Abstract
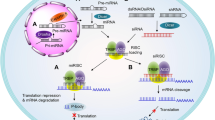
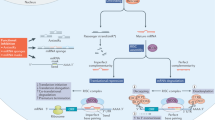
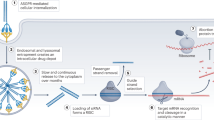
As soon as RNA interference (RNAi) was found to work in mammalian cells, research quickly focused on harnessing this powerful endogenous and specific mechanism of gene silencing for human therapy. RNAi uses small RNAs, less than 30 nucleotides in length, to suppress expression of genes with complementary sequences. Two strategies can introduce small RNAs into the cytoplasm of cells, where they are active – a drug approach where double-stranded RNAs are administered in complexes designed for intracellular delivery and a gene therapy approach to express precursor RNAs from viral vectors. Phase I clinical studies have already begun to test the therapeutic potential of small RNA drugs that silence disease-related genes by RNAi. This review will discuss progress in developing and testing small RNAi-based drugs and potential obstacles.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahante JE, Daul AL, Li M, Volk ML, Tennessen JM, Miller EA et al. The Caenorhabditis elegans hunchback-like gene lin-57/hbl-1 controls developmental time and is regulated by microRNAs. Dev Cell 2003; 4: 625–637.
Brennecke J, Hipfner DR, Stark A, Russell RB, Cohen SM . Bantam encodes a developmentally regulated microRNA that controls cell proliferation and regulates the proapoptotic gene hid in Drosophila. Cell 2003; 113: 25–36.
Schramke V, Allshire R . Hairpin RNAs and retrotransposon LTRs effect RNAi and chromatin-based gene silencing. Science 2003; 301: 1069–1074.
Tabara H, Sarkissian M, Kelly WG, Fleenor J, Grishok A, Timmons L et al. The rde-1 gene, RNA interference, and transposon silencing in C. elegans. Cell 1999; 99: 123–132.
Djikeng A, Shi H, Tschudi C, Ullu E . RNA interference in Trypanosoma brucei: cloning of small interfering RNAs provides evidence for retroposon-derived 24–26-nucleotide RNAs. RNA 2001; 7: 1522–1530.
Aravin AA, Lagos-Quintana M, Yalcin A, Zavolan M, Marks D, Snyder B et al. The small RNA profile during Drosophila melanogaster development. Dev Cell 2003; 5: 337–350.
Dykxhoorn DM, Novina CD, Sharp PA . Killing the messenger: short RNAs that silence gene expression. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2003; 4: 457–467.
Dykxhoorn DM, Lieberman J . The silent revolution: RNA interference as basic biology, research tool, and therapeutic. Annu Rev Med 2005; 56: 401–423.
Doench JG, Sharp PA . Specificity of microRNA target selection in translational repression. Genes Dev 2004; 18: 504–511.
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP . Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 2005; 120: 15–20.
Parker JS, Roe SM, Barford D . Structural insights into mRNA recognition from a PIWI domain-siRNA guide complex. Nature 2005; 434: 663–666.
Parker JS, Roe SM, Barford D . Crystal structure of a PIWI protein suggests mechanisms for siRNA recognition and slicer activity. EMBO J 2004; 23: 4727–4737.
Ma JB, Yuan YR, Meister G, Pei Y, Tuschl T, Patel DJ . Structural basis for 5′-end-specific recognition of guide RNA by the A. fulgidus Piwi protein. Nature 2005; 434: 666–670.
Elbashir SM, Martinez J, Patkaniowska A, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T . Functional anatomy of siRNAs for mediating efficient RNAi in Drosophila melanogaster embryo lysate. EMBO J 2001; 20: 6877–6888.
Tuschl T, Zamore PD, Lehmann R, Bartel DP, Sharp PA . Targeted mRNA degradation by double-stranded RNA in vitro. Genes Dev 1999; 13: 3191–3197.
Zamore PD, Tuschl T, Sharp PA, Bartel DP . RNAi: double-stranded RNA directs the ATP-dependent cleavage of mRNA at 21 to 23 nucleotide intervals. Cell 2000; 101: 25–33.
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Lendeckel W, Yalcin A, Weber K, Tuschl T . Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature 2001; 411: 494–498.
Bertrand JR, Pottier M, Vekris A, Opolon P, Maksimenko A, Malvy C . Comparison of antisense oligonucleotides and siRNAs in cell culture and in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2002; 296: 1000–1004.
Hutvagner G, Zamore PD . A microRNA in a multiple-turnover RNAi enzyme complex. Science 2002; 297: 2056–2060.
Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R, Agami R . Stable suppression of tumorigenicity by virus-mediated RNA interference. Cancer Cell 2002; 2: 243–247.
Ding H, Schwarz DS, Keene A, Affar el B, Fenton L, Xia X et al. Selective silencing by RNAi of a dominant allele that causes amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Aging Cell 2003; 2: 209–217.
Miller VM, Xia H, Marrs GL, Gouvion CM, Lee G, Davidson BL et al. Allele-specific silencing of dominant disease genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 7195–7200.
Persengiev SP, Zhu X, Green MR . Nonspecific, concentration-dependent stimulation and repression of mammalian gene expression by small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). RNA 2004; 10: 12–18.
Sledz CA, Holko M, de Veer MJ, Silverman RH, Williams BR . Activation of the interferon system by short-interfering RNAs. Nat Cell Biol 2003; 5: 834–839.
Bridge AJ, Pebernard S, Ducraux A, Nicoulaz AL, Iggo R . Induction of an interferon response by RNAi vectors in mammalian cells. Nat Genet 2003; 34: 263–264.
Dorsett Y, Tuschl T . siRNAs: applications in functional genomics and potential as therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2004; 3: 318–329.
Kariko K, Bhuyan P, Capodici J, Ni H, Lubinski J, Friedman H et al. Exogenous siRNA mediates sequence-independent gene suppression by signaling through toll-like receptor 3. Cells Tissues Organs 2004; 177: 132–138.
Kariko K, Bhuyan P, Capodici J, Weissman D . Small interfering RNAs mediate sequence-independent gene suppression and induce immune activation by signaling through toll-like receptor 3. J Immunol 2004; 172: 6545–6549.
Hornung V, Guenthner-Biller M, Bourquin C, Ablasser A, Schlee M, Uematsu S et al. Sequence-specific potent induction of IFN-alpha by short interfering RNA in plasmacytoid dendritic cells through TLR7. Nat Med 2005; 11: 263–270.
Sioud M . Induction of inflammatory cytokines and interferon responses by double-stranded and single-stranded siRNAs is sequence-dependent and requires endosomal localization. J Mol Biol 2005; 348: 1079–1090.
Judge AD, Sood V, Shaw JR, Fang D, McClintock K, MacLachlan I . Sequence-dependent stimulation of the mammalian innate immune response by synthetic siRNA. Nat Biotechnol 2005; 23: 457–462.
Saxena S, Jonsson ZO, Dutta A . Small RNAs with imperfect match to endogenous mRNA repress translation. Implications for off-target activity of small inhibitory RNA in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 44312–44319.
Jackson AL, Bartz SR, Schelter J, Kobayashi SV, Burchard J, Mao M et al. Expression profiling reveals off-target gene regulation by RNAi. Nat Biotechnol 2003; 21: 635–637.
Doench JG, Petersen CP, Sharp PA . siRNAs can function as miRNAs. Genes Dev 2003; 17: 438–442.
Ambros V . The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 2004; 431: 350–355.
Bartel DP . MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004; 116: 281–297.
Khvorova A, Reynolds A, Jayasena SD . Functional siRNAs and miRNAs exhibit strand bias. Cell 2003; 115: 209–216.
Schwarz DS, Hutvagner G, Du T, Xu Z, Aronin N, Zamore PD . Asymmetry in the assembly of the RNAi enzyme complex. Cell 2003; 115: 199–208.
Reynolds A, Leake D, Boese Q, Scaringe S, Marshall WS, Khvorova A . Rational siRNA design for RNA interference. Nat Biotechnol 2004; 22: 326–330.
Fedorov Y, King A, Anderson E, Karpilow J, Ilsley D, Marshall W et al. Different delivery methods – different expression profiles. Nat Methods 2005; 2: 241.
Heidel JD, Hu S, Liu XF, Triche TJ, Davis ME . Lack of interferon response in animals to naked siRNAs. Nat Biotechnol 2004; 22: 1579–1582.
Bitko V, Musiyenko A, Shulyayeva O, Barik S . Inhibition of respiratory viruses by nasally administered siRNA. Nat Med 2005; 11: 50–55.
Lu S, Cullen BR . Adenovirus VA1 noncoding RNA can inhibit small interfering RNA and microRNA biogenesis. J Virol 2004; 78: 12868–12876.
Song E, Lee SK, Dykxhoorn DM, Novina C, Zhang D, Crawford K et al. Sustained small interfering RNA-mediated human immunodeficiency virus type 1 inhibition in primary macrophages. J Virol 2003; 77: 7174–7181.
Lee SK, Dykxhoorn DM, Kumar P, Ranjbar S, Song E, Maliszewski LE et al. Lentiviral delivery of short hairpin RNAs protects CD4 T cells from multiple clades and primary isolates of HIV. Blood 2005; 106: 818–826.
Kim DH, Behlke MA, Rose SD, Chang MS, Choi S, Rossi JJ . Synthetic dsRNA Dicer substrates enhance RNAi potency and efficacy. Nat Biotechnol 2005; 23: 222–226.
Brown KM, Chu CY, Rana TM . Target accessibility dictates the potency of human RISC. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2005; 12: 469–470.
Overhoff M, Alken M, Far RK, Lemaitre M, Lebleu B, Sczakiel G et al. Local RNA target structure influences siRNA efficacy: a systematic global analysis. J Mol Biol 2005; 348: 871–881.
Novina CD, Murray MF, Dykxhoorn DM, Beresford PJ, Riess J, Lee SK et al. siRNA-directed inhibition of HIV-1 infection. Nat Med 2002; 8: 681–686.
Soutschek J, Akinc A, Bramlage B, Charisse K, Constien R, Donoghue M et al. Therapeutic silencing of an endogenous gene by systemic administration of modified siRNAs. Nature 2004; 432: 173–178.
Layzer JM, McCaffrey AP, Tanner AK, Huang Z, Kay MA, Sullenger BA . In vivo activity of nuclease-resistant siRNAs. RNA 2004; 10: 766–771.
Schiffelers RM, Ansari A, Xu J, Zhou Q, Tang Q, Storm G et al. Cancer siRNA therapy by tumor selective delivery with ligand-targeted sterically stabilized nanoparticle. Nucleic Acids Res 2004; 32: e149.
Harborth J, Elbashir SM, Vandenburgh K, Manninga H, Scaringe SA, Weber K et al. Sequence, chemical, and structural variation of small interfering RNAs and short hairpin RNAs and the effect on mammalian gene silencing. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev 2003; 13: 83–105.
Chiu YL, Rana TM . siRNA function in RNAi: a chemical modification analysis. RNA 2003; 9: 1034–1048.
Czauderna F, Fechtner M, Dames S, Aygun H, Klippel A, Pronk GJ et al. Structural variations and stabilising modifications of synthetic siRNAs in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res 2003; 31: 2705–2716.
Dorn G, Patel S, Wotherspoon G, Hemmings-Mieszczak M, Barclay J, Natt FJ et al. siRNA relieves chronic neuropathic pain. Nucleic Acids Res 2004; 32: e49.
Braasch DA, Jensen S, Liu Y, Kaur K, Arar K, White MA et al. RNA interference in mammalian cells by chemically-modified RNA. Biochemistry 2003; 42: 7967–7975.
Morrissey DV, Blanchard K, Shaw L, Jensen K, Lockridge JA, Dickinson B et al. Activity of stabilized short interfering RNA in a mouse model of hepatitis B virus replication. Hepatology 2005; 41: 1349–1356.
Chiu YL, Rana TM . RNAi in human cells: basic structural and functional features of small interfering RNA. Mol Cell 2002; 10: 549–561.
Schwarz DS, Hutvagner G, Haley B, Zamore PD . Evidence that siRNAs function as guides, not primers, in the Drosophila and human RNAi pathways. Mol Cell 2002; 10: 537–548.
Amarzguioui M, Holen T, Babaie E, Prydz H . Tolerance for mutations and chemical modifications in a siRNA. Nucleic Acids Res 2003; 31: 589–595.
Morrissey DV, Lockridge JA, Shaw L, Blanchard K, Jensen K, Breen W et al. Potent and persistent in vivo anti-HBV activity of chemically modified siRNAs. Nat Biotechnol 2005; 23: 1002–1007.
Song E, Lee SK, Wang J, Ince N, Ouyang N, Min J et al. RNA interference targeting Fas protects mice from fulminant hepatitis. Nat Med 2003; 9: 347–351.
McCaffrey AP, Meuse L, Pham TT, Conklin DS, Hannon GJ, Kay MA . RNA interference in adult mice. Nature 2002; 418: 38–39.
McCaffrey AP, Nakai H, Pandey K, Huang Z, Salazar FH, Xu H et al. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus in mice by RNA interference. Nat Biotechnol 2003; 21: 639–644.
Giladi H, Ketzinel-Gilad M, Rivkin L, Felig Y, Nussbaum O, Galun E . Small interfering RNA inhibits hepatitis B virus replication in mice. Mol Ther 2003; 8: 769–776.
Wesche-Soldato DE, Chung CS, Lomas-Neira J, Doughty LA, Gregory SH, Ayala A . In vivo delivery of Caspase 8 or Fas siRNA improves the survival of septic mice. Blood 2005; 106: 2295–2301.
Boutros M, Kiger AA, Armknecht S, Kerr K, Hild M, Koch B et al. Genome-wide RNAi analysis of growth and viability in Drosophila cells. Science 2004; 303: 832–835.
Tabara H, Grishok A, Mello CC . RNAi in C. elegans: soaking in the genome sequence. Science 1998; 282: 430–431.
Stewart SA, Dykxhoorn DM, Palliser D, Mizuno H, Yu EY, An DS et al. Lentivirus-delivered stable gene silencing by RNAi in primary cells. RNA 2003; 9: 493–501.
Tolentino MJ, Brucker AJ, Fosnot J, Ying GS, Wu IH, Malik G et al. Intravitreal injection of vascular endothelial growth factor small interfering RNA inhibits growth and leakage in a nonhuman primate, laser-induced model of choroidal neovascularization. Retina 2004; 24: 132–138.
Reich SJ, Fosnot J, Kuroki A, Tang W, Yang X, Maguire AM et al. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting VEGF effectively inhibits ocular neovascularization in a mouse model. Mol Vis 2003; 9: 210–216.
Zhang X, Shan P, Jiang D, Noble PW, Abraham NG, Kappas A et al. Small interfering RNA targeting heme oxygenase-1 enhances ischemia-reperfusion-induced lung apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 10677–10684.
Palliser D, Chowdhury D, Wang QY, Lee SJ, Bronson RT, Knipe DM et al. An siRNA-based microbicide protects mice from lethal herpes simplex virus 2 infection. Nature 2005; doi:10.1038/nature04263.
Aharinejad S, Paulus P, Sioud M, Hofmann M, Zins K, Schafer R et al. Colony-stimulating factor-1 blockade by antisense oligonucleotides and small interfering RNAs suppresses growth of human mammary tumor xenografts in mice. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 5378–5384.
Takei Y, Kadomatsu K, Yuzawa Y, Matsuo S, Muramatsu T . A small interfering RNA targeting vascular endothelial growth factor as cancer therapeutics. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 3365–3370.
Minakuchi Y, Takeshita F, Kosaka N, Sasaki H, Yamamoto Y, Kouno M et al. Atelocollagen-mediated synthetic small interfering RNA delivery for effective gene silencing in vitro and in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res 2004; 32: e109.
Leng Q, Mixson AJ . Small interfering RNA targeting Raf-1 inhibits tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Gene Ther 2005; 12: 682–690.
Simeoni F, Morris MC, Heitz F, Divita G . Peptide-based strategy for siRNA delivery into mammalian cells. Methods Mol Biol 2005; 309: 251–260.
Simeoni F, Morris MC, Heitz F, Divita G . Insight into the mechanism of the peptide-based gene delivery system MPG: implications for delivery of siRNA into mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res 2003; 31: 2717–2724.
Hamar P, Song E, Kokeny G, Chen A, Ouyang N, Lieberman J . Small interfering RNA targeting Fas protects mice against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 14883–14888.
Hagstrom JE, Hegge J, Zhang G, Noble M, Budker V, Lewis DL et al. A facile nonviral method for delivering genes and siRNAs to skeletal muscle of mammalian limbs. Mol Ther 2004; 10: 386–398.
Ge Q, Filip L, Bai A, Nguyen T, Eisen HN, Chen J . Inhibition of influenza virus production in virus-infected mice by RNA interference. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 8676–8681.
Song E, Zhu P, Lee SK, Chowdhury D, Kussman S, Dykxhoorn DM et al. Antibody mediated in vivo delivery of small interfering RNAs via cell-surface receptors. Nat Biotechnol 2005; 23: 709–717.
de Fougerolles A, Manoharan M, Meyers R, Vornlocher HP . RNA interference in vivo: toward synthetic small inhibitory RNA-based therapeutics. Methods Enzymol 2005; 392: 278–296.
Stevenson M . Therapeutic potential of RNA interference. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 1772–1777.
Ryther RC, Flynt AS, Phillips 3rd JA, Patton JG . siRNA therapeutics: big potential from small RNAs. Gene Therapy 2005; 12: 5–11.
Izquierdo M . Short interfering RNAs as a tool for cancer gene therapy. Cancer Gene Ther 2005; 12: 217–227.
Wiznerowicz M, Trono D . Conditional suppression of cellular genes: lentivirus vector-mediated drug-inducible RNA interference. J Virol 2003; 77: 8957–8961.
Gupta S, Schoer RA, Egan JE, Hannon GJ, Mittal V . Inducible, reversible, and stable RNA interference in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 1927–1932.
Berns K, Hijmans EM, Mullenders J, Brummelkamp TR, Velds A, Heimerikx M et al. A large-scale RNAi screen in human cells identifies new components of the p53 pathway. Nature 2004; 428: 431–437.
Westbrook TF, Martin ES, Schlabach MR, Leng Y, Liang AC, Feng B et al. A genetic screen for candidate tumor suppressors identifies REST. Cell 2005; 121: 837–848.
Paddison PJ, Silva JM, Conklin DS, Schlabach M, Li M, Aruleba S et al. A resource for large-scale RNA-interference-based screens in mammals. Nature 2004; 428: 427–431.
Tompkins SM, Lo CY, Tumpey TM, Epstein SL . Protection against lethal influenza virus challenge by RNA interference in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 8682–8686.
Lomas-Neira JL, Chung CS, Wesche DE, Perl M, Ayala A . In vivo gene silencing (with siRNA) of pulmonary expression of MIP-2 versus KC results in divergent effects on hemorrhage-induced, neutrophil-mediated septic acute lung injury. J Leukoc Biol 2005; 77: 846–853.
Yano J, Hirabayashi K, Nakagawa S, Yamaguchi T, Nogawa M, Kashimori I et al. Antitumor activity of small interfering RNA/cationic liposome complex in mouse models of cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 7721–7726.
Urban-Klein B, Werth S, Abuharbeid S, Czubayko F, Aigner A . RNAi-mediated gene-targeting through systemic application of polyethylenimine (PEI)-complexed siRNA in vivo. Gene Therapy 2005; 12: 461–466.
Kishida T, Asada H, Gojo S, Ohashi S, Shin-Ya M, Yasutomi K et al. Sequence-specific gene silencing in murine muscle induced by electroporation-mediated transfer of short interfering RNA. J Gene Med 2004; 6: 105–110.
Golzio M, Mazzolini L, Moller P, Rols MP, Teissie J . Inhibition of gene expression in mice muscle by in vivo electrically mediated siRNA delivery. Gene Therapy 2005; 12: 246–251.
Kim B, Tang Q, Biswas PS, Xu J, Schiffelers RM, Xie FY et al. Inhibition of ocular angiogenesis by siRNA targeting vascular endothelial growth factor pathway genes: therapeutic strategy for herpetic stromal keratitis. Am J Pathol 2004; 165: 2177–2185.
Lingor P, Koeberle P, Kugler S, Bahr M . Down-regulation of apoptosis mediators by RNAi inhibits axotomy-induced retinal ganglion cell death in vivo. Brain 2005; 128: 550–558.
Xia H, Mao Q, Eliason SL, Harper SQ, Martins IH, Orr HT et al. RNAi suppresses polyglutamine-induced neurodegeneration in a model of spinocerebellar ataxia. Nat Med 2004; 10: 816–820.
Raoul C, Abbas-Terki T, Bensadoun JC, Guillot S, Haase G, Szulc J et al. Lentiviral-mediated silencing of SOD1 through RNA interference retards disease onset and progression in a mouse model of ALS. Nat Med 2005; 11: 423–428.
Ralph GS, Radcliffe PA, Day DM, Carthy JM, Leroux MA, Lee DC et al. Silencing mutant SOD1 using RNAi protects against neurodegeneration and extends survival in an ALS model. Nat Med 2005; 11: 429–433.
Akaneya Y, Jiang B, Tsumoto T . RNAi-induced gene silencing by local electroporation in targeting brain region. J Neurophysiol 2005; 93: 594–602.
Hassani Z, Lemkine GF, Erbacher P, Palmier K, Alfama G, Giovannangeli C et al. Lipid-mediated siRNA delivery down-regulates exogenous gene expression in the mouse brain at picomolar levels. J Gene Med 2005; 7: 198–207.
Zhang Y, Zhang YF, Bryant J, Charles A, Boado RJ, Pardridge WM . Intravenous RNA interference gene therapy targeting the human epidermal growth factor receptor prolongs survival in intracranial brain cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 3667–3677.
McRobert L, McConkey GA . RNA interference (RNAi) inhibits growth of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2002; 119: 273–278.
Aphasizhev R, Sbicego S, Peris M, Jang SH, Aphasizheva I, Simpson AM et al. Trypanosome mitochondrial 3′ terminal uridylyl transferase (TUTase): the key enzyme in U-insertion/deletion RNA editing. Cell 2002; 108: 637–648.
Mohmmed A, Dasaradhi PV, Bhatnagar RK, Chauhan VS, Malhotra P . In vivo gene silencing in Plasmodium berghei – a mouse malaria model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003; 309: 506–511.
Liu F, Song Y, Liu D . Hydrodynamics-based transfection in animals by systemic administration of plasmid DNA. Gene Therapy 1999; 6: 1258–1266.
Zhang G, Budker V, Wolff JA . High levels of foreign gene expression in hepatocytes after tail vein injections of naked plasmid DNA. Hum Gene Ther 1999; 10: 1735–1737.
Crespo A, Peydro A, Dasi F, Benet M, Calvete JJ, Revert F et al. Hydrodynamic liver gene transfer mechanism involves transient sinusoidal blood stasis and massive hepatocyte endocytic vesicles. Gene Therapy 2005; 12: 927–935.
Lewis DL, Hagstrom JE, Loomis AG, Wolff JA, Herweijer H . Efficient delivery of siRNA for inhibition of gene expression in postnatal mice. Nat Genet 2002; 32: 107–108.
Kondo T, Suda T, Fukuyama H, Adachi M, Nagata S . Essential roles of the Fas ligand in the development of hepatitis. Nat Med 1997; 3: 409–413.
Rust C, Gores GJ . Apoptosis and liver disease. Am J Med 2000; 108: 567–574.
Siegel RM, Fleisher TA . The role of Fas and related death receptors in autoimmune and other disease states. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1999; 103: 729–738.
Ogasawara J, Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Adachi M, Matsuzawa A, Kasugai T, Kitamura Y et al. Lethal effect of the anti-Fas antibody in mice. Nature 1993; 364: 806–809.
Li XK, Fujino M, Sugioka A, Morita M, Okuyama T, Guo L et al. Fulminant hepatitis by Fas-ligand expression in MRL-lpr/lpr mice grafted with Fas-positive livers and wild-type mice with Fas-mutant livers. Transplantation 2001; 71: 503–508.
Zender L, Hutker S, Liedtke C, Tillmann HL, Zender S, Mundt B et al. Caspase 8 small interfering RNA prevents acute liver failure in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 7797–7802.
Mast EE, Alter MJ, Margolis HS . Strategies to prevent and control hepatitis B and C virus infections: a global perspective. Vaccine 1999; 17: 1730–1733.
Bradley DW . Studies of non-A, non-B hepatitis and characterization of the hepatitis C virus in chimpanzees. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2000; 242: 1–23.
Kao JH, Chen DS . Global control of hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet Infect Dis 2002; 2: 395–403.
Sells MA, Chen ML, Acs G . Production of hepatitis B virus particles in Hep G2 cells transfected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1987; 84: 1005–1009.
Yang PL, Althage A, Chung J, Chisari FV . Hydrodynamic injection of viral DNA: a mouse model of acute hepatitis B virus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 13825–13830.
Klein C, Bock CT, Wedemeyer H, Wustefeld T, Locarnini S, Dienes HP et al. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication in vivo by nucleoside analogues and siRNA. Gastroenterology 2003; 125: 9–18.
Merl S, Michaelis C, Jaschke B, Vorpahl M, Seidl S, Wessely R . Targeting 2A protease by RNA interference attenuates coxsackieviral cytopathogenicity and promotes survival in highly susceptible mice. Circulation 2005; 111: 1583–1592.
Khan A, Benboubetra M, Sayyed PZ, Ng KW, Fox S, Beck G et al. Sustained polymeric delivery of gene silencing antisense ODNs, siRNA, DNAzymes and ribozymes: in vitro and in vivo studies. J Drug Target 2004; 12: 393–404.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH grants AI058695 and AI056900. We thank members of the laboratory and our collaborators for many useful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dykxhoorn, D., Palliser, D. & Lieberman, J. The silent treatment: siRNAs as small molecule drugs. Gene Ther 13, 541–552 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302703
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302703
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A comprehensive review on RNA interference-mediated targeting of interleukins and its potential therapeutic implications in colon cancer
3 Biotech (2023)
-
Discovery of a novel EGFR ligand DPBA that degrades EGFR and suppresses EGFR-positive NSCLC growth
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2020)
-
Emerging ways to treat breast cancer: will promises be met?
Cellular Oncology (2018)
-
Effect of inhibiting MMP13 and ADAMTS5 by intra-articular injection of small interfering RNA in a surgically induced osteoarthritis model of mice
Cell and Tissue Research (2017)
-
Highly efficient gene silencing and bioimaging based on fluorescent carbon dots in vitro and in vivo
Nano Research (2017)