dishongh R, Moore SC, Whitt MA, Chow M, Machaca K . RNA interference is an antiviral defence mechanism in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 2005; 436: 1044–1047.
Stevenson M . Dissecting HIV-1 through RNA interference. Nat Rev Immunol 2003; 3: 851–858.
Radhakrishnan SK, Layden TJ, Gartel AL . RNA interference as a new strategy against viral hepatitis. Virology 2004; 323: 173–181.
Colbere-Garapin F, Blondel B, Saulnier A, Pelletier I, Labadie K . Silencing viruses by RNA interference. Microbes Infect 2005; 7: 767–775.
Giladi H, Ketzinel-Gilad M, Rivkin L, Felig Y, Nussbaum O, Galun E . Small interfering RNA inhibits hepatitis B virus replication in mice. Mol Ther 2003; 8: 769–776.
Klein C, Bock CT, Wedemeyer H, Wustefeld T, Locarnini S, Dienes HP et al. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication in vivo by nucleoside analogues and siRNA. Gastroenterology 2003; 125: 9–18.
McCaffrey AP, Nakai H, Pandey K, Huang Z, Salazar FH, Xu H et al. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus in mice by RNA interference. Nat Biotechnol 2003; 21: 639–644.
Morrissey DV, Blanchard K, Shaw L, Jensen K, Lockridge JA, Dickinson B et al. Activity of stabilized short interfering RNA in a mouse model of hepatitis B virus replication. Hepatology 2005; 41: 1349–1356.
Morrissey DV, Lockridge JA, Shaw L, Blanchard K, Jensen K, Breen W et al. Potent and persistent in vivo anti-HBV activity of chemically modified siRNAs. Nat Biotechnol 2005; 23: 1002–1007.
Uprichard SL, Boyd B, Althage A, Chisari FV . Clearance of hepatitis B virus from the liver of transgenic mice by short hairpin RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 773–778.
Carmona S, Ely A, Crowther C, Moolla N, Salazar FH, Marion PL et al. Effective Inhibition of HBV Replication in vivo by Anti-HBx Short Hairpin RNAs. Mol Ther 2006; 13: 411–421.
Cavanaugh VJ, Guidotti LG, Chisari FV . Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication during adenovirus and cytomegalovirus infections in transgenic mice. J Virol 1998; 72: 2630–2637.
St George JA . Gene therapy progress and prospects: adenoviral vectors. Gene Therapy 2003; 10: 1135–1141.
Raper SE, Yudkoff M, Chirmule N, Gao GP, Nunes F, Haskal ZJ et al. A pilot study of in vivo liver-directed gene transfer with an adenoviral vector in partial ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. Hum Gene Ther 2002; 13: 163–175.
Li C, Bowles DE, van Dyke T, Samulski RJ . Adeno-associated virus vectors: potential applications for cancer gene therapy. Cancer Gene Ther 2005; 12: 913–925.
Carter BJ . Adeno-associated virus vectors in clinical trials. Hum Gene Ther 2005; 16: 541–550.
Miao CH, Nakai H, Thompson AR, Storm TA, Chiu W, Snyder RO et al. Nonrandom transduction of recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors in mouse hepatocytes in vivo: cell cycling does not influence hepatocyte transduction. J Virol 2000; 74: 3793–3803.
Chirmule N, Propert K, Magosin S, Qian Y, Qian R, Wilson J . Immune responses to adenovirus and adeno-associated virus in humans. Gene Ther 1999; 6: 1574–1583.
Gao GP, Alvira MR, Wang L, Calcedo R, Johnston J, Wilson JM . Novel adeno-associated viruses from rhesus monkeys as vectors for human gene therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 11854–11859.
Lebherz C, Gao G, Louboutin JP, Millar J, Rader D, Wilson JM . Gene therapy with novel adeno-associated virus vectors substantially diminishes atherosclerosis in a murine model of familial hypercholesterolemia. J Gene Med 2004; 6: 663–672.
Sun B, Zhang H, Franco LM, Young SP, Schneider A, Bird A et al. Efficacy of an adeno-associated virus 8-pseudotyped vector in glycogen storage disease type II. Mol Ther 2005; 11: 57–65.
Sarkar R, Tetreault R, Gao G, Wang L, Bell P, Chandler R et al. Total correction of hemophilia A mice with canine FVIII using an AAV 8 serotype. Blood 2004; 103: 1253–1260.
Wang L, Calcedo R, Nichols TC, Bellinger DA, Dillow A, Verma IM et al. Sustained correction of disease in naive and AAV2-pretreated hemophilia B dogs: AAV2/8-mediated, liver-directed gene therapy. Blood 2005; 105: 3079–3086.
McCarty DM, Monahan PE, Samulski RJ . Self-complementary recombinant adeno-associated virus (scAAV) vectors promote efficient transduction independently of DNA synthesis. Gene Therapy 2001; 8: 1248–1254.
Wang Z, Ma HI, Li J, Sun L, Zhang J, Xiao X . Rapid and highly efficient transduction by double-stranded adeno-associated virus vectors in vitro and in vivo. Gene Therapy 2003; 10: 2105–2111.
Ganem D, Schneider RJ . Hepadnaviridae: the viruses and their replication. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM (eds). Fundamental Virology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, 2001, pp 1285–1331.
Wu HL, Huang LR, Huang CC, Lai HL, Liu CJ, Huang YT et al. RNA interference-mediated control of hepatitis B virus and emergence of resistant mutant. Gastroenterology 2005; 128: 708–716.
Chou YC, Jeng KS, Chen ML, Liu HH, Liu TL, Chen YL et al. Evaluation of transcriptional efficiency of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA by reverse transcription-PCR combined with the restriction enzyme digestion method. J Virol 2005; 79: 1813–1823.
Guidotti LG, Borrow P, Hobbs MV, Matzke B, Gresser I, Oldstone MB et al. Viral cross talk: intracellular inactivation of the hepatitis B virus during an unrelated viral infection of the liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: 4589–4594.
Tompkins SM, Lo CY, Tumpey TM, Epstein SL . Protection against lethal influenza virus challenge by RNA interference in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 8682–8686.
Ge Q, Filip L, Bai A, Nguyen T, Eisen HN, Chen J . Inhibition of influenza virus production in virus-infected mice by RNA interference. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 8676–8681.
Bitko V, Musiyenko A, Shulyayeva O, Barik S . Inhibition of respiratory viruses by nasally administered siRNA. Nat Med 2005; 11: 50–55.
Zhang W, Yang H, Kong X, Mohapatra S, San Juan-Vergara H, Hellermann G et al. Inhibition of respiratory syncytial virus infection with intranasal siRNA nanoparticles targeting the viral NS1 gene. Nat Med 2005; 11: 56–62.
Yang PL, Althage A, Chung J, Chisari FV . Hydrodynamic injection of viral DNA: a mouse model of acute hepatitis B virus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 13825–13830.
Morrey JD, Bailey KW, Korba BE, Sidwell RW . Utilization of transgenic mice replicating high levels of hepatitis B virus for antiviral evaluation of lamivudine. Antiviral Res 1999; 42: 97–108.
Julander JG, Sidwell RW, Morrey JD . Characterizing antiviral activity of adefovir dipivoxil in transgenic mice expressing hepatitis B virus. Antiviral Res 2002; 55: 27–40.
Raney AK, Eggers CM, Kline EF, Guidotti LG, Pontoglio M, Yaniv M et al. Nuclear covalently closed circular viral genomic DNA in the liver of hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha-null hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. J Virol 2001; 75: 2900–2911.
Nakai H, Fuess S, Storm TA, Muramatsu S, Nara Y, Kay MA . Unrestricted hepatocyte transduction with adeno-associated virus serotype 8 vectors in mice. J Virol 2005; 79: 214–224.
Thomas CE, Storm TA, Huang Z, Kay MA . Rapid uncoating of vector genomes is the key to efficient liver transduction with pseudotyped adeno-associated virus vectors. J Virol 2004; 78: 3110–3122.
Ren C, Kumar S, Shaw DR, Ponnazhagan S . Genomic stability of self-complementary adeno-associated virus 2 during early stages of transduction in mouse muscle in vivo. Hum Gene Ther 2005; 16: 1047–1057.
McClary H, Koch R, Chisari FV, Guidotti LG . Relative sensitivity of hepatitis B virus and other hepatotropic viruses to the antiviral effects of cytokines. J Virol 2000; 74: 2255–2264.
Davidoff AM, Gray JT, Ng CY, Zhang Y, Zhou J, Spence Y et al. Comparison of the ability of adeno-associated viral vectors pseudotyped with serotype 2, 5, and 8 capsid proteins to mediate efficient transduction of the liver in murine and nonhuman primate models. Mol Ther 2005; 11: 875–888.
Grimm D, Streetz KL, Jopling CL, Storm TA, Pandey K, Davis CR et al. Fatality in mice due to oversaturation of cellular microRNA/short hairpin RNA pathways. Nature 2006; 441: 537–541.
Gao G, Vandenberghe LH, Alvira MR, Lu Y, Calcedo R, Zhou X et al. Clades of Adeno-associated viruses are widely disseminated in human tissues. J Virol 2004; 78: 6381–6388.
Gitlin L, Karelsky S, Andino R . Short interfering RNA confers intracellular antiviral immunity in human cells. Nature 2002; 418: 430–434.
Boden D, Pusch O, Lee F, Tucker L, Ramratnam B . Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 escape from RNA interference. J Virol 2003; 77: 11531–11535.
Xiao X, Li J, Samulski RJ . Production of high-titer recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors in the absence of helper adenovirus. J Virol 1998; 72: 2224–2232.
Acknowledgements
We thank SR Roffler for critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, CC., Ko, TM., Ma, HI. et al. Long-term inhibition of hepatitis B virus in transgenic mice by double-stranded adeno-associated virus 8-delivered short hairpin RNA. Gene Ther 14, 11–19 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302846
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302846
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Advances in designing Adeno-associated viral vectors for development of anti-HBV gene therapeutics
Virology Journal (2021)
-
Sexual dimorphism in hepatitis B and C and hepatocellular carcinoma
Seminars in Immunopathology (2019)
-
MicroRNA miR-204 and miR-1236 inhibit hepatitis B virus replication via two different mechanisms
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Combinatorial RNA Interference Therapy Prevents Selection of Pre-existing HBV Variants in Human Liver Chimeric Mice
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
Inhibition of hepatitis B virus (HBV) gene expression and replication by HBx gene silencing in a hydrodynamic injection mouse model with a new clone of HBV genotype B
Virology Journal (2013)