Abstract
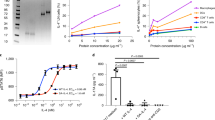
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) is a T-cell-mediated autoimmune disease. Chemokine receptor CCR5 has been shown to be essential for the T-cell recruitment to the inflammatory site in EAE. In this study, we assumed that an immunotoxin directed at CCR5+ cells would be able to reduce the disease activity of EAE. A recombinant immunotoxin, DT390-RANTES-SRα, was constructed in an eukaryotic cell expression plasmid consisting of regulated on activation normal T cells expressed and secreted (RANTES) as the targeting moiety and DT390 as the toxic moiety. DT390-RANTES was expressed in vitro and was highly toxic to activated mouse T cells with the inhibitory concentration 50 at 0.18 ng/ml. To evaluate whether DT390-RANTES was effective in preventing EAE, C57BL/6 mice were immunized with myelin basic protein, emulsified with complete Freund's adjuvant and were treated by injecting cationic liposome-embedded plasmid DNA into the muscle of hind limbs. Mice treated with DT390-RANTES-SRα developed a much milder EAE compared to mice treated with phosphate-buffered saline or the empty plasmid DNA. Much less CCR5+-infiltrating cells were found in the central nervous system in DT390-RANTES-SRα-treated mice than in the control mice. This study indicates that recombinant immunotoxin can be expressed in vivo, and targeting CCR5 can attenuate the disease activity of EAE in mice.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Petry KG, Boullerne AI, Pousset F, Brochet B, Caille JM, Dousset V . Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis animal models for analyzing features of multiple sclerosis [J]. Pathol Biol (Paris) 2000; 48: 47–53.
Stinissen P, Raus J, Zhang J . Autoimmune pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis: role of autoreactive T lymphocytes and new immunotherapeutic strategies [J]. Crit Rev Immunol 1997; 17: 33–75.
Xu B, Scott DW . A novel retroviral gene therapy approach to inhibit specific antibody production and suppress experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis induced by MOG and MBP. Clin Immunol 2004; 111: 47–52.
Namer IJ, Steibel J, Klinguer C, Trifilieff E, Mohr M, Poulet P . Magnetic resonance imaging of PLP-induced experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats. J Neuroimmunol 1998; 92: 22–28.
Jalonen TO, Pulkkinen K, Ukkonen M, Saarela M, Elovaara I . Differential intracellular expression of CCR5 and chemokines in multiple sclerosis subtypes. J Neurol 2002; 249: 576–583.
Garcia-Vicuna R, Gomez-Gaviro MV, Dominguez-Luis MJ, Pec MK, Gonzalez-Alvaro I, Alvaro-Gracia JM et al. CC and CXC chemokine receptors mediate migration, proliferation, and matrix metalloproteinase production by fibroblast-like synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum 2004; 50: 3866–3877.
Emingil G, Atilla G, Huseyinov A . Gingival crevicular fluid monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and RANTES levels in patients with generalized aggressive periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol 2004; 31: 829–834.
Schall TJ, Jongstra J, Dyer BJ, Jorgensen J, Clayberger C, Davis MM et al. A human T cell-specific molecule is a member of a new gene family. J Immunol 1988; 141: 1018–1025.
Li Z, Yu T, Zhao P, Ma J . Immunotoxins and cancer therapy. Cell Mol Immunol 2005; 2: 106–112.
Cui JX, Ji JF, Lv AG, Wu WF . Construction and expression of novel immunotoxin cpIL-4(13D)-PE38KDEL with increased activity. Biochemistry (Moscow) 2005; 70: 62–68.
Foss FM, Bacha P, Osann KE, Demierre MF, Bell T, Kuzel T . Biological correlates of acute hypersensitivity events with DAB(389) IL-2 (denileukin diftitox, ONTAK) in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: decreased frequency and severity with steroid premedication. Clin Lymphoma 2001; 1: 298–302.
Kreitman RJ, Wilson WH, Bergeron K, Raggio M, Stetler-Stevenson M, FitzGerald DJ et al. Efficacy of anti-CD22 recombinant immunotoxin BL22 in chemotherapy-resistant hairy-cell leukemia. N Engl J Med 2001; 345: 241–247.
Baker D, Hankey DJ . Gene therapy in autoimmune, demyelinating disease of the central nervous system. Gene Therapy 2003; 10: 844–853.
Furlan R, Pluchino S, Martino G . The therapeutic use of gene therapy in inflammatory demyelinating diseases of the central nervous system. Curr Opin Neurol 2003; 16: 385–392.
Weiner LP, Louie KA, Atalla LR, Kochounian HH, Du J, Wei W et al. Gene therapy in a murine model for clinical application to multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 2004; 55: 390–399.
Fife BT, Paniagua MC, Lukacs NW, Kunkel SL, Karpus WJ . Selective CC chemokine receptor expression by central nervous system-infiltrating encephalitogenic T cells during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neurosci Res 2001; 66: 705–714.
Diedrichs-Mohring M, Nelson PJ, Proudfoot AE, Thurau SR, Wildner G . The effect of the CC chemokine receptor antagonist Met-RANTES on experimental autoimmune uveitis and oral tolerance. J Neuroimmunol 2005; 164: 22–30.
Panzer U, Reinking RR, Steinmetz OM, Zahner G, Sudbeck U, Fehr S et al. CXCR3 and CCR5 positive T-cell recruitment in acute human renal allograft rejection. Transplantation 2004; 78: 1341–1350.
Schroppel B, Zhang N, Chen P, Zang W, Chen D, Hudkins KL et al. Differential expression of chemokines and chemokine receptors in murine islet allografts: the role of CCR2 and CCR5 signaling pathways. J Am Soc Nephrol 2004; 15: 1853–1861.
Chao K, He D, Yang H, Zhang Z, Lin Q, Guo AG et al. Soluble expression of recombinant immunotoxin against human bladder carcinoma and its anti-tumor activity. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi 2004; 20: 568–571.
Zhang J, Liu YF, Yang SJ, Qiao Q, Cheng H, Zhang CS et al. Primary targeting of recombinant Fv-immunotoxin hscFv(25)-mTNFalpha against hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10: 1872–1875.
Melani C, Figini M, Nicosia D, Luison E, Ramakrishna V, Casorati G et al. Targeting of interleukin 2 to human ovarian carcinoma by fusion with a single-chain Fv of antifolate receptor antibody. Cancer Res 1998; 58: 4146–4154.
Yoshioka Y, Tsutsumi Y, Nakagawa S, Mayumi T . Recent progress on tumor missile therapy and tumor vascular targeting therapy as a new approach. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 2004; 2: 259–270.
Tremblay CL, Giguel F, Guan Y, Chou TC, Takashima K, Hirsch MS . TAK-220, a novel small-molecule CCR5 antagonist, has favorable anti-human immunodeficiency virus interactions with other antiretrovirals in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2005; 49: 3483–3485.
Seibert C, Sakmar TP . Small-molecule antagonists of CCR5 and CXCR4: a promising new class of anti-HIV-1 drugs. Curr Pharm Des 2004; 10: 2041–2062.
Tsamis F, Gavrilov S, Kajumo F, Seibert C, Kuhmann S, Ketas T et al. Analysis of the mechanism by which the small-molecule CCR5 antagonists SCH-351125 and SCH-350581 inhibit human immunodeficiency virus type 1 entry. J Virol 2003; 77: 5201–5208.
Koning FA, Koevoets C, van der Vorst TJ, Schuitemaker H . Sensitivity of primary R5 HTV-1 to inhibition by RANTES correlates with sensitivity to small-molecule R5 inhibitors. Antivir Ther 2005; 10: 231–237.
Misu T, Onodera H, Fujihara K, Matsushima K, Yoshie O, Okita N et al. Chemokine receptor expression on T cells in blood and cerebrospinal fluid at relapse and remission of multiple sclerosis: imbalance of Th1/Th2-associated chemokine signaling. J Neuroimmunol 2001; 114: 207–212.
Deibler GE, Martenson RE, Kies MW . Large scale preparation of myelin basic protein from central nervous system tissue of several mammalian species [J]. Prep Biochem 1972; 2: 139–165.
Thompson J, Hu H, Scharff J, Neville Jr DM . An anti-CD3 single-chain immunotoxin with a truncated diphtheria toxin avoids inhibition by pre-existing antibodies in human blood. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 28037–28041.
Sun X, Zhang ZR . Preparation of lipid–protamine–DNA complexes and evaluation of their transfection efficiencies in vitro. Yao Xue Xue Bao 2004; 39: 792–796.
Wefer J, Harris RA, Lobell A . Protective DNA vaccination against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis is associated with induction of IFNbeta. J Neuroimmunol 2004; 149: 66–76.
Kono DH, Urban JL, Horvath SJ, Ando DG, Saavedra RA, Hood L . Two minor determinants of myelin basic protein induce experimental allergic encephalo-myelitis in SJL/J mice. J Exp Med 1988; 168: 213–227.
Fischer FR, Santambrogio L, Luo Y, Berman MA, Hancock WW, Dorf ME . Modulation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: effect of altered peptide ligand on chemokine and chemokine receptor expression. J Neuroimmunol 2000; 110: 195–208.
Magliozzi R, Columba-Cabezas S, Serafini B, Aloisi F . Intracerebral expression of CXCL13 and BAFF is accompanied by formation of lymphoid follicle-like structures in the meninges of mice with relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 2004; 148: 11–23.
Alheim M, Lazdina U, Milich DR, Sallberg M . Flow cytometric determination of cytokine production and proliferation in hepatitis B core antigen specific murine CD4 cells: lack of correlation between number of cytokine producing cells and cytokine levels in supernatant. J Immunol Methods 2001; 258: 157–167.
Kerttula TO, Collin P, Maki M, Hurme M . Normal T-helper 1/T-helper 2 balance in peripheral blood of coeliac disease patients. Scand J Immunol 1999; 49: 197–202.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Project of Nation Natural Sciences Foundation of China, National 863 projects (2002AA214101), Fund for Creative Research Groups from National Natural Science Foundation of China (30221001) and Applied Basic Project of Sichuan Province (04JY029-002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Y., Li, H., Chen, W. et al. Prevention of murine experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by in vivo expression of a novel recombinant immunotoxin DT390-RANTES. Gene Ther 13, 1351–1359 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302799
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302799
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Amelioration of autoimmune neuroinflammation by the fusion molecule Fn14·TRAIL
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2013)