Abstract
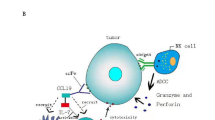
Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) represents a caspase-independent apoptotic pathway in the cell, and a mitochondrial localization sequence-truncated AIF (AIFΔ1–120) can be relocated from the cytoplasm to the nucleus and exhibit a constitutive proapoptotic activity. Here, we generated a chimeric immuno-AIF protein, which comprised an HER2 antibody, a Pseudomonas exotoxin translocation domain and AIFΔ1–120. Human Jurkat cells transfected with the immuno-AIF gene could express and secrete the chimeric protein, which selectively recognized HER2-overexpressing tumor cells and was endocytosed. Subsequent cleavage of truncated AIF from immuno-AIF and its release from the internalized vesicles resulted in apoptosis of tumor cells. Intramuscular injection of the immuno-AIF gene caused significant suppression of tumors and substantially prolonged mice survival in an HER2-overexpressing xenograft tumor model. Our study demonstrates the feasibility of the immuno-AIF gene as a novel approach to treating cancers that overexpress HER2.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schlessinger J . Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 2000; 103: 211–225.
Tewari KS, Kyshtoobayeva AS, Mehta RS, Yu IR, Burger RA, DiSaia PJ et al. Biomarker conservation in primary and metastatic epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 2000; 278: 130–136.
Menard S, Casalini P, Campiglio M, Pupa S, Agresti R, Tagliabue E . HER2 overexpression in various tumor types, focusing on its relationship to the development of invasive breast cancer. Ann Oncol 2001; 12: S15–S19.
Hynes NE, Stern DF . The biology of erbB-2/neu/HER-2 and its role in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1994; 1198: 165–184.
Salomon DS, Brandt R, Ciardiello F, Normanno N . Epidermal growth factor-related peptides and their receptors in human malignancies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 1995; 19: 183–232.
Braun S, Schlimok G, Heumos I, Schaller G, Riethdorf L, Riethmuller G et al. ErbB2 overexpression on occult metastatic cells in bone marrow predicts poor clinical outcome of stage I–III breast cancer patients. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 1890–1895.
Riese DJ, Stern DF . Specificity within the EGF family/ErbB receptor family signaling network. Bioessays 1998; 20: 41–48.
Eccles SA . The role of c-erbB-2/HER2/neu in breast cancer progression and metastases. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2001; 6: 393–406.
Gancberg D, Di Leo A, Cardoso F, Rouas G, Pedrocchi M, Paesmans M et al. Comparison of HER-2 status between primary breast cancer and corresponding distant metastatic sites. Ann Oncol 2002; 13: 1036–1043.
Nahta R, Esteva FJ . HER-2-targeted therapy: lessons learned and future directions. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9: 5078–5084.
Mukai K, Yasutomi Y, Watanabe M, Kenjo A, Aota T, Wang L et al. HER2 peptide-specific CD8(+) T cells are proportionally detectable long after multiple DNA vaccinations. Gene Therapy 2002; 9: 879–888.
De Bono JS, Rowinsky EK . The ErbB receptor family: a therapeutic target for cancer. Trends Mol Med 2001; 8: S19–S26.
Wester K, Sjostrom A, de la Torre M, Carlsson J, Malmstrom PU . HER-2 – a possible target for therapy of metastatic urinary bladder carcinoma. Acta Oncol 2002; 41: 282–288.
Lorenzo HK, Susin SA, Penninger J, Kroemer G . Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF): a phylogenetically old, caspase-independent effector of cell death. Cell Death Differ 1999; 6: 516–524.
Susin SA, Daugas E, Ravagnan L, Samejima K, Zamzami N, Loeffler M et al. Two distinct pathways leading to nuclear apoptosis. J Exp Med 2000; 192: 571–579.
Cande C, Cohen I, Daugas E, Ravagnan L, Larochette N, Zamzami N et al. Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF): a novel caspase-independent death effector released from mitochondria. Biochimie 2002; 84: 215–222.
Mate MJ, Ortiz-Lombardia M, Boitel B, Haouz A, Tello D, Susin SA et al. The crystal structure of the mouse apoptosis-inducing factor AIF. Nat Struct Biol 2002; 9: 442–446.
Ye H, Cande C, Stephanou NC, Jiang S, Gurbuxani S, Larochette N et al. DNA binding as a structural requirement for the apoptogenic action of AIF. Nat Struct Biol 2002; 9: 680–684.
Susin SA, Lorenzo HK, Zamzami N, Marzo I, Snow BE, Brothers GM et al. Molecular characterization of mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor. Nature 1999; 397: 441–446.
Miramar MD, Costantini P, Ravagnan L, Saraiva LM, Haouzi D, Brothers G et al. NADH-oxidase activity of mitochondrial apoptosis inducing factor (AIF). J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 16391–16398.
Daugas E, Nochy D, Ravagnan L, Loeffler M, Susin SA, Zamzami N et al. Apoptosis inducing factor: an ubiquitous mitochondrial oxidoreductase involved in apoptosis regulation. FEBS Lett 2000; 476: 118–123.
Loeffler M, Daugas E, Susin SA, Zamzami N, Metivier D, Nieminen AL et al. Dominant cell death induction by extramitochondrially targeted apoptosis inducing factor. FASEB J 2001; 15: 758–767.
Dawson VL, Dawson TM . Deadly conversations: nuclear–mitochondrial cross-talk. J Bioenerg Biomembr 2004; 36: 287–294.
Lipton SA, Bossy-Wetzel E . Dueling activities of AIF in cell death versus survival: DNA binding and redox activity. Cell 2002; 111: 147–150.
Joza N, Susin SA, Daugas E, Stanford WL, Cho SK, Li CY et al. Essential role of the mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor in programmed cell death. Nature 2001; 410: 549–554.
Arnoult D, Tatischeff I, Estaquier J, Girard M, Sureau F, Tissier JP et al. On the evolutionary conservation of the cell death pathway: mitochondrial release of an apoptosis inducing factor during Dictyostelium discoideum cell death. Mol Biol Cell 2001; 12: 3016–3030.
Braun JS, Novak R, Murray PJ, Eischen CM, Susin SA, Kroemer G et al. Apoptosis-inducing factor mediates microglial and neuronal apoptosis caused by pneumococcus. J Infect Dis 2001; 184: 1300–1309.
Cregan SP, Dawson VL, Slack RS . Role of AIF in caspase-dependent and caspase-independent cell death. Oncogene 2004; 23: 2785–2796.
Wang X, Yang C, Chai J, Shi Y, Xue D . Mechanisms of AIF-mediated apoptotic DNA degradation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 2002; 298: 1587–1592.
Wissing S, Ludovico P, Herker E, Buttner S, Engelhardt SM, Decker T et al. An AIF orthologue regulates apoptosis in yeast. J Cell Biol 2004; 166: 969–974.
Zhang X, Chen J, Graham SH, Du L, Kochanek PM, Draviam R et al. Intranuclear localization of apoptosis inducing factor (AIF) and large scale DNA fragmentation after traumatic brain injury in rats and in neuronal cultures exposed to peroxynitrite. J Neurochem 2002; 82: 181–191.
Lang-Rollin IC, Rideout HJ, Noticewala M, Stefanis L . Mechanisms of caspase-independent neuronal death: energy depletion and free radical generation. J Neurosci 2003; 23: 11015–11025.
Batra JK, Kasprzyk PG, Bird RE, Pastan I, King CR . Recombinant anti-erbB2 immunotoxins containing Pseudomonas exotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992; 89: 5867–5871.
Chen SY, Yang AG, Chen JD, Kute T, King CR, Collier J et al. Potent antitumor activity of a new class of tumour specific killer cells. Nature 1997; 385: 78–80.
Siegall CB, Chaudhary VK, FitzGerald DJ, Pastan I . Functional analysis of domains II, Ib, and III of Pseudomonas exotoxin. J Biol Chem 1989; 264: 14256–14261.
Siegall CB, Ogata M, Pastan I, FitzGerald DJ . Analysis of sequences in domain II of Pseudomonas exotoxin A which mediate translocation. Biochemistry 1991; 30: 7154–7159.
Jia LT, Zhang LH, Yu CJ, Zhao J, Xu YM, Gui JH et al. Specific tumoricidal activity of a secreted proapoptotic protein consisting of HER2 antibody and constitutively active caspase-3. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 3257–3262.
Xu YM, Wang LF, Jia LT, Qiu XC, Zhao J, Yu CJ et al. A caspase-6 and anti-human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2) antibody chimeric molecule suppresses the growth of HER2-overexpressing tumors. J Immunol 2004; 173: 61–67.
Zhao J, Zhang LH, Jia LT, Zhang L, Xu YM, Wang Z et al. Secreted antibody/granzyme B fusion protein stimulates selective killing of HER2-overexpressing tumor cells. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 21343–21348.
Yu SW, Wang H, Dawson TM, Dawson VL . Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 and apoptosis inducing factor in neurotoxicity. Neurobiol Dis 2003; 14: 303–317.
Alano CC, Ying W, Swanson RA . Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1-mediated cell death in astrocytes requires NAD+ depletion and mitochondrial permeability transition. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 18895–18902.
Cande C, Vahsen N, Kouranti I, Schmitt E, Daugas E, Spahr C et al. AIF and cyclophilin A cooperate in apoptosis-associated chromatinolysis. Oncogene 2004; 23: 1514–1521.
Hong SJ, Dawson TM, Dawson VL . Nuclear and mitochondrial conversations in cell death: PARP-1 and AIF signaling. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2004; 25: 259–264.
Wang H, Shimoji M, Yu SW, Dawson TM, Dawson VL . Apoptosis inducing factor and PARP-mediated injury in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson's disease. Ann NY Acad Sci 2003; 991: 132–139.
Zhang XD, Gillespie SK, Hersey P . Staurosporine induces apoptosis of melanoma by both caspase-dependent and -independent apoptotic pathways. Mol Cancer Ther 2004; 3: 187–197.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (No. 2001AA217101), the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2004CB518805) and the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Teams in Universities (PCSIRT) from Ministry of Education of People's Republic of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, CJ., Jia, LT., Meng, YL. et al. Selective proapoptotic activity of a secreted recombinant antibody/AIF fusion protein in carcinomas overexpressing HER2. Gene Ther 13, 313–320 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302672
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302672
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Recombinant immunotoxins development for HER2-based targeted cancer therapies
Cancer Cell International (2021)
-
Downregulation of AIF-2 Inhibits Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Human Glioma Cells via Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2019)
-
Mitochondria as therapeutic targets for cancer chemotherapy
Oncogene (2006)