Abstract
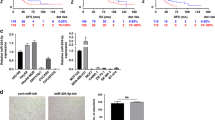
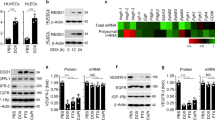
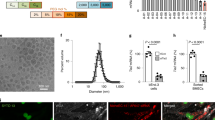
RNA interference (RNAi) entails the potential for novel therapeutic strategies through the silencing of disease-causing genes in vivo. However, recent studies have raised an issue regarding applicable routes of administration for small interfering RNA (siRNA) molecules as therapeutics. In this study, we demonstrate that liposomally formulated siRNA molecules, the so-called siRNA-lipoplexes, but not naked siRNAs, are delivered to the tumor endothelial cells in vivo by microscopy. In addition, functional intracellular delivery of formulated siRNA targeting the tumor suppressor PTEN is shown in endothelial cells of the liver and tumor. Finally, the therapeutic potential of systemically administered siRNACD31-lipoplexes is established by inhibition of tumor growth in two different xenograft mouse models. Our findings corroborate the applicability of this liposomal siRNA delivery technology for inducing RNAi to modulate gene expression levels in angiogenesis-dependent processes. In addition, our results advocate CD31 as a promising therapeutic target for antiangiogenic intervention. Therefore, our study provides a basis for the development of antiangiogenic cancer therapies based on RNAi.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hammond SM . Dicing and slicing the core machinery of the RNA interference pathway. FEBS Lett 2005; 579: 5822–5829.
Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC . Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998; 391: 806–811.
Uprichard SL . The therapeutic potential of RNA interference. FEBS Lett 2005; 579: 5996–6007.
Dykxhoorn DM, Novina CD, Sharp PA . Killing the messenger: short RNAs that silence gene expression. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2003; 4: 457–467.
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Lendeckel W, Yalcin A, Weber K, Tuschl T . Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature 2001; 411: 494–498.
Urban-Klein B, Werth S, Abuharbeid S, Czubayko F, Aigner A . RNAi-mediated gene-targeting through systemic application of polyethylenimine (PEI)-complexed siRNA in vivo. Gene Therapy 2005; 12: 461–466.
Zhang Y, Zhang YF, Bryant J, Charles A, Boado RJ, Pardridge WM . Intravenous RNA interference gene therapy targeting the human epidermal growth factor receptor prolongs survival in intracranial brain cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 3667–3677.
Yano J, Hirabayashi K, Nakagawa S, Yamaguchi T, Nogawa M, Kashimori I et al. Antitumor activity of small interfering RNA/cationic liposome complex in mouse models of cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 7721–7726.
Liang Z, Yoon Y, Votaw J, Goodman MM, Williams L, Shim H . Silencing of CXCR4 blocks breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 967–971.
Duxbury MS, Ito H, Zinner MJ, Ashley SW, Whang EE . EphA2: a determinant of malignant cellular behavior and a potential therapeutic target in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2004; 23: 1448–1456.
Chien PY, Wang J, Carbonaro D, Lei S, Miller B, Sheikh S et al. Novel cationic cardiolipin analogue-based liposome for efficient DNA and small interfering RNA delivery in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Gene Ther 2005; 12: 321–328.
Song E, Zhu P, Lee SK, Chowdhury D, Kussman S, Dykxhoorn DM et al. Antibody mediated in vivo delivery of small interfering RNAs via cell-surface receptors. Nat Biotechnol 2005; 23: 709–717.
Filleur S, Courtin A, Ait-Si-Ali S, Guglielmi J, Merle C, Harel-Bellan A et al. SiRNA-mediated inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor severely limits tumor resistance to antiangiogenic thrombospondin-1 and slows tumor vascularization and growth. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 3919–3922.
Landen Jr CN, Chavez-Reyes A, Bucana C, Schmandt R, Deavers MT, Lopez-Berestein G et al. Therapeutic EphA2 gene targeting in vivo using neutral liposomal small interfering RNA delivery. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 6910–6918.
Leng Q, Mixson AJ . Small interfering RNA targeting Raf-1 inhibits tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Gene Ther 2005; 12: 682–690.
Barron LG, Uyechi LS, Szoka Jr C . Cationic lipids are essential for gene delivery mediated by intravenous administration of lipoplexes. Gene Therapy 1999; 6: 1179–1183.
Liu TG, Yin JQ, Shang BY, Min Z, He HW, Jiang JM et al. Silencing of hdm2 oncogene by siRNA inhibits p53-dependent human breast cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 2004; 11: 748–756.
Nogawa M, Yuasa T, Kimura S, Tanaka M, Kuroda J, Sato K et al. Intravesical administration of small interfering RNA targeting PLK-1 successfully prevents the growth of bladder cancer. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 978–985.
Chae SS, Paik JH, Furneaux H, Hla T . Requirement for sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor-1 in tumor angiogenesis demonstrated by in vivo RNA interference. J Clin Invest 2004; 114: 1082–1089.
Bollerot K, Sugiyama D, Escriou V, Gautier R, Tozer S, Scherman D et al. Widespread lipoplex-mediated gene transfer to vascular endothelial cells and hemangioblasts in the vertebrate embryo. Dev Dyn 2006; 235: 105–114.
Thurston G, McLean JW, Rizen M, Baluk P, Haskell A, Murphy TJ et al. Cationic liposomes target angiogenic endothelial cells in tumors and chronic inflammation in mice. J Clin Invest 1998; 101: 1401–1413.
McLean JW, Fox EA, Baluk P, Bolton PB, Haskell A, Pearlman R et al. Organ-specific endothelial cell uptake of cationic liposome-DNA complexes in mice. Am J Physiol 1997; 273: H387–H404.
Gasparini G, Longo R, Toi M, Ferrara N . Angiogenic inhibitors: a new therapeutic strategy in oncology. Natl Clin Pract Oncol 2005; 2: 562–577.
Willett CG, Boucher Y, di Tomaso E, Duda DG, Munn LL, Tong RT et al. Direct evidence that the VEGF-specific antibody bevacizumab has antivascular effects in human rectal cancer. Natl Med 2004; 10: 145–147.
Kerbel R, Folkman J . Clinical translation of angiogenesis inhibitors. Natl Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 727–739.
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J . The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Natl Med 2003; 9: 669–676.
Watt SM, Gschmeissner SE, Bates PA . PECAM-1: its expression and function as a cell adhesion molecule on hemopoietic and endothelial cells. Leuk Lymphoma 1995; 17: 229–244.
Newman PJ, Berndt MC, Gorski J, White 2nd GC, Lyman S, Paddock C et al. PECAM-1 (CD31) cloning and relation to adhesion molecules of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily. Science 1990; 247: 1219–1222.
Ilan N, Madri JA . PECAM-1: old friend, new partners. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2003; 15: 515–524.
Bergom C, Gao C, Newman PJ . Mechanisms of PECAM-1-mediated cytoprotection and implications for cancer cell survival. Leuk Lymphoma 2005; 46: 1409–1421.
Czauderna F, Fechtner M, Dames S, Aygun H, Klippel A, Pronk GJ et al. Structural variations and stabilising modifications of synthetic siRNAs in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res 2003; 31: 2705–2716.
Santel A, Aleku M, Keil O, Endruschat J, Esche V, Fisch G et al. A novel siRNA-lipoplex technology for RNAi in the mouse vascular endothelium. Gene Therapy 2006, E-pub ahead of print, 20 April 2006; doi:10.1038/sj.gt.3302777.
Stambolic V, Suzuki A, de la Pompa JL, Brothers GM, Mirtsos C, Sasaki T et al. Negative regulation of PKB/Akt-dependent cell survival by the tumor suppressor PTEN. Cell 1998; 95: 29–39.
Klippel A, Escobedo MA, Wachowicz MS, Apell G, Brown TW, Giedlin MA et al. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is sufficient for cell cycle entry and promotes cellular changes characteristic of oncogenic transformation. Mol Cell Biol 1998; 18: 5699–5711.
Vermeulen PB, Verhoeven D, Hubens G, Van Marck E, Goovaerts G, Huyghe M et al. Microvessel density, endothelial cell proliferation and tumour cell proliferation in human colorectal adenocarcinomas. Ann Oncol 1995; 6: 59–64.
Fox SB, Harris AL . Histological quantitation of tumour angiogenesis. Apmis 2004; 112: 413–430.
Uzzan B, Nicolas P, Cucherat M, Perret GY . Microvessel density as a prognostic factor in women with breast cancer: a systematic review of the literature and meta-analysis. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 2941–2955.
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR, Folkman J . Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis – correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med 1991; 324: 1–8.
Stephenson RA, Dinney CP, Gohji K, Ordonez NG, Killion JJ, Fidler IJ . Metastatic model for human prostate cancer using orthotopic implantation in nude mice. J Natl Cancer Inst 1992; 84: 951–957.
Czauderna F, Santel A, Hinz M, Fechtner M, Durieux B, Fisch G et al. Inducible shRNA expression for application in a prostate cancer mouse model. Nucleic Acids Res 2003; 31: e127.
Karagiannis TC, El-Osta A . RNA interference and potential therapeutic applications of short interfering RNAs. Cancer Gene Ther 2005; 12: 787–795.
Hu-Lieskovan S, Heidel JD, Bartlett DW, Davis ME, Triche TJ . Sequence-specific knockdown of EWS-FLI1 by targeted, nonviral delivery of small interfering RNA inhibits tumor growth in a Murine model of metastatic Ewing's Sarcoma. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 8984–8992.
Schiffelers RM, Ansari A, Xu J, Zhou Q, Tang Q, Storm G et al. Cancer siRNA therapy by tumor selective delivery with ligand-targeted sterically stabilized nanoparticle. Nucleic Acids Res 2004; 32: e149.
Solowiej A, Biswas P, Graesser D, Madri JA . Lack of platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 attenuates foreign body inflammation because of decreased angiogenesis. Am J Pathol 2003; 162: 953–962.
Fleming I, Fisslthaler B, Dixit M, Busse R . Role of PECAM-1 in the shear-stress-induced activation of Akt and the endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) in endothelial cells. J Cell Sci 2005; 118: 4103–4111.
Limaye V, Li X, Hahn C, Xia P, Berndt MC, Vadas MA et al. Sphingosine kinase-1 enhances endothelial cell survival through a PECAM-1-dependent activation of PI-3K/Akt and regulation of Bcl-2 family members. Blood 2005; 105: 3169–3177.
Oliner J, Min H, Leal J, Yu D, Rao S, You E et al. Suppression of angiogenesis and tumor growth by selective inhibition of angiopoietin-2. Cancer Cell 2004; 6: 507–516.
Klippel A, Escobedo JA, Hirano M, Williams LT . The interaction of small domains between the subunits of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase determines enzyme activity. Mol Cell Biol 1994; 14: 2675–2685.
Leenders F, Mopert K, Schmiedeknecht A, Santel A, Czauderna F, Aleku M et al. PKN3 is required for malignant prostate cell growth downstream of activated PI 3-kinase. EMBO J 2004; 23: 3303–3313.
Acknowledgements
We thank Hüseyin Aygün (BioSpring, Frankfurt a. M., Germany) for providing high-quality siRNA molecules and Ralf Sägebarth for bioinformatic design of siRNA sequences. We acknowledge Katharina Ahrens for critically reading the manuscript. This study was supported in part by a grant from the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (Grant #0313066E), the Senatsverwaltung Berlin (Grant #SenBB3066E) and the European Union (European Fond for regional Development).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Gene Therapy website (http://www.nature.com/gt)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santel, A., Aleku, M., Keil, O. et al. RNA interference in the mouse vascular endothelium by systemic administration of siRNA-lipoplexes for cancer therapy. Gene Ther 13, 1360–1370 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302778
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302778
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Lipid Nanoparticles for Nucleic Acid Delivery to Endothelial Cells
Pharmaceutical Research (2023)
-
Delivery of siRNA to Endothelial Cells In Vivo Using Lysine/Histidine Oligopeptide-Modified Poly(β-amino ester) Nanoparticles
Cardiovascular Engineering and Technology (2021)
-
Liver-specific Bid silencing inhibits APAP-induced cell death in mice
Apoptosis (2019)
-
Therapeutic siRNA targeting endothelial KDR decreases portosystemic collateralization in portal hypertension
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Cancer nanomedicine: progress, challenges and opportunities
Nature Reviews Cancer (2017)